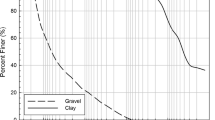
This study investigates the influence of soil composition on soil strength by performing direct shear test on various samples, including artificial soil with different components, artificial mixed soil with different amounts, natural soil with different moisture contents, and sandy soil with different sizes. The test results show that soil strength is determined by the joint effect of inter-particle friction and cohesion. Mineral composition and water content are the main factors affecting clay strength. Changes in the mineral composition and water content of clay alter the contact state and connection of its particles, thereby significantly affecting the macroscopic properties of the soil. Different grain compositions modified the shear deformation characteristics by altering the arrangement and intergranular engagement of the particles, consequently affecting the strength. The results of this study provide further insight into the micro and fine mechanism of the soil shear strength characteristics of different components. This study also offers guiding significance in engineering practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Li, W. Liu, and M. Zhang, "Discussion on Coulomb earth pressure theory," Chin. J. Geotech. Eng., 27, 677-681 (2005).
T. W. Lambe and R. V. Whitman, Soil Mechanics, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1969).
K. Terzaghi, "Record earth pressure testing machine," Eng. News-Rec., 109, 365-369 (1932).
K. Terzaghi, "Large retaining-wall tests, II-pressure of saturated sand," Eng. News-Rec., 112, 259-262, 316-318 (1900).
K. Terzaghi, Theoretical Soil Mechanics, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1943).
J. H. Qian and Z. Z. Yin, Geotechnical Principles and Calculation, 2th ed, China Water Power Press, Beijing (1996).
A. W. Bishop, I. Alpan, G. E. Blight, and I. B. Donald, "Factors controlling the strength of partly saturated cohesive soils," Research Conf. on Shear Strength of Cohesive Soils, ASCE (1960).
A. W. Bishop and G. E. Blight, "Some aspects of effective stress in saturated and partly saturated soils," Geotechnique., 13, 177-197 (1963).
D. G. Fredlund, N. R. Morgenstern, and R. A. Widger, "The shear strength of unsaturated soils," Can. Geotech. J., 15, 313-321 (1978).
J. K. M. Gan, D. G. Fredlund, and H. Rahardjo, "Determination of the shear strength parameters of an unsaturated soil using the direct shear test," Can. Geotech. J., 25, 500-510 (1988).
V. I. Osipov, "Friction and cohesion as multifaceted factors of soil shear resistance," Soil Mech. Found. Eng., 53, 143-151 (2016).
J. Wang, H. Mo, S. Liu, Y. Z. Wang, and F. H. Jiang, "Effect of mineral composition on macroscopic and microscopic consolidation properties of soft soil," Soil Mech. Found. Eng., 50, 232-237 (2014).
J. W. Liang, Y. G. Fang, and S. Chen, "Experiment and mechanism analysis on strength characteristics of coastal saline soil," J. Yangtze River. Sci. Res. Inst., 27, 36-40 (2010).
J. Liang, Y. Fang, and S. Chen, "Experimental research on effect of salt content on strength of tinyparticle clay," Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng., 28, 3821-3829 (2009).
J. W. Liang, "Experimental study on soft soil deformation and seepage characteristics with microscopic parameter analysis," PhD. thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China (2010).
W. Li and H. Liang, "The influence of the water ratio on the shearing strength of silty clay," J. Inner. Mongol. Agric. Univ., Nat. Sci. Ed., 1, 170-174 (2009).
J. K. Mitchell, Fundamentals of Soil Behavior, 2th ed, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1993).
R. G. Gu, "The study of composition effects on soft soil creep behavior and ion effects on soft soil seepage," PhD. thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China (2007).
M. J. Chi, X. J. Li, Z. H. Zhou, J. S. Zhao, and G. L. Zhou, "Meso-scale study of effects of intermediate principal stress on strength of sand," Rock Soil Mech., 31, 3751-3757 (2010).
M. Jia, L. Wang, and J. Zhou, "Experimental research on macro-meso consolidation mechanism of sandy soil with dynamic compaction," Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng., 28, 3282-3290 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Osnovaniya, Fundamenty i Mekhanika Gruntov, No. 5, p. 18, September-October, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Liu, Zh., Hu, Gx. et al. Experimental Analysis of the Influence of Soil Composition on Strength Characteristics. Soil Mech Found Eng 55, 325–332 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-018-9544-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-018-9544-y