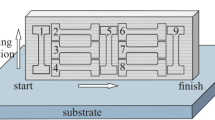
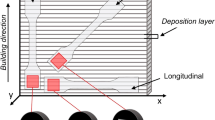
The features of crack formation near the fracture region and the fracture micromechanism are investigated during uniaxial tension of specimens of Ni–Cr stainless steels, Fe–19Cr–9Ni–0.1C and Fe–19Cr–9Ni–1.4Nb–0.1C, produced by the method of 3D wire-feed electron beam additive manufacturing (EBAM) as a function of the phase composition and phase distribution in the structure. It is found out that in the specimens with a twophase (austenite/δ-ferrite) microstructure the ferrite morphology and its volume content (up 25%) affect the plastic shear distribution in austenite and ferrite and exert a slight influence on the formation of strain localization micro- and macrobands in the pre-fracture stage, and the crack-formation mechanism is similar to that observed in cast stainless steels of similar compositions, which possess single-phase austenitic structure. In additively-manufactured steel containing niobium the formation of brittle niobium- and iron-based intermetallic phases favors the formation of pores and microcracks at the austenite/NbFeCrNi-phase or the δ- ferrite/NbFeCrNi-phase interfaces, while the processes of cracking in the strain localization bands (and their formation) turn out to be suppressed. Irrespective of the elemental and phase compositions of steel specimensformed by the method of 3D additive manufacturing, the principal micromechanism of their fracture, transgranular dimple fracture, is similar to that observed in the cast specimens of austenitic stainless steels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Ding, Z. I. Pan, D. Cuiuri, and H. Li, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 81, 465−481 (2015).
K. H. Lo, C. H. Shek, and J. K.L. Lai, Mat. Sci. and Eng.: R: Reports, 65, 39−104 (2009).
N. Li, S. Huang, G. Zhang, et. al., J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 35, 249–269 (2019).
C. R. Cunningham, J. M. Flynn, A. Shokrani, et. al., Add. Manuf., 22, 672−686 (2018).
W. E. Frazier, Metal Additive Manufacturing. A. Rev. J. Mater. Eng. Performance, 23(6), 1917–1928 (2014).
V. Laghi, M. Palermo, L. Tonelli, et al., Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 106, 3693– 3705 (2020).
S.Yu. Tarasov, A. V. Filippov, N. N. Shamarin, et al., J. Alloys Compd., 803, 364–370 (2019).
Zh. Wang, T. A. Palmer, and A. M. Beese, Acta Mater., 110, 226–235 (2016).
X. Chen, J. Li, X. Cheng, et al., Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 715, 307–314 (2018).
K. Zhang, S. Wang, W. Liu, and X. Shang, Mater. Des., 55, 104–119 (2014).
M. Godec, S. Zaefferer, B. Podgornik, et al., Mat. Charact., 160, 110074 (2020).
E. G. Astafurova, M.Yu. Panchenko, V. A. Moskvina, et al., J. Mater. Sci., 55, 9211–9224 (2020).
A. V. Kolubaev, S. Yu. Tarasov, A. V. Filippov, et al., Russ. Phys. J., 61, No. 7, 1491–1498 (2018).
Y. D. Wang, H. B. Tang, Y. L. Fang, and H. M. Wang, Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 527, 4804−4809 (2010).
X. Chen, J. Li, X. Cheng, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 703, 567–577 (2017).
A. Yadollahi, N. Shamsaei, S. M. Thompson, and D. W. Seely, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 644, 171−183 (2015).
M. Yu. Panchenko, E. G. Astafurova, V. A. Moskvina, et al., Nanosci. Technol.: Int. J. (2020) (in print).
E. G. Astafurova, E. V. Melnikov, S. V. Astafurov, et al., Phys. Mesomech., 22(4), 313−326 (2019).
M. A. Shtremel, Fracture, Book 2, Fracture of Structures [in Russian], MISIS, Moscow (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 6, pp. 16–24, June, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Astafurova, E.G., Moskvina, V.A., Panchenko, M.Y. et al. The Influence of Phase Composition and Phase Distribution on Crack Formation and Fracture Mechanisms of Cr–Ni Steels Produced by the Method of 3D Electron-Beam Printing. Russ Phys J 63, 917–925 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-020-02118-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-020-02118-z