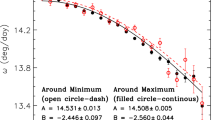Abstract
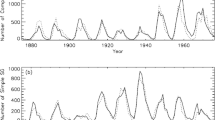
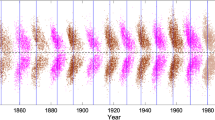
Based on the Debrecen Photoheliographic Data (DPD) sunspot catalog, we investigate the cyclical behaviors of tilt angles of all sunspot groups (SGs) and SGs with angular separation constraint \(S > 2.5^{\circ}\) in Solar Cycles (SCs) 21 – 23. It is found that, the cyclical behaviors of tilt angles during SC 23 are different from those of SCs 21 and 22, confirmed by using the SDD sunspot catalog where possible, which are embodied in the following five aspects: (i) For all SGs (SGs with separation constraint), the percentage of SGs with larger absolute values of tilt angles in the declining phase than during the maximum phase is about 80% (60%) in SCs 21 and 22. In SC 23, the percentage of SGs with larger absolute values of tilt angles during the declining phase is about 1.10 times (at least not lower than) that during the maximum. (ii) During SCs 21 – 23, the yearly mean of tilt angles decreases with time for all SGs (SGs with separation constraint) and the slopes of the linear regression lines are negative: −0.404, −0.910, and −0.740/−1.005 (−0.500, −1.138, and −0.764/−0.576). (iii) During SCs 21 and 22, the yearly mean of the absolute value of tilt angles generally decreases with time for all SGs (SGs with separation constraint) and the slopes of the linear regression lines also are negative: −0.347 and −0.451 (−0.504 and −0.397). (iv) During SC 23, for all SGs, the yearly mean of the absolute value of tilt angles generally increases with time and the slope of the linear regression line is positive: 0.281/0.429. For SGs with separation constraint, the linear regression line to the yearly mean of the absolute value of tilt angles is almost horizontal and its slope is −0.008/0.014. (v) The yearly mean of latitude of SGs decreases steadily with time during each SC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The SG data used in our analysis are taken from the DPD sunspot catalog, which are available at http://fenyi.solarobs.epss.hu/test/tiltangle/dpd/, and the SDD sunspot catalog, which are available at http://fenyi.solarobs.epss.hu/test/tiltangle/sdd/.
References
Babcock, H.W.: 1961, The topology of the Sun’s magnetic field and the 22-year cycle. Astrophys. J. 133, 572. DOI. ADS.
Baranyi, T.: 2015, Comparison of Debrecen and Mount Wilson/Kodaikanal sunspot group tilt angles and the Joy’s law. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 447, 1857. DOI. ADS.
Baranyi, T., Győri, L., Ludmány, A.: 2016, On-line tools for Solar Data Compiled at the Debrecen Observatory and their extensions with the Greenwich sunspot data. Solar Phys. 291, 3081. DOI. ADS.
Basu, S., Broomhall, A.-M., Chaplin, W.J., Elsworth, Y.: 2012, Thinning of the Sun’s magnetic layer: the peculiar solar minimum could have been predicted. Astrophys. J. 758, 43. DOI. ADS.
Brunner, W.: 1930, Gesetzmäßigkeiten in der Anordnung der Sonnenflecken zu Gruppen. Astronomische Mitteilungen der Eidgenössischen Sternwarte Zurich 13, 67. ADS.
Cameron, R.H., Jiang, J., Schmitt, D., Schussler, M.: 2010, Surface flux transport modeling for solar cycles 15 – 21: effects of cycle-dependent tilt angles of sunspot groups. Astrophys. J. 719, 264. DOI. ADS.
Charbonneau, P.: 2020, Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 17, 4. DOI. ADS.
Dasi-Espuig, M., Solanki, S.K., Krivova, N.A., Cameron, R., Penuela, T.: 2010, Sunspot group tilt angles and the strength of the solar cycle. Astron. Astrophys. 518, A7. DOI. ADS.
de Toma, G., White, O.R., Chapman, G.A., Walton, S.R., Preminger, D.G., Cookson, A.M.: 2004, Solar cycle 23: an anomalous cycle? Astrophys. J. 609, 1140. DOI. ADS.
D’Silva, S., Choudhuri, A.R.: 1993, A theoretical model for tilts of bipolar magnetic regions. Astron. Astrophys. 272, 621. ADS.
Fisher, G.H., Fan, Y., Longcope, D.W., Linton, M.G., Pevtsov, A.A.: 2000, The solar dynamo and emerging flux - (invited review). Solar Phys. 192, 119. DOI. ADS.
Gao, P.-X.: 2020a, Phase relation between large and simple sunspot groups in solar cycles 22 – 24. Solar Phys. 295, 23. DOI. ADS.
Gao, P.X.: 2020b, Curious changes in association of complex sunspot groups with X-ray flares (≥M1) in solar cycles 22 – 24. Astrophys. J. 894, 77. DOI. ADS.
Győri, L., Baranyi, T., Ludmány, A.: 2011, Photospheric data programs at the Debrecen Observatory. In: Prasad Choudhary, D., Strassmeier, K.G. (eds.) Physics of Sun and Star Spots, IAU Symp. 273, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 403. DOI. ADS.
Győri, L., Ludmány, A., Baranyi, T.: 2017, Comparative analysis of Debrecen sunspot catalogues. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 465, 1259. DOI. ADS.
Hale, G.E., Ellerman, F., Nicholson, S.B., Joy, A.H.: 1919, The magnetic polarity of sun-spots. Astrophys. J. 49, 153. DOI. ADS.
Harvey, K.L.: 1992, The cyclic behavior of solar activity. In: Harvey, K.L. (ed.) The Solar Cycle, ASP Conference Series 27, ASP, San Francisco, 335. ADS.
