Abstract
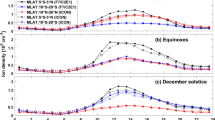
The Ionospheric CONnections (ICON) mission has been continuously operating during the period from January 2020 to December 2021 providing simultaneous measurements of the thermal plasma properties near 600 km altitude and the neutral atmosphere and ionosphere in the altitude range 100 km to 500 km at low and middle latitudes. During this period of extremely low to moderately low solar activity, the evolving properties of the topside ionospheric density, composition, temperature and drift velocity at the satellite location are described using measurements from the Ion Velocity Meter (IVM). In the early months of 2020, the very low solar activity and relatively high abundance of H+ in the total plasma density present a challenge to a robust description of the full local time distribution of the topside ion drifts. However, the quality of measurements of the ionospheric composition and temperature are not impacted by low solar activity conditions and changes in the O+ and H+ concentrations and their effects on the energy balance in the topside can be investigated as solar activity changes. As the relative abundance of O+ increases, the susceptibility of the ion drift determination to the local plasma environment around the spacecraft is reduced and a more robust determination of the ion drift at all local times is possible. From October 2020 onward, the relationships between the topside ionospheric dynamics and the ionospheric density and temperature can be investigated and the relationships between the plasma drifts and the underlying neutral wind drivers can be established.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey GJ, Moffett RJ, Hanson WB, Sanatani S (1973) Effects of interhemisphere transport on plasma temperatures at low latitudes. J Geophys Res 78:5597–5610. https://doi.org/10.1029/JA078i025p05597
Chapagain NP, Fejer BG, Chau JL (2009) Climatology of postsunset equatorial spread \(F\) over Jicamarca. J Geophys Res 114:A07307. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JA013911
Emmert JT, Richmond AD, Drob DP (2010) A computationally compact representation of Magnetic-Apex and Quasi-Dipole coordinates with smooth base vectors. J Geophys Res 115:A08322. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JA015326
England SL, Immel TJ, Huba JD, Hagan ME, Maute A, DeMajistre R (2010) Modeling of multiple effects of atmospheric tides on the ionosphere: an examination of possible coupling mechanisms responsible for the longitudinal structure of the equatorial ionosphere. J Geophys Res 115:A05308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JA014894
Forbes JM, Zhang X, Heelis R, Stoneback R, Englert CR, Harlander JM et al. (2021) Atmosphere-ionosphere (A-I) coupling as viewed by ICON: day-to-day variability due to planetary wave (PW)-tide interactions. J Geophys Res Space Phys 126:e2020JA028927. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JA028927
Gasperini F, Azeem I, Crowley G, Perdue M, Depew M, Immel T et al. (2021) Dynamical coupling between the low-latitude lower thermosphere and ionosphere via the nonmigrating diurnal tide as revealed by concurrent satellite observations and numerical modeling. Geophys Res Lett 48:e2021GL093277. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL093277
Hartman WA, Heelis RA (2007) Longitudinal variations in the equatorial vertical drift in the topside ionosphere. J Geophys Res 112:A03305. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JA011773
Heelis R, Hanson W (1980) Interhemispheric transport induced by neutral zonal winds in the \(F\) region. J Geophys Res 85(A6):3045–3047. https://doi.org/10.1029/JA085iA06p03045
Heelis RA, Hanson WB (1998) Measurements of thermal ion drift velocity and temperature using planar sensors. American geophysical union monograph, measurement techniques in space plasmas: particles. https://doi.org/10.1029/GM102p0061
Heelis RA, Stoneback RA, Perdue MD, Depew MD, Morgan WA, Mankey MW, Lippincott CR, Harmon LL, Holt BJ (2017) Ion velocity measurements for the ionospheric connections explorer. Space Sci Rev 212(1–2):615–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0383-3
Heelis RA, Chen Y-J, Depew MD, Harding BJ, Immel TJ, Wu Y-J et al. (2022) Topside plasma flows in the equatorial ionosphere and their relationships to F-region winds near 250 km. J Geophys Res Space Phys 127:e2022JA030415. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022JA030415
