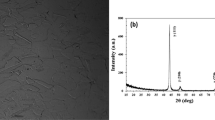
The effect of the modes of thermomechanical treatment (TMT), involving warm plastic deformation (e = 2) by rolling in the temperature interval of 600 – 900°C, on the austenitic steel microstructure is studied. Using the methods of transmission electron microscopy, it is shown that this plastic deformation results in the formation of a highly defective fragmented microstructure with a high density of low-angle misorientation boundaries. Numerous grains/subgrains flattened in the rolling plane and elongated in the rolling direction are revealed. It is shown that as the TMT temperature is increased, the fraction of low-angle boundaries decreases and so does the dislocation density. It is noted that the average transverse subgrain size varies from 112 nm (TMT-1) to 306 nm (TMT-4). These peculiarities of the steel microstructure ensure advanced strength properties as a result of all TMT modes. The optimal mechanical properties are achieved in this steel after TMT-1, in which case the resulting microstructure is highly homogeneous with a high dislocation density retained; the yield strength values are 808 MPa at 20°C and 516 MPa at 650°C, with the elongation to failure of about 7%. The principal fracture mechanism of the steel samples is that of ductile dimple transgranular fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kozlov, K. Kozlov and I. Portnykh, J. Nucl. Mater. 549, 152915 (2021). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2021.152915.
N. M. Mitrofanova and T. A. Churyumova, Voprosy Atomnoy Nauki i Tekhniki. Seriya: Materialovedeniye i Novyye Materialy 2(98), 100 (2019).
N. M. Mitrofanova, M. G. Bogolepov, F. G. Reshetnikov, Yu. K. Bibishvili, T. A. Topilina, N. K. Zhitkov, V. N. Voyevodin, Yu. I. Kazennov, and V. M. Zakharkin, Austenitic Steel, RF Patent No. 2068022 [in Russian]. Appl. 17.06.1994; Publ. 20.10.1996.
N. M. Mitrofanova, M. V. Leontieva-Smirnova, Yu. A. Ivanov, T. A. Churyumova, B. A. Vasiliev, M. R. Farakshin, O. M. Saraev, N. N. Oshkanov, V. V. Chuev, S. A. Bychkov, and M. I. Ilyashik, Fast Neutron Reactor Fuel Cell, a Utility Model to RF Patent No. 127235 [in Russian]. Appl. 20.11.2012; Publ. 20.04.2013. Bull. No. 11.
Z. Yanushkevich, A. Lugovskaya, A. Belyakov and R. Kaibyshev, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 667, 279 (2016). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.05.008.
F. K. Yan, G. Z. Liu, N. R. Tao and K. Lu, Acta Mater. 60, 1059 (2012). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.11.009.
Y. Xiong, Y. Yue, T. He, et al., Materials 11, 1557 (2018). Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091557.
J. Zhao and Z. Jiang, Progr. Mater. Sci. 94, 174 (2018). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.01.006.
A. Järvenpää, M. Jaskari, A. Kisko and P. Karjalainen, Metals 10, 281 (2020). Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020281.
G. S. Sun, L. X. Du, J. Hu and R. D. K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 709, 254 (2018). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.10.054.
S. A. Akkuzin and I. Yu. Litovchenko, Vektor Nauki Tol'yattinskogo Gosudarstvennogo Universiteta 2(52), 7 (2020). Doi: https://doi.org/10.18323/2073-5073-2020-2-7-14.
S. J. Wang, T. Jozaghi, I. Karaman, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A 694, 121 (2017). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.03.073.
S. Akkuzin, I. Litovchenko, N. Polekhina, et al., Metals. 12, 63 (2022). Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/met12010063.
S. A. Akkuzin, I. Yu. Litovchenko, A. N. Tyumentsev and V. M. Chernov, Russ. Phys. J. 62(4), 698 (2019). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-019-01766-0.
S. A. Akkuzin, I. Yu. Litovchenko, A. V. Kim, et al., Letters on Materials 12, 399 (2022). Doi: https://doi.org/10.22226/2410-3535-2022-4-394-398.
ASM Handbook. Volume 12 of the 9th Edition, Fractography. Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akkuzin, S.A., Polekhina, N.A., Kim, A.V. et al. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Fracture of Austenitic Steel EK-164 After Warm Deformation at 600–900°C. Russ Phys J 66, 1235–1241 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-03067-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-03067-z