Abstract
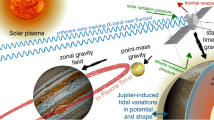
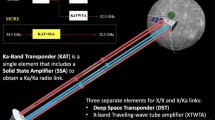
The Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment (RISE) on-board the InSight mission will use the lander’s X-band (8 GHz) radio system in combination with tracking stations of the NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) to determine the rotation of Mars. RISE will measure the nutation of the Martian spin axis, detecting for the first time the effect of the liquid core of Mars and providing in turn new constraints on the core radius and density. RISE will also measure changes in the rotation rate of Mars on seasonal time-scales thereby constraining the atmospheric angular momentum budget. Finally, RISE will provide a superb tie between the cartographic and inertial reference frames. This paper describes the RISE scientific objectives and measurements, and provides the expected results of the experiment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A first low accuracy estimate of polar motion amplitudes has been inferred from gravity degree-2 coefficients by Konopliv et al. (2006), but no direct measurements of it has been performed until now.
References
B.A. Archinal, C.H. Acton, M.F. A’Hearn, A. Conrad et al., Report of the IAU working group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2015. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 130(3), 22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-017-9805-5
R.E. Arvidson, R.C. Anderson, P. Bartlett, J.F. Bell et al., Localization and physical properties experiments conducted by Spirit at Gusev crater. Science 305, 821–824 (2004a)
R.E. Arvidson, R.C. Anderson, P. Bartlett, J.F. Bell et al., Localization and physical properties experiments conducted by opportunity at Meridiani Planum. Science 306, 1730–1733 (2004b)
S.W. Asmar, J.W. Armstrong, L. Iess, P. Tortora, Spacecraft Doppler tracking: Noise budget and accuracy achievable in precision radio science observations. Radio Sci. 40, RS2001 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1029/2004RS003101
W.B. Banerdt et al., The InSight mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2018), this issue
Y.E. Bar-Sever, C.S. Jacobs, S. Keihm, G.E. Lanyi et al., Atmospheric media calibration for the deep space network. Proc. IEEE 95, 2180–2192 (2007)
J.-P. Barriot, V. Dehant, J.-C. Cerisier, W. Folkner et al., NEIGE: NetLander ionosphere and geodesy experiment. Adv. Space Res. 28, 1237–1249 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(01)00295-2
N. Bergeot, O. Witasse, W. Kofman, C. Grima et al., Study of the total electron content in Mars ionosphere from MARSIS data set, in EGU General Assembly 2016, Vienna, Austria (2016)
A. Cazenave, G. Balmino, Meteorological effects on the seasonal variations on the rotation of Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 245–248 (1981)
B.F. Chao, D.P. Rubincam, Variations of Mars’ gravitational field and rotation due to seasonal CO2 exchange. J. Geophys. Res. 95(B9), 14755–14760 (1990)
S. Chapman, The absorption and dissociative or ionizing effect of monochromatic radiation in an atmosphere on a rotating Earth. Proc. Phys. Soc. 43, 26–45 (1931)
J.A.D. Connolly, Computation of phase equilibria by linear programming: A tool for geodynamic modeling and its application to subduction zone decarbonation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 236, 524–541 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.04.033
F.A. Dahlen, J. Tromp, Theoretical Global Seismology (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1998)
P. Defraigne, O. de Viron, V. Dehant, T. Van Hoolst, F. Hourdin, Mars rotation variations induced by atmospheric CO2 and winds. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 105, 24563–24570 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JE001227
P. Defraigne, A. Rivoldini, T. Van Hoolst, V. Dehant, Mars nutation resonance due to free inner core nutation. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 108(E12), 5128 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JE002145
V. Dehant, P.M. Mathews, Precession, Nutation and Wobble of the Earth (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2015)
V. Dehant, P. Defraigne, T. Van Hoolst, Computation of Mars’ transfer function for nutation tides and surface loading. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 117, 385–395 (2000a). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9201(99)00108-9
V. Dehant, T. Van Hoolst, P. Defraigne, Comparison between the nutations of the planet Mars and the nutations of the Earth. Geophys. Surv. 21, 89–110 (2000b)
V. Dehant, W. Folkner, E. Renotte, D. Orban et al., Lander radioscience for obtaining the rotation and orientation of Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 57, 1050–1067 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2008.08.009
V. Dehant, S. Le Maistre, A. Rivoldini, M. Yseboodt et al., Revealing Mars’ deep interior: Future geodesy missions using radio links between landers, orbiters, and the Earth. Planet. Space Sci. 57, 1069–1081 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2010.03.014
G. Dreibus, H. Wanke, Mars, a volatile-rich planet. Meteoritics 20, 367–381 (1985)
R. Fergason, R.L. Kirk, G. Cushing, D.M. Galuzska et al., Analysis of local slopes at the InSight landing site on Mars. Space Sci. Rev. 211, 109–133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-016-0292-x
W.M. Folkner, C.F. Yoder, D.N. Yuan, E.M. Standish, R.A. Preston, Interior structure and seasonal mass redistribution of Mars from radio tracking of Mars Pathfinder. Science 278, 1749–1752 (1997)
