Abstract
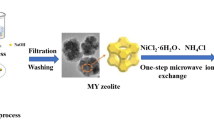
Micro-mesoporous zeolite shows great potential in the field of fuel denitrogenation. However, the current preparation method of zeolite with composite pores still has the problems of high cost and low denitrification rate. Herein, we prepared a low-cost phosphorus doped zeolite by directly impregnated Y zeolite in phosphoric acid and calcinated at 400 °C firstly. Experimental results showed that phosphorus doped 10 wt.% PA/MY provided optimum denitrogenation performance with denitrogenation rate as high as 97% compared to unmodified MY zeolite (21.11%) and ion exchanged 1.0 MHY zeolite (91.38%). What's more, it was found that the introduction of phosphorus led to the formation of P–O tetrahedra and Al–O–P bonds in zeolite, which increased the amount of mesopore and the Lewis acid in zeolite. Meanwhile, the comparative study found that ion exchanged MHY zeolite depended on the limited pore matching effect of micropores and nitrogen-containing molecules and the chemisorption reaction of non-regenerable Brøsted acid to achieve denitrogenation performance. However, phosphorus doped zeolite PA/MY not only had a better size matching effect between the mesopore and the size of nitrogen-containing molecules, but also had more Lewis acid to play a major role in denitrogenation. The Lewis acid on PA/MY zeolite also had the advantage of being easy to regenerate by desorption of the nitrogen-containing molecules absorbed. This study showed good prospects for the industrial application of the doped zeolite.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary material.
References
J. Dickson, N.A. Conroy, Y. Xie, Chem. Eng. J. 402, 126268 (2020)
Y. Pukcothanung, T. Siritanon, K. Rangsriwatananon, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 258, 131 (2018)
V. Blay, B. Louis, R. Miravalles, T. Yokoi, K.A. Peccatiello, M. Clough, B. Yilmaz, Acs Catal. 10, 6542 (2017)
S.M. Kanan, M.A. Moyet, Res. Chem. Intermed. 47, 433–445 (2021)
F. Tian, Q.C. Shen, Z.K. Fu, Y.H. Wu, C.Y. Jia, Fuel Process. Technol. 128, 176 (2014)
X.S. Lu, Y.X. Peng, H. Chen, J. Dai, Ni. Bai, J. Wang, Chem. Pap. (2023)
S. Abelló, A. Bonilla, J. Pérez-Ramírez, Appl Catal A- Gen. 364, 191 (2009)
I.I. Ivanova, I.A. Kasyanov, A.A. Maerle, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 189, 163 (2014)
J.C. Groen, L.A. Peffer, J. Pérez-Ramírez Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 60, 1 (2003)
X. Jia, W. Khan, Z. Wu, J. Choi, Adv. Powder Technol. 30, 467 (2019)
F. Wang, H. Li, H. Zhao, Catal. Ind. 20, 34 (2012)
X. Hong, K. Tang, Pet. Sci. Technol. 33, 15 (2015)
X. Hong, K. Tang, Energy Source Part A. 38, 2560 (2016)
X. Fan, B. Zhang, Z. Su, M. Wang, F. Li, Chem. Phys. 558, 111512 (2022)
P. Lv, Y. Lan, Y. Liu, J. Energy Inst. 93, 4 (2020)
F. Xu, M. Zhang, Z.H. Li, C.D. Guan, L.J. Zhu, D.H. Xia, J. Porous Mater. 29, 5 (2022)
W.Q. Fu, L. Zhang, T. Tang, Q.P. Ke, S. Wang, J.B. Hu, G.Y. Fang, J.X. Li, F.S. Xiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 15346 (2011)
Z.H. Huang, N.W. Liu, J.J. Yao, P. Xin, L. Shi, Huagong Jinzhan 35, 138 (2016)
X. Colom, F. Carrillo, J. Wood. Chem. Technol. 25, 1 (2005)
K.K. Pandey, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 71, 1969 (1999)
S.F. Alam, M.Z. Kim, A.U. Rehman, A. Devipriysnks, S. Pankaj, H.C. Churl, Nanomaterials 11, 3198 (2021)
Y.C. Fan, X.P. Zhen, C.G. Niu, L.J. Song, J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 45, 1467 (2017)
Y.J. Lee, Y.W. Kim, N. Viswanadham, K.W. Jun, J.W. Bae, Appl Catal. A-Gen. 374, 18 (2010)
R. Prajapati, D. Jadav, M. Pandey, K. Nishimura, S. Inagak, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 18, (2022)
L.F. Chen, X.L. Zhou, L.E. Norena, J.A. Wang, J. Navarrete, P. Salas, A. Montoya, P. Del Angel, M.E. Llanos, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 2443 (2006)
Y.L. Gu, S.Z. Liu, C.Y. Li, Q.K. Cui, J. Catal. 301, 93 (2013)
W.X. Zhu, C. Tang, D.N. Liu, J.L. Wang, A.M. Asiri, X.P. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. A. 4, 7169 (2016)
K. Damodaran, J.W. Wiench, S.M. Cabral, Y.L. Lam, J. Trebosc, J.P. Amoureux, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 95, 296 (2006)
J.C. Soh, S.L. Chong, S.S. Hossain, C.K. Cheng, Fuel Process. Technol. 158, 85 (2017)
K.S.W. Sing, Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 1217 (1985)
F. Li, Z. Liu, M. Zhang, Huagong Jinzhan 32, 31 (2015)
M. Sharma, B. Das, A. Hazarika, N.S.V.M. Rao Mangina, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 272, 31 (2018)
M.M.J. Treacy, J.B. Higgins, Zeolites 10, 26 (2001)
Funding
This work was partially supported by the postgraduate innovation project of China University of Petroleum (East China) under grant YCX2020047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F. Xu contributed to Methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing and editing. Y. Zhao and M. Zhang contributed to methodology, validation. Z. Li and L. Zhu contributed to investigation, resources. D. Xia contributed to conceptualization, funding acquisition, chief review and editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with any other people or organizations.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Zhao, Y., Zhang, M. et al. Phosphorus-doped Y zeolites for increasing mesopore and Lewis acid in high-efficiency denitrogenation. Res Chem Intermed 49, 4939–4954 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-023-05079-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-023-05079-3