Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on health-related quality of life (HRQOL), the relationship between disease activity and HRQOL, and potential factors affecting HRQOL in Chinese SLE patients.
Methods
This study recruited 1568 patients and 2610 controls to explore the effects of SLE on HRQOL. The association between disease activity and HRQOL, and the influencing factors of HRQOL were determined in 1568 patients. Then, we prospectively followed 1096 patients to explore the association between reduced disease activity and improved HRQOL, and the influencing factors of improved HRQOL. The Short-Form 36 (SF-36) and SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) were used to evaluate HRQOL and disease activity.
Results
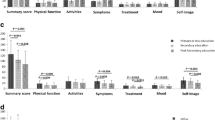
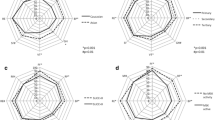
Chinese SLE patients had lower HRQOL than controls in all domains (P < 0.001), especially in role-physical (RP) and role-emotional (RE). Compared with SLE patients from outside China, the HRQOL of Chinese patients appeared to be higher in mental component summary (MCS) but lower in RP and RE. SLEDAI was negatively correlated with HRQOL, which was validated using the results of a follow-up study, where SLEDAI reduction was positively associated with HRQOL improvements (P < 0.05). Furthermore, personality, life nervous and experiences of adverse life events may influence HRQOL and HRQOL improvements.
Conclusion
SLE significantly affected the HRQOL of Chinese patients, especially in RP and RE. Disease activity was negatively correlated with HRQOL. We also found for the first time some factors affecting HRQOL, which can be regarded as the basis for improving the HRQOL of SLE patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon reasonable request.
References
Tektonidou, M. G., Lewandowski, L. B., Hu, J., Dasgupta, A., & Ward, M. M. (2017). Survival in adults and children with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis of studies from 1950 to 2016. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 76(12), 2009–2016.
Thumboo, J., & Strand, V. (2007). Health-related quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: An update. Annals of the Academy of Medicine of Singapore, 36(2), 115–122.
Strand, V., Levy, R. A., Cervera, R., Petri, M. A., Birch, H., Freimuth, W. W., Zhong, Z. J., Clarke, A. E., BLISS-52 and -76 Study Groups. (2014). Improvements in health-related quality of life with belimumab, a B-lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, in patients with autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus from the randomised controlled BLISS trials. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 73(5), 838–844.
Pettersson, S., Boström, C., Eriksson, K., Svenungsson, E., Gunnarsson, I., & Henriksson, E. W. (2015). Lifestyle habits and fatigue among people with systemic lupus erythematosus and matched population controls. Lupus, 24(9), 955–965.
Zheng, Y., Ye, D. Q., Pan, H. F., Li, W. X., Li, L. H., Li, J., Li, X. P., & Xu, J. H. (2009). Influence of social support on health-related quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Rheumatology, 28(3), 265–269.
Liu, N. Y., & Chen, M. Z. (2011). Relationship between psychological health and quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. National Medical Frontiers of China, 6(07), 77–78. (In Chinese).
Mok, C. C., Ho, L. Y., Cheung, M. Y., Yu, K. L., & To, C. H. (2009). Effect of disease activity and damage on quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A 2-year prospective study. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 38(2), 121–127.
Wang, H., Yuan, F. F., Dai, Z. W., Dong, Y. Y., Wang, Z. H., Wang, B., & Ye, D. Q. (2019). Canonical correlation analysis of the quality of life with negative emotion in SLE patients. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 36(06), 802–805. (In Chinese).
Shu, Q., Liu, J., Liu, H. X., & Li, X. F. (2004). Quality of life of 151 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chinese Journal of Rheumatology, 8(07), 420–423. (In Chinese).
Jiang, Y., Wei, W., & Zhao, Y. (2010). Analysis on health-related quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tianjin Journal of Nursing, 18(01), 1–2. (In Chinese).
Li, Y. L., Wang, P., Chen, W. W., & Jiang, C. Y. (2006). Evaluation of life quality of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and study of intervention of traditional Chinese medicine. Journal of Capital University of Medical Science, 27(06), 735–737. (In Chinese).
Yao, L. Y., Xiao, S. Y., Liang, W., Li, J. S., & Yang, T. T. (2005). Study on the mental health status and quality of life in patients with SLE. Journal of Chinese Physician, 7(07), 955–956. (In Chinese).
Chen, H., & Xie, H. F. (2005). Investigation and analysis of quality of life in patients with SLE. Chinese Journal of Dermatology, 38(05), 309–310. (In Chinese).
Men, Q. M. (2005). Health evaluation of the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and nursing strategy. Journal of Nursing Science, 20(09), 24–25. (In Chinese).