A. Genova, S. Goossens, F.G. Lemoine, E. Mazarico et al., Seasonal and static gravity field of Mars from MGS, Mars Odyssey and MRO radio science. Icarus 272, 228–245 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2016.02.050
M.P. Golombek, R.A. Cook, T. Economou, W. Folkner et al., Overview of the Mars Pathfinder mission and assessment of landing site predictions. Science 278, 1743–1748 (1997)
M.P. Golombek, R.C. Anderson, J.R. Barnes, J.F. Bell et al., Overview of the Mars Pathfinder mission: Launch through landing, surface operations, data sets, and science results. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 8523–8553 (1999a)
M.P. Golombek, H.J. Moore, A.F.C. Haldemann, T.J. Parker, J.T. Schofield, Assessment of Mars Pathfinder landing site predictions. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 8585–8594 (1999b)
M.P. Golombek, D. Kipp, N. Warner, I.J. Daubar et al., Selection of the InSight landing site. Space Sci. Rev. 211, 5–95 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-016-0321-9
M.P. Golombek, M. Grott, G. Kargl, J. Andrade et al., Geology and physical properties investigations by the InSight lander. Space Sci. Rev. (2018), this issue. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-018-0512-7
K. Gwinner, F. Scholten, F. Preusker, S. Elgner et al., Topography of Mars from global mapping by HRSC high-resolution digital terrain models and orthoimages: Characteristics and performance. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 294, 506–519 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.11.007
Ö. Karatekin, T. Van Hoolst, J. Tastet, O. de Viron, V. Dehant, The effects of seasonal mass redistribution and interior structure on length-of-day variations of Mars. Adv. Space Res. 38, 739–744 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.117
Ö. Karatekin, O. de Viron, S. Lambert, P. Rosenblatt et al., Atmospheric angular momentum variations of Earth, Mars and Venus at seasonal time scales. Planet. Space Sci. 59, 923–933 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2010.09.010
S.J. Keihm, A. Tanner, H. Rosenberger, Measurements and calibration of tropospheric delay at Goldstone from the Cassini media calibration system, in Interplanetary Network Progress Report 42-158 (2004)
A. Khan, C. Liebske, A. Rozel, A. Rivoldini et al., A geophysical perspective on the bulk composition of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 123(2), 575–611 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JE005371
A.S. Konopliv, C.F. Yoder, E.M. Standish, D.N. Yuan, W.L. Sjogren, A global solution for the Mars static and seasonal gravity, Mars orientation, Phobos and Deimos masses, and Mars ephemeris. Icarus 182, 23–50 (2006)
A.S. Konopliv, S.W. Asmar, W.M. Folkner, Ö. Karatekin et al., Mars high resolution gravity fields from MRO, Mars seasonal gravity, and other dynamical parameters. Icarus 211, 401–428 (2011)
A.S. Konopliv, R.S. Park, W.M. Folkner, An improved JPL Mars gravity field and orientation from Mars orbiter and lander tracking data. Icarus 274, 253–260 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2016.02.052
P. Kuchynka, W.M. Folkner, A.S. Konopliv, R.S. Park, S. Le Maistre, V. Dehant, New constraints on Mars rotation determined from radiometric tracking of the opportunity Mars exploration rover. Icarus 229, 340–347 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2013.11.015
S. Le Maistre, InSight coordinates determination from direct-to-Earth radio-tracking and Mars topography model. Planet. Space Sci. 121, 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2015.11.003
S. Le Maistre, P. Rosenblatt, A. Rivoldini, V. Dehant et al., Lander radio science experiment with a direct link between Mars and the Earth. Planet. Space Sci. 68, 105–122 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2011.12.020
R.J. Lillis, D.A. Brain, S.L. England, P. Withers et al., Total electron content in the Mars ionosphere: Temporal studies and dependence on solar EUV flux. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115, A11314 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JA015698
K. Lodders, B. Fegley, An oxygen isotope model for the composition of Mars. Icarus 126, 373–394 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1006/icar.1996.5653
P. Lognonne, W.B. Banerdt, D. Giardini, W.T. Pike et al., SEIS: The seismic experiment for internal structure on InSight. Space Sci. Rev. (2018), this issue
A.J. Mannucci, B.D. Wilson, D.N. Yuan, C.H. Ho et al., A global mapping technique for GPS-derived ionospheric total electron content. Radio Sci. 33, 565–582 (1998)
P.M. Mathews, B.A. Buffett, T.A. Herring, I.I. Shapiro, Forced nutations of the Earth: Influence of inner core dynamics: 1. Theory. J. Geophys. Res., Solid Earth 96(B5), 8219–8242 (1991a)
P.M. Mathews, B.A. Buffett, T.A. Herring, I.I. Shapiro, Forced nutations of the Earth: Influence of inner core dynamics, 2. Numerical results and comparisons. J. Geophys. Res., Solid Earth 96(B5), 8243–8257 (1991b). https://doi.org/10.1029/90JB01956
R.K. Mohapatra, S.V.S. Murty, Precursors of Mars: Constraints from nitrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of Martian meteorites. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 38(2), 225–241 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1945-5100.2003.tb00261.x
J.W. Morgan, E. Anders, Chemical composition of Mars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 43(10), 1601–1610 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(79)90180-7
P. Morgan, S.E. Smrekar, R. Lorenz, M. Grott, O. Kroemer, O. Müller, Potential effects of surface temperature variations and disturbances and thermal convection on the Mars InSight HP3 heat-flow determination. Space Sci. Rev. 211, 277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0388-y
