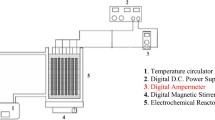
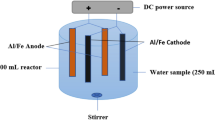
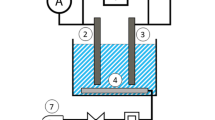
Abstract
This study used conventional and enhanced electrocoagulation with aeration and H2O2 to remove arsenite from water. Electrocoagulation and enhanced electrocoagulation, with aeration and H2O2, can remove arsenite with concentrations of 1, 2, and 10 mg/L to meet drinking water standards. The removal of arsenic in electrocoagulation (R2: 0.99) and enhanced electrocoagulation with aeration (R2: 0.99) and H2O2 (R2: 0.0.99) follow the pseudo-first-order kinetics. The data on the adsorption of arsenic to aluminum produced in EC (R2: 0.90) and enhanced electrocoagulation with aeration (R2: 0.90) and H2O2 (R2: 0.81) is consistent with the Langmuir isotherm. The enhanced electrocoagulation with aeration and H2O2 had a higher ability to remove arsenic than in previous studies. For the first time, using enhanced electrocoagulation with H2O2, arsenic-contaminated water at a 10 mg/L concentration was treated to the drinking water standard. Therefore, preparing drinking water from arsenic-contaminated water sources can be an efficient process up to 10 mg/L.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng Z, Fu F, Dionysiou DD, Tang B (2016) Adsorption, oxidation, and reduction behavior of arsenic in the removal of aqueous As(III) by mesoporous Fe/Al bimetallic particles. Water Res 96:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.020
Fazal MA, Kawachi T, Ichion E (2001) Extent and severity of groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Water Int 26(3):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060108686929
Viraraghavan T, Subramanian KS, Aruldoss JA (1999) Arsenic in drinking water—problems and solutions. Water Sci Technol 40(2):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00432-1
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2001) Source and behaviour of arsenic in natural waters. United Nations synthesis report on arsenic in drinking water. World Health Organization, Geneva
Jiang J-Q (2001) Removing arsenic from groundwater for the developing world—a review. Water Sci Technol 44(6):89–98. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2001.0348
WHO, Staff WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Waste USEPAOoS, Response E (2002) Arsenic treatment technologies for soil, waste, and water. DIANE Publishing, Collingdale
Song P, Yang Z, Zeng G, Yang X, Xu H, Wang L et al (2017) Electrocoagulation treatment of arsenic in wastewaters: a comprehensive review. Chem Eng J 317:707–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.086
Aghapour AA, Dolati M, Khorsandi H (2022) Boron removal using enhanced electrocoagulation (EEC) with hydrogen peroxide under natural conditions to prepare drinking water. Reac Kinet Mech Cat. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02246-2
Dolati M, Aghapour AA, Khorsandi H, Karimzade S (2017) Boron removal from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation at low concentrations. J Environ Chem Eng 5(5):5150–5156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.09.055
Sahu O, Mazumdar B, Chaudhari PK (2014) Treatment of wastewater by electrocoagulation: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(4):2397–2413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2208-6
Eyvaz M, Kirlaroglu M, Aktas TS, Yuksel E (2009) The effects of alternating current electrocoagulation on dye removal from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 153(1):16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.05.028
Kobya M, Can OT, Bayramoglu M (2003) Treatment of textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation using iron and aluminum electrodes. J Hazard Mater 100(1):163–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00102-X
Merzouk B, Gourich B, Sekki A, Madani K, Vial C, Barkaoui M (2009) Studies on the decolorization of textile dye wastewater by continuous electrocoagulation process. Chem Eng J 149(1):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.10.018
Holt PK, Barton GW, Mitchell CA (2005) The future for electrocoagulation as a localised water treatment technology. Chemosphere 59(3):355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.023
Gökkuş Ö, Çoşkun F, Kocaoğlu M, Yıldız YŞ (2014) Determination of optimum conditions for color and COD removal of reactive blue 19 by Fenton oxidation process. Desalin Water Treat 52(31–33):6156–6165. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.812523
Yıldıza N, Gökkuşa Ö, Koparalb AS, Yıldıza YŞ (2019) Peroxi-coagulation process: a comparison of the effect of oxygen level on color and TOC removals. Desalin Water Treat 1(9):106
Lakshmanan D, Clifford DA, Samanta G (2010) Comparative study of arsenic removal by iron using electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation. Water Res 44(19):5641–5652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.018
Ratna Kumar P, Chaudhari S, Khilar KC, Mahajan SP (2004) Removal of arsenic from water by electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 55(9):1245–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.12.025
Wan W, Pepping TJ, Banerji T, Chaudhari S, Giammar DE (2011) Effects of water chemistry on arsenic removal from drinking water by electrocoagulation. Water Res 45(1):384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.016
Song P, Yang Z, Xu H, Huang J, Yang X, Yue F et al (2016) Arsenic removal from contaminated drinking water by electrocoagulation using hybrid Fe–Al electrodes: response surface methodology and mechanism study. Desalin Water Treat 57(10):4548–4556. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.992973
Bandaru SRS, van Genuchten CM, Kumar A, Glade S, Hernandez D, Nahata M et al (2020) Rapid and efficient arsenic removal by iron electrocoagulation enabled with in situ generation of hydrogen peroxide. Environ Sci Technol 54(10):6094–6103. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00012
Ghanizadeh G, Safavi SN, Akbari H, Hazrati S (2016) Elimination of arsenic (III) from urban drinking water by electrocoagulation process. Mil Med 18(2):197–206
Goren AY, Kobya M (2021) Arsenic removal from groundwater using an aerated electrocoagulation reactor with 3D Al electrodes in the presence of anions. Chemosphere 263:128253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128253