Wang, X. S., & Wang, G. (2001). The median test was applied in the skewed distribution data. China Public Health, 17(05), 81–82. (In Chinese).
Onishi, A., Tsuji, H., Takase, Y., Nakakubo, Y., Iwasaki, T., Kozuki, T., Yoshida, T., Shirakashi, M., Onizawa, H., Hiwa, R., Kitagori, K., Akizuki, S., Nakashima, R., Yoshifuji, H., Tanaka, M., & Morinobu, A. (2023). Comparisons of SLE-DAS and SLEDAI-2K and classification of disease activity based on the SLE-DAS with reference to patient-reported outcomes. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kead132
Jolly, M., Annapureddy, N., Arnaud, L., & Devilliers, H. (2019). Changes in quality of life in relation to disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: Post-hoc analysis of the BLISS-52 Trial. Lupus, 28(14), 1628–1639.
Pereira, M. G., Duarte, S., Ferraz, A., Santos, M., & Fontes, L. (2020). Quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: The mediator role of psychological morbidity and disease activity. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 25(10), 1247–1257.
Nantes, S. G., Strand, V., Su, J., & Touma, Z. (2018). Comparison of the sensitivity to change of the 36-item short form health survey and the lupus quality of life measure using various definitions of minimum clinically important differences in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care & Research (Hoboken), 70(1), 125–133.
Chaiamnuay, S., Lomaratana, V., Sumransurp, S., Phukongchai, S., Narongroeknawin, P., & Asavatanabodee, P. (2010). Health-related quality of life and disease severity of SLE patients in Phramongkutklao Hospital. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand, 93(Suppl 6), S125–S130.
Urowitz, M., Gladman, D. D., Ibañez, D., Sanchez-Guerrero, J., Bae, S. C., Gordon, C., Fortin, P. R., Clarke, A., Bernatsky, S., Hanly, J. G., Wallace, D. J., Isenberg, D., Rahman, A., Merrill, J., Ginzler, E., Alarcón, G. S., Fessler, B., Khamashta, M., Steinsson, K.,…, Stoll, T. (2014). Changes in quality of life in the first 5 years of disease in a multicenter cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care & Research (Hoboken), 66(9), 1374–1379.
Ibañez, D., Gladman, D. D., Touma, Z., Nikpour, M., & Urowitz, M. B. (2011). Optimal frequency of visits for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus to measure disease activity over time. Journal of Rheumatology, 38(1), 60–63.
Thumboo, J., Feng, P. H., Boey, M. L., Soh, C. H., Thio, S., & Fong, K. Y. (2000). Validation of the Chinese SF-36 for quality of life assessment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus, 9(9), 708–712.
Koh, E. T., Leong, K. P., Tsou, I. Y., Lim, V. H., Pong, L. Y., Chong, S. Y., Seow, A., Tan Tock Seng Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis (TTSH RA) Study Group. (2006). The reliability, validity and sensitivity to change of the Chinese version of SF-36 in oriental patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford), 45(8), 1023–8.
Zou, Y. F., Xu, J. H., Pan, F. M., Tao, J. H., Xu, S. Q., Xiao, H., Liu, S., Cai, J., Lian, L., Chen, P. L., Wang, D. G., Liu, S. X., Liang, C. M., Ye, Q. L., Tian, G., Wu, M., Gu, Y. Y., Pan, H. F., Su, H., & Ye, D. Q. (2015). Glucocorticoid receptor genetic polymorphisms is associated with improvement of health-related quality of life in Chinese population with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Rheumatology, 34(9), 1537–1544.
Chen, K. F. (2009). Study on TCM constitution factors of health-related quality of life of general population in 9 provinces and cities. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. (In Chinese).
Li, N. X., Liu, C. J., Li, J., & Ren, X. H. (2001). The norms of SF-36 scale scores in urban and rural residents of Sichuan Province. Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences, 32(01), 43–47. (In Chinese).
Wang, H. M., Li, L., & Shen, Y. (2001). The Chinese version of SF-36 scale was used to study the quality of life of urban residents in Hangzhou. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine, 35(06), 69–71. (In Chinese).
Pettersson, S., Lövgren, M., Eriksson, L. E., Moberg, C., Svenungsson, E., Gunnarsson, I., & Welin, H. E. (2012). An exploration of patient-reported symptoms in systemic lupus erythematosus and the relationship to health-related quality of life. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 41(5), 383–390.
Chaigne, B., Finckh, A., Alpizar-Rodriguez, D., Courvoisier, D., Ribi, C., Chizzolini, C., Swiss Clinical Quality Management Program For Rheumatoid Arthritis, Swiss Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Cohort Study Group. (2017). Differential impact of systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis on health-related quality of life. Quality of Life Research, 26(7), 1767–1775.