M.P. Panning, P. Lognonne, W.B. Banerdt, R. Garcia et al., Planned products of the Mars structure service for the InSight mission to Mars. Space Sci. Rev. 211, 611–650 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-016-0317-5
T.J. Parker, F.J. Calef, M.P. Golombek, T.M. Hare, High-resolution basemaps for localization, mission planning, and geologic mapping at Meridiani Planum and Gale crater, in The 43rd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2012). Abstract #2535
T.J. Parker, M.C. Malin, F.J. Calef, R.G. Deen et al., Localization and ‘contextualization’ of Curiosity in Gale crater, and other landed Mars missions, in The 44th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, 2013). Abstract #2534
A.C. Plesa, M. Grott, N. Tosi, D. Breuer et al., How large are present-day heat flux variations across the surface of Mars? J. Geophys. Res., Planets 121, 2386–2403 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JE005126
A. Rivoldini, T. Van Hoolst, The interior structure of Mercury constrained by the low-degree gravity field and the rotation of Mercury. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 377, 62–72 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.07.021
A. Rivoldini, T. Van Hoolst, O. Verhoeven, A. Mocquet, V. Dehant, Geodesy constraints on the interior structure and composition of Mars. Icarus 213, 451–472 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2011.03.024
F. Roosbeek, Analytical developments of rigid Mars nutation and tide generating potential series. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 75, 287–300 (1999)
C. Sanloup, A. Jambon, P. Gillet, A simple chondritic model of Mars. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 112, 43–54 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9201(98)00175-7
T. Sasao, S. Okubo, M. Saito, A simple theory on the dynamical effects of a stratified fluid core upon nutational motion of the Earth, in Symposium-International Astronomical Union, vol. 78 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1980), pp. 165–183
D.E. Smith, M.T. Zuber, H.V. Frey, J.B. Garvin et al., Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA): Experiment summary after the first year of global mapping of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 23689–23722 (2001)
A. Spiga, N. Teanby, A. Lucas, B. Kenda et al., Atmospheric science with InSight. Space Sci. Rev. (2018), this issue
T. Spohn, M. Grott et al., The heat flow and physical properties package (HP3) for the InSight mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2018), this issue. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-018-0531-4
G.J. Taylor, The bulk composition of Mars. Chem. Erde 73, 401–420 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2013.09.006
E. Van den Acker, T. Van Hoolst, O. de Viron, P. Defraigne et al., Influence of the winds and of the CO2 mass exchange between the atmosphere and the polar ice caps on Mars’ rotation. J. Geophys. Res. 107(E7), 5055 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JE001539
T. Van Hoolst, V. Dehant, Influence of triaxiality and second-order terms in flattenings on the rotation of terrestrial planets: I. Formalism and rotational normal modes. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 134, 17–33 (2002)
T. Van Hoolst, V. Dehant, P. Defraigne, Sensitivity of the free core nutation and the Chandler Wobble to changes in the interior structure of Mars. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 117, 397–405 (2000a)
T. Van Hoolst, V. Dehant, P. Defraigne, Chandler Wobble and free core nutation for Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 1145–1151 (2000b)
T. Van Hoolst, V. Dehant, F. Roosbeek, P. Lognonné, Tidally induced surface displacements, external potential variations, and gravity variations on Mars. Icarus 161, 281–296 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-1035(02)00045-3
M.A. Wieczorek, M.T. Zuber, Thickness of the Martian crust: Improved constraints from geoid-to-topography ratios. J. Geophys. Res. 109, E1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JE002153
R. Woo, F.-C. Yang, K.W. Yip, W.B. Kendall, Measurements of large-scale density fluctuations in the solar wind using dual-frequency phase scintillations. Astrophys. J. 210, 568–574 (1976)
C.F. Yoder, E.M. Standish, Martian precession and rotation from Viking lander range data. J. Geophys. Res. 102(E2), 4065–4080 (1997)
C.F. Yoder, A.S. Konopliv, D.N. Yuan, E.M. Standish, W.M. Folkner, Fluid core size of Mars from detection of the solar tide. Science 300, 299–303 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1079645
M. Yseboodt, V. Dehant, M.J. Péters, Signatures of the Martian rotation parameters in the Doppler and range observables. Planet. Space Sci. 144, 74–88 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was carried out in part by the InSight Project at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration; and in part at the Royal Observatory of Belgium with financial support by the Belgian PRODEX program managed by the European Space Agency in collaboration with the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office. This is InSight Contribution Number 53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The InSight Mission to Mars II
Edited by William B. Banerdt and Christopher T. Russell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Folkner, W.M., Dehant, V., Le Maistre, S. et al. The Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment on the InSight Mission to Mars. Space Sci Rev 214, 100 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-018-0530-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-018-0530-5