Abstract
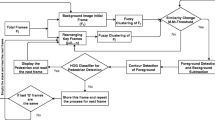
Background subtraction approaches are used to detect moving objects with a high recognition rate and less computation time. These methods face two challenges: selecting the appropriate threshold value and removing shadow pixels for correct foreground detection. In this paper, we solve these challenges by proposing a new background subtraction method called ABGS Segmenter, which is based on a two-level adaptive thresholding approach where a reference frame is created using mean-based thresholding to generate the initial value of the threshold and accelerates the process of foreground segmentation for remaining frames by adaptively updating the threshold value at the pixel level. ABGS Segmenter is also capable of removing shadow pixels by fusing the chromaticity-based YCbCr color space model with the intensity ratio method for improving the percentage of correct pixels’ classification measure. Comprehensive experiments are evaluated on three benchmark datasets (Highway, PETS 2006, and SBU) and observed that the proposed work achieves better results than existing methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data are easily available online. http://changedetection.net/https://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cvl/projects/shadow_noisy_label/index.html.
References
Cheng FC, Huang SC, Ruan SJ (2010) “Advanced motion detection for intelligent video surveillance systems,” in Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, 983–984. https://doi.org/10.1145/1774088.1774295.
Bouwmans T (2014) Traditional and recent approaches in background modeling for foreground detection: An overview. Computer Science Review. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2014.04.001
Shaikh SH, Saeed K, Chaki N (2014) Moving Object Detection Using Background Subtraction. In: Shaikh SH, Saeed K, Chaki N (eds) Moving Object Detection Using Background Subtraction. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 15–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07386-6_3
K. Sehairi, F. Chouireb, and J. Meunier (2015) “Comparison study between different automatic threshold algorithms for motion detection,” In 4th Int. Conf. on Electrical Engineering (ICEE 2015), 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1109/INTEE.2015.7416840
Piccardi M, “Background subtraction techniques: A review,” 2004. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSMC.2004.1400815
Garcia-Garcia B, Bouwmans T, Silva AJR (2020) Background subtraction in real applications: Challenges, current models and future directions. Compt Sci Rev 35:100204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2019.100204
Sajid H, Cheung SS (2015) “Background subtraction for static & moving camera,” In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). 4530–4534. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2015.7351664.
Zhang R, Ding J (2012) Object tracking and detecting based on adaptive background subtraction. Proced Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.01.139
Zivkovic Z (2004) “Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction,” In: Proceedings - International Conference on Pattern Recognition 28–31. https://doi.org/10.1109/icpr.2004.1333992.
Tian Y, Wang Y, Hu Z, Huang T (2013) Selective eigenbackground for background modeling and subtraction in crowded scenes. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 23(11):1849–1864. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2013.2248239
Akilan T, Wu QMJ, Yang Y (2018) Fusion-based foreground enhancement for background subtraction using multivariate multi-model Gaussian distribution. Inf Sci (Ny) 430–431:414–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.11.062
“Changedetection.net.” http://jacarini.dinf.usherbrooke.ca/dataset2012
Barnich O, Van Droogenbroeck M (2009) “ViBE: A powerful random technique to estimate the background in video sequences,” In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 945–948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4959741.
L. Xu, F. Qi, R. Jiang, Y. Hao, and G. Wu, “Shadow Detection and Removal in Real Images: A Survey,” Citeseer, 2006, [Online]. Available: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.86.1017&rep=rep1&type=pdf%5Cnpapers2://publication/uuid/F739EA7E-1488-4E22-88DC-DFD83F059410
Agrawal S, Natu P (2020) Segmentation of moving objects using numerous background subtraction methods for surveillance applications. Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng 9(3):2553–2563. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijitee.c8811.019320
Khan SH, Bennamoun M, Sohel F, Togneri R (2016) Automatic shadow detection and removal from a single image. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(3):431–446. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2462355
Abdusalomov A, Whangbo T (2017) An improvement for the foreground recognition method using shadow removal technique for indoor environments. Int J Wavelets Multiresolution Inf Process. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219691317500394
Hofmann M, Tiefenbacher P, Rigoll G (2012) “Background segmentation with feedback: The Pixel-Based Adaptive Segmenter,” In: 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 38–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2012.6238925
Ebner M, Yuan X, Wang Z (2015) Single-image shadow detection and removal using local colour constancy computation. IET Image Process 9:118–126. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-ipr.2014.0242
Sezgin M, Sankur B (2004) Survey over Image Thresholding Techniques and Quantitative Performance Evaluation. J Electron Imaging 13:146–165. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.1631315
Pai CJ, Tyan HR, Liang YM, HY. M. Liao, and Chen SW (2003) “Pedestrian detection and tracking at crossroads,” In: Proceedings 2003 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No.03CH37429), 2, II–101. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2003.1246626.