Qian A, Yuan S, Zhang P, Tong M (2015) A new mechanism in electrochemical process for arsenic oxidation: production of H2O2 from anodic O2 reduction on the cathode under automatically developed alkaline conditions. Environ Sci Technol 49(9):5689–5696. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00808
Singare PU, Trivedi MP, Mishra RM (2012) Sediment heavy metal contaminants in Vasai Creek of Mumbai: pollution impacts. Am J Chem 2(3):171–180
Gökkuş Ö, Yıldız YŞ (2015) Application of electrocoagulation for treatment of medical waste sterilization plant wastewater and optimization of the experimental conditions. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17(6):1717–1725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0897-2
Balasubramanian N, Kojima T, Basha CA, Srinivasakannan C (2009) Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution using electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater 167(1):966–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.081
Lacasa E, Cañizares P, Sáez C, Fernández FJ, Rodrigo MA (2011) Removal of arsenic by iron and aluminium electrochemically assisted coagulation. Sep Purif Technol 79(1):15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.03.005
Song P, Yang Z, Xu H, Huang J, Yang X, Wang L (2014) Investigation of influencing factors and mechanism of antimony and arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using Fe–Al electrodes. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(33):12911–12919. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie501727a
Aghapour AA, Khorsandi H, Dehghani A, Karimzade S (2018) Preparation and characterization and application of activated alumina (AA) from alum sludge for the adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solutions: new approach to alum sludge recycling. Water Supply 18(5):1825–1831. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2018.006
Hu C, Wang S, Sun J, Liu H, Qu J (2016) An effective method for improving electrocoagulation process: optimization of Al13 polymer formation. Colloids Surf A 489:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.10.063
Cerqueira AA, da Costa Marques MR (2012) Electrolytic treatment of wastewater in the oil industry. New technologies in the oil and gas industry. IntechOpen, London, pp 3–28
Jiang J-Q, Xu Y, Quill K, Simon J, Shettle K (2006) Mechanisms of boron removal with electrocoagulation. Environ Chem 3(5):350–354
Gökkuș Ö, Yıldız Y (2014) Investigation of the effect of process parameters on the coagulation-flocculation treatment of textile wastewater using the Taguchi experimental method. Fresenius Environ Bull 23(2):463–470
Murthy ZVP, Parmar S (2011) Removal of strontium by electrocoagulation using stainless steel and aluminum electrodes. Desalination 282:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.08.058
Modirshahla N, Behnajady MA, Kooshaiian S (2007) Investigation of the effect of different electrode connections on the removal efficiency of tartrazine from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation. Dyes Pigm 74(2):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.02.006
Kobya M, Gebologlu U, Ulu F, Oncel S, Demirbas E (2011) Removal of arsenic from drinking water by the electrocoagulation using Fe and Al electrodes. Electrochim Acta 56(14):5060–5070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.03.086
Hansen HK, Nuñez P, Raboy D, Schippacasse I, Grandon R (2007) Electrocoagulation in wastewater containing arsenic: comparing different process designs. Electrochim Acta 52(10):3464–3470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2006.01.090
Gomes JAG, Daida P, Kesmez M, Weir M, Moreno H, Parga JR et al (2007) Arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using combined Al–Fe electrode system and characterization of products. J Hazard Mater 139(2):220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.108
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. J Appl Geochem 17(5):517–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
Zhang S, Zhang J, Wang W, Li F, Cheng X (2013) Removal of phosphate from landscape water using an electrocoagulation process powered directly by photovoltaic solar modules. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 117:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2013.05.027
Omwene PI, Çelen M, Öncel MS, Kobya M (2019) Arsenic removal from naturally arsenic contaminated ground water by packed-bed electrocoagulator using Al and Fe scrap anodes. Process Saf Environ Prot 121:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.10.003
Parga JR, Cocke DL, Valenzuela JL, Gomes JA, Kesmez M, Irwin G et al (2005) Arsenic removal via electrocoagulation from heavy metal contaminated groundwater in La Comarca Lagunera México. J Hazard Mater 124(1):247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.05.017
Barrera-Díaz C, Frontana-Uribe B, Bilyeu B (2014) Removal of organic pollutants in industrial wastewater with an integrated system of copper electrocoagulation and electrogenerated H2O2. Chemosphere 105:160–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.026
Qiang Z, Chang J-H, Huang C-P (2002) Electrochemical generation of hydrogen peroxide from dissolved oxygen in acidic solutions. Water Res 36(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00235-4
Lente G (2018) Facts and alternative facts in chemical kinetics: remarks about the kinetic use of activities, termolecular processes, and linearization techniques. Curr Opin Chem Eng 21:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2018.03.007
Acknowledgements
This paper is a part of the results of a master's thesis in Environmental Health Engineering. We would like to express our gratitude to Urmia University of Medical Sciences that financed the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aghapour, A.A., Ebrahimi, I., bargeshadi, R. et al. Removal of arsenite using conventional and enhanced electrocoagulation with aeration and hydrogen peroxide up to drinking water quality standards. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 135, 2681–2696 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02278-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02278-8