Abstract
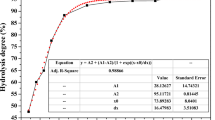
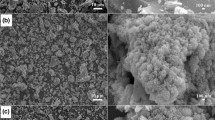
Hydrolysis of titanyl sulfate solutions with TiO2 concentrations of 140–180 g/L was investigated. The effects of the concentrations of impurities present in ilmenite, for example iron(II), magnesium, and aluminium, on hydrolytic conversion, and on the morphology and composition of the hydrolysates, were examined. The results showed that with increasing impurity concentrations, the conversion was gradually decreased, but still maintained at ~95 %. The concentrations of these impurity ions substantially affected the morphology of the hydrolysates. The higher the concentrations of the impurities were, the more irregular and non-uniform were the hydrolysate particles. When iron-to-titanium dioxide (Fe/TiO2) mass ratios in the precipitate liquors were >0.50, the hydrolysates became very compact and difficult to filter and disperse. It was found that the hydrolysate crystallites first formed primary particles which had a very similar particle sizes of 30–50 nm, despite different concentrations of titanium and the impurity ions used. The primary particles further aggregated and formed secondary aggregates probably via sulfate bridge bonds. The concentrations of the impurities substantially affected the amounts of hydrated SO3 adsorbed by the hydrolysates, which increased with increasing impurity concentrations, resulting in increased agglomeration of the primary particles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Barksdale, Chemistry and Technology, 2nd edn. (Springer, New York, 1966), p. 414
A.W. Hixon, W.W. Plechner, Ind. Eng. Chem. 3, 25 (1933)
B. Xiang, N.B. Li, S.T. Zhang, B.R. Hou, Southwest Normal University 2, 29 (2004)
L. Hao, W.Q. Ji, X.G. Chen, Y.H. Wei, Inorganic. Chem. Ind. 2, 38 (2006)
C.X. Tian et al., Trans. Nonferrous Met. Sco. China 19, S829–S833 (2009)
J.P. Jalava, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 31, 608–611 (1992)
W. Hixson, C. Ralphe, Ind. Eng. Chem. 7, 37 (1945)
B.U. Grzmil, D. Grela, B. Kic, M. Podsiadly, Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 1, 62 (2008)
X. Yang, T.Y. Xue, L.N. Wang, T. Qi, Wet Metallurgy 4, 29 (2010)
B.U. Grzmil, D. Grela, B. Kic, Chem. Pap. 1, 62 (2008)
V.D. Bavykin, P. Vera, V. Alerxander, V.N. Parmon, Res. Chem. Intermed 3–5, 33 (2007)
B.U. Grzmil, D. Grela, B. Kic, Pol. J. Chem. Tech. 3, 11 (2009)
G.R. Eric, D.S. Alan, E.G. Philip, N. Sarah, in United States Patent No. US 7,326,390 B2 (2008)
W. Twist, in British Patent, No. 1135787 (1966)
K.S. Kamala, C.A. Thomas, M. Devabrata, A. Archana, Waste Manage. Res. 24, 74–79 (2006)
S.L. Zhang, X.Z. Cheng, H.F. Hu, Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium 1, 24 (2003)
X.L. Hao, L. Li, B. Liang, C. Li, Hydrometallurgy 113, 185–191 (2012)
A. Deep, P. Malik, B. Gupta, Sep. Sci. Technol. 4, 36 (2001)
E. Narita, H. Takeuchi, H. Ichikawa, T. Odagawa, T. Okabe, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 56, 1832–1836 (1983)
K.C. Sole, Hydrometallurgy 3, 51 (1999)
H. Song, B. Liang, L. Li, P. Wu, C. Li, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 19(7), 642–650 (2012)
M.L. Reynolds, J. Chem. Soc. 4, 2993–2995 (1965)
S. Sekhar et al., Cryst. Growth Des. 2, 1 (2001)
E. Santacesaria, M. Tonello, G. Storti, R.C. Pace, S.J. Carra, Colloid. Interface Sci. 1, 111 (1986)
M.P. Finnegan, H.Z. Zhang, J.F. Banfield, J. Phys. Chem. C 5, 111 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21236004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Liang, B., Lü, L. et al. Effect of impurities on the hydrolysis of low-concentration titanyl sulfate solutions. Res Chem Intermed 41, 5423–5438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1643-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1643-4