Wren CR, Azarbayejani A, Darrell T, Pentland AP (1997) Pfinder: real-time tracking of the human body. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):780–785. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.598236
Hassan MA, Malik AS, Nicolas W, Faye I (2015) Adaptive Foreground Extraction for Crowd Analytics Surveillance on Unconstrained Environments. In: Jawahar CV, Shan S (eds) Computer Vision - ACCV 2014 Workshops. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 390–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16631-5_29
Stauffer C, Grimson WEL (1999) “Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking,” Proceedings. 1999 IEEE computer society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.1999.784637.
Haines T, Xiang T (2014) Background subtraction with dirichlet process mixture models. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 36:670–683. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2013.239
Karpagavalli P, Ramprasad V (2017) An adaptive hybrid GMM for multiple human detection in crowd scenario. Multimed. Tools Appl. 76(12):14129–14149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3777-4
Sengar SS, Mukhopadhyay S (2019) Moving object detection using statistical background subtraction in wavelet compressed domain. Multimed Tools Appl 79(9–10):5919–5940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08506-z
Liu Z, Huang K, Tan T (2012) Foreground object detection using top-down information based on em framework. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(9):4204–4217. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2200492
Jeevith SH, Lakshmikanth S (2021) Detection and tracking of moving object using modified background subtraction and Kalman filter. Int J Electr Comput Eng 11(1):217–223. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v11i1.pp217-223
Zhang J, Guo X, Zhang C, Liu P (2021) A vehicle detection and shadow elimination method based on greyscale information, edge information, and prior knowledge. Comput Electr Eng 94:107366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107366
Kim K, Chalidabhongse TH, Harwood D, Davis L (2005) Real-time foreground-background segmentation using codebook model. Real-Time Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rti.2004.12.004
Liu R, Ruichek Y, El-Bagdouri M (2019) Extended Codebook with Multispectral Sequences for Background Subtraction. Sensors 19(3):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030703
Liao J, Wang H, Yan Y, Zheng J (2018) A Novel Background Subtraction Method Based on ViBe. In: Zeng B, Huang Q, El Saddik A, Li H, Jiang S, Fan X (eds) Advances in Multimedia Information Processing – PCM 2017. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 428–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77383-4_42
Li W, Zhang J, Wang Y (2019) WePBAS: A Weighted Pixel-Based Adaptive Segmenter for Change Detection. Sensors (Basel) 19(12):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122672
Li S, Liu P, Han G (2017) Moving object detection based on codebook algorithm and three-frame difference. Int J Signal Process Image Process Pattern Recognit 10(3):23–32
Guo J, Wang J, Bai R, Zhang Y, Li Y (2017) A new moving object detection method based on frame-difference and background subtraction. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 242:12115. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/242/1/012115
Chen J, Lu X, Ye M, Ming Z, Zhou F, Luo Y (2018) “A Moving Object Extraction Algorithm Based on Hybrid Background Subtraction and Pixel Mean Technique BT: Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 2018),” pp. 360–368. https://doi.org/10.2991/amcce-18.2018.62.
Dhingra G, Kumar V, Joshi HD (2021) Clustering-based shadow detection from images with texture and color analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 80(25):33763–33778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11427-5
Cucchiara R, Grana C, Piccardi M, Prati A (2003) Detecting moving objects, ghosts, and shadows in video streams. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1233909
Izadi M, Saeedi P (2008) “Robust region-based background subtraction and shadow removing using color and gradient information. https://doi.org/10.1109/icpr.2008.4761133.
Zhang W, Fang XZ, Xu Y (2006) “Detection of moving cast shadows using image orthogonal transform,” In 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06) 1, 626–629. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2006.441.
Wu M, Chen R, Tong Y (2020) Shadow elimination algorithm using color and texture features. Comput Intell Neurosci 2020:2075781. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2075781
Murali S (2013) Shadow Detection and Removal from a Single Image Using LAB Color Space. Cybern Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.2478/cait-2013-0009
Wang Y, Luo Z, Jodoin P-M (2017) Interactive deep learning method for segmenting moving objects. Pattern Recognit Lett 96:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2016.09.014
Babaee M, Dinh DT, Rigoll G (2018) A deep convolutional neural network for video sequence background subtraction. Pattern Recognit 76:635–649
K. Saarinen (1994) Image processing, analysis and machine vision, 35(1).https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1684(94)90202-x.
Varghese A, Sreelekha G (2017) Sample-based integrated background subtraction and shadow detection. IPSJ Transact Comput Vision Appl. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41074-017-0036-1
“SBU.” https://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cvl/projects/shadow_noisy_label/index.html
Montero VJ, Jung WY, Jeong YJ (2021) Fast background subtraction with adaptive block learning using expectation value suitable for real-time moving object detection. J Real-Time Image Process 18(3):967–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-020-01058-8
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript has been written by author 1 and reviewed by author 2.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, S., Natu, P. ABGS Segmenter: pixel wise adaptive background subtraction and intensity ratio based shadow removal approach for moving object detection. J Supercomput 79, 7937–7969 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04972-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04972-9