Hsu C-T, Heelis RA (2017) Modeling the daytime energy balance of the topside ionosphere at middle latitudes. J Geophys Res Space Phys 122:5733–5742. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JA024112
Huang C–S (2019) Long-lasting penetration electric fields during geomagnetic storms: observations and mechanisms. J Geophys Res Space Phys 124:9640–9664. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JA026793
Huba JD, Heelis RA, Maute A (2021) Large-scale O+ depletions observed by ICON in the post-midnight topside ionosphere: data/model comparison. Geophys Res Lett 48:7. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL092061
Immel TJ, Sagawa E, England SL, Henderson SB, Hagan ME, Mende SB, Frey HU, Swenson CM, Paxton LJ (2006) Control of equatorial ionospheric morphology by atmospheric tides. Geophys Res Lett 33:L15108. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL026161
Immel TJ, England SL, Mende SB, Heelis RA et al. (2018) The ionospheric connection explorer mission: mission goals and design. Space Sci Rev 2018(214):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0449-2
Immel TJ, Harding BJ, Heelis RA et al. (2021) Regulation of ionospheric plasma velocities by thermospheric winds. Nat Geosci 14:893–898. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-021-00848-4
Kakinami Y, Watanabe S, Liu J-Y, Balan N (2011) Correlation between electron density and temperature in the topside ionosphere. J Geophys Res 116:A12331. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JA016905
Kil H, Oh S-J, Kelley MC, Paxton LJ, England SL, Talaat E, Min K-W, Su S-Y (2007) Longitudinal structure of the vertical E x B drift and ion density seen from ROCSAT-1. Geophys Res Lett 34:L14110. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL030018
Kil H, Oh S-J, Paxton LJ, Fang T-W (2009) High-resolution vertical \(\mathbf{E} \times \mathbf{B}\) drift model derived from ROCSAT-1 data. J Geophys Res 114:A10314. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JA014324
Liu G, England SL, Lin CS, Pedatella NM, Klenzing JH, Englert CR et al. (2021) Evaluation of atmospheric 3-day waves as a source of day-to-day variation of the ionospheric longitudinal structure. Geophys Res Lett 48:e2021GL094877. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL094877
Murphy JA, Heelis RA (1986) Implications of the relationship between electromagnetic drift components at mid and low latitudes. Planet Space Sci 34:645. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-0633(86)90042-5
Pedatella NM, Forbes JM, Maute A, Richmond AD, Fang T-W, Larson KM, Millward G (2011) Longitudinal variations in the F region ionosphere and the topside ionosphere-plasmasphere: observations and model simulations. J Geophys Res 116:A12309. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JA016600
Stoneback RA, Heelis RA, Burrell AG, Coley WR, Fejer BG, Pacheco E (2011) Observations of quiet time vertical ion drift in the equatorial ionosphere during the solar minimum period of 2009. J Geophys Res 116:A12327. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JA016712
Acknowledgement
ICON is supported by NASA’s Explorers Program through contracts NNG12FA45C and NNG12FA42I. The authors would like to thank Tori Fae and the ICON Science Operations Center for diligently maintaining the ground processing procedures. The data utilized in this study are available as the IVM Level 2.7 data product at the ICON data center (https://icon.ssl.berkeley.edu/Data).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
No conflicts of interest have been identified during the conduct of this work.
Consent for publication
All co-authors have participated in and reviewed this work and it is submitted for publication with their consent.
The research project does not engage human subjects or animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) Mission: First Results
Edited by David E. Siskind and Ruth S. Lieberman
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Heelis, R.A., Depew, M.D., Chen, YJ. et al. Ionospheric Connections (ICON) Ion Velocity Meter (IVM) Observations of the Equatorial Ionosphere at Solar Minimum. Space Sci Rev 218, 68 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-022-00936-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-022-00936-w