Howard, R.F.: 1991, Axial tilt angles of sunspot groups. Solar Phys. 136, 251. DOI. ADS.
Howe, R., Davies, G.R., Chaplin, W.J., Elsworth, Y., Basu, S., Hale, S.J., Ball, W.H., Komm, R.W.: 2017, The Sun in transition? Persistence of near-surface structural changes through cycle 24. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 470, 1935. DOI. ADS.
Ivanov, V.G.: 2012, Joy’s law and its features according to the data of three sunspot catalogs. Geomagn. Aeron. 52, 999. DOI. ADS.
Jiao, Q., Jiang, J., Wang, Z.-F.: 2021, Sunspot tilt angles revisited: dependence on the solar cycle strength. Astron. Astrophys. 653, A27. DOI. ADS.
Jha, B.K., Karak, B.B., Mandal, S., Banerjee, D.: 2020, Magnetic field dependence of bipolar magnetic region tilts on the Sun: indication of tilt quenching. Astrophys. J. Lett. 889, L19. DOI. ADS.
Kilcik, A., Yurchyshyn, V.B., Ozguc, A., Rozelot, J.P.: 2014, Solar cycle 24: curious changes in the relative numbers of sunspot group types. Astrophys. J. Lett. 794, L2. DOI. ADS.
Leighton, R.B.: 1969, A magneto-kinematic model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 156, 1. DOI. ADS.
Li, K.J., Yun, H.S., Gu, X.M.: 2001, Hemispheric variation in solar activity. Astrophys. J. 554, L115. DOI. ADS.
Li, J., Ulrich, R.K.: 2012, Long-term measurements of sunspot magnetic tilt angles. Astrophys. J. 758, 115. DOI. ADS.
Li, J.: 2018, A systematic study of hale and anti-Hale sunspot physical parameters. Astrophys. J. 867, 89. DOI. ADS.
López Fuentes, M.C., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H., Pevtsov, A.A., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2003, Magnetic twist and writhe of active regions. On the origin of deformed flux tubes. Astron. Astrophys. 397, 305. DOI. ADS.
McClintock, B.H., Norton, A.A.: 2013, Recovering Joy’s law as a function of solar cycle, hemisphere, and longitude. Solar Phys. 287, 215. DOI. ADS.
Nagovitsyn, Y.A., Osipova, A.A., Pevtsov, A.A.: 2021, Tilt angle and lifetime of sunspot groups. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 501, 2782. DOI. ADS.
Senthamizh Pavai, V., Arlt, R., Dasi-Espuig, M., Krivova, N.A., Solanki, S.K.: 2015, Sunspot areas and tilt angles for solar cycles 7 – 10. Astron. Astrophys. 584, A73. DOI. ADS.
Senthamizh Pavai, V., Arlt, R., Diercke, A., Denker, C., Vaquero, J.M.: 2016, Sunspot group tilt angle measurements from historical observations. Adv. Space Res. 58, 1468. DOI. ADS.
Sivaraman, K.R., Gupta, S.S., Howard, R.F.: 1999, Measurement of Kodaikanal white-light images - IV. Axial tilt angles of sunspot groups. Solar Phys. 189, 69. DOI. ADS.
Stenflo, J.O., Kosovichev, A.G.: 2012, Bipolar magnetic regions on the sun: global analysis of the SOHO/MDI data set. Astrophys. J. 745, 129. DOI. ADS.
Tian, L.R., Liu, Y., Yang, J., Alexander, D.: 2015, The role of the kink instability of a long-lived active region AR 9604. Solar Phys. 229, 237. DOI. ADS.
Tlatov, A., Illarionov, E., Sokoloff, D., Pipin, V.: 2013, A new dynamo pattern revealed by the tilt angle of bipolar sunspot groups. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 432, 2975. DOI. ADS.
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Green, L.M.: 2015, Evolution of active regions. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 12, 1. DOI. ADS.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1989, Average properties of bipolar magnetic regions during sunspot CYCLE-21. Solar Phys. 124, 81. DOI. ADS.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1991, Magnetic flux transport and the Sun’s dipole moment: new twists to the Babcock-Leighton model. Astrophys. J. 375, 761. DOI. ADS.
Wang, Y.-M., Colaninno, R.C., Baranyi, T., Li, J.: 2015, Active-region tilt angles: magnetic versus white-light determinations of Joy’s law. Astrophys. J. 798, 50. DOI. ADS.
Wang, Y.-M.: 2017, Surface flux transport and the evolution of the Sun’s polar fields. Space Sci. Rev. 210, 351. DOI. ADS.
Wilson, R.M.: 1987, On the prospect of using butterfly diagrams to predict cycle minimum. Solar Phys. 111, 255. DOI. ADS.
Wilson, R.M., Hathaway, D.H., Reichmann, E.J.: 1996, On the behavior of the sunspot cycle near minimum. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 19967. DOI. ADS.
Yiğit, E., Kilcik, A., Elias, A.G., Dönmez, B., Ozguc, A., Yurchshyn, V., Rozelot, J.-P.: 2018, Critical frequencies of the ionospheric F1 and F2 layers during the last four solar cycles: sunspot group type dependencies. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 171, 157. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the reviewer very much for the careful reading and the constructive comments that improved the original version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11903077), the Basic Research Foundation of Yunnan Province, China (Grant Nos. 202101AT070019, 202201AS070042), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng-Xin Gao wrote the manuscript text, prepared all figures, and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, PX. Cyclical Behaviors of Sunspot-Group Tilt Angles in Solar Cycles 21 – 23. Sol Phys 298, 21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02117-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02117-6