Takase, Y., Iwasaki, T., Doi, H., Tsuji, H., Hashimoto, M., Ueno, K., Inaba, R., Kozuki, T., Taniguchi, M., Tabuchi, Y., Watanabe, R., Kitagori, K., Akizuki, S., Murakami, K., Nakashima, R., Yoshifuji, H., Itaya, T., Yamamoto, W., Uozumi, R., …, Morinobu, A. (2021). Correlation between irreversible organ damage and the quality of life of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: The Kyoto Lupus Cohort survey. Lupus, 30(10), 1577–1585.
Moon, S. J., Kang, K. Y., Kwok, S. K., Ju, J. H., Hong, Y. S., Park, S. H., Jeon, C. H., Choi, S. T., Song, J. S., & Min, J. K. (2018). Differences in quality of life determinants according to the presence of fibromyalgia in middle-aged female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multicenter, cross-sectional, single-ethnicity cohort. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, 21(6), 1173–1184.
Fortin, P. R., Abrahamowicz, M., Neville, C., du Berger, R., Fraenkel, L., Clarke, A. E., & Danoff, D. (1998). Impact of disease activity and cumulative damage on the health of lupus patients. Lupus, 7(2), 101–107.
Benitha, R., & Tikly, M. (2007). Functional disability and health-related quality of life in South Africans with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Rheumatology, 26(1), 24–29.
Pons-Estel, G. J., Ugarte-Gil, M. F., & Alarcón, G. S. (2017). Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology, 13(8), 799–814.
Bruce, I. N., Gladman, D. D., & Urowitz, M. B. (2000). Factors associated with refractory renal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: The role of patient nonadherence. Arthritis Care & Research, 13(6), 406–408.
Dong, J., Xiao, T., Xu, Q., Liang, F., Gu, S., Wang, F., & Huang, J. H. (2022). Anxious personality traits: Perspectives from basic emotions and neurotransmitters. Brain Sciences, 12(9), 1141.
Cardona, N. D., Southward, M. W., Furbish, K., Comeau, A., & Sauer-Zavala, S. (2021). Nomothetic and idiographic patterns of responses to emotions in borderline personality disorder. Personality Disorders: Theory, Research, and Treatment, 12(4), 354–364.
Knight, E. L., Majd, M., Graham-Engeland, J. E., Smyth, J. M., Sliwinski, M. J., & Engeland, C. G. (2022). Depressive symptoms and other negative psychological states relate to ex vivo inflammatory responses differently for men and women: Cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence. Physiology & Behavior, 244, 113656.
Natalucci, F., Ceccarelli, F., Cipriano, E., Perricone, C., Olivieri, G., Pirone, C., Mettola, G., Truglia, S., Spinelli, F. R., Alessandri, C., & Conti, F. (2021). Joint involvement influences quality of life in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus, 30(3), 478–483.
Silverberg, J. I., Gelfand, J. M., Margolis, D. J., Boguniewicz, M., Fonacier, L., Grayson, M. H., Simpson, E. L., Ong, P. Y., & Chiesa Fuxench, Z. C. (2018). Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: A population-based cross-sectional study. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology, 121(3), 340–347.
Shakeri, H., Arman, F., Hossieni, M., Omrani, H. R., Vahdani, A., & Shakeri, J. (2015). Depression, anxiety and disease-related variables and quality of life among individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus living in Kermanshah Province, Iran. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal, 17(12), e31047.
Bush, R. A., Beaumont, J. L., Liotta, E. M., Maas, M. B., & Naidech, A. M. (2018). Fever burden and health-related quality of life after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurocritical Care, 29(2), 189–194.
Manzano, B. R., da Silva Santos, P. S., Bariquelo, M. H., Merlini, N. R. G., Honório, H. M., & Rubira, C. M. F. (2021). A case-control study of oral diseases and quality of life in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Oral Investigations, 25(4), 2081–2092.
Paralikas, T., Maria, M., Dimitrios, T., Christina, B., Nikolaos, C., Antigoni, F., Georgios, T., & Stiliani, K. (2021). Physical and mental health level of the elderly living in Central Greece. Materia Socio-Medica, 33(1), 16–20.
Hanly, J. G., O’Keeffe, A. G., Su, L., Urowitz, M. B., Romero-Diaz, J., Gordon, C., Bae, S. C., Bernatsky, S., Clarke, A. E., Wallace, D. J., Merrill, J. T., Isenberg, D. A., Rahman, A., Ginzler, E. M., Fortin, P., Gladman, D. D., Sanchez-Guerrero, J., Petri, M., Bruce, I. N., …, Farewell, V. (2016). The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: Results from an international inception cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford), 55(2), 252–262.
Jayawickreme, E., & Infurna, F. J. (2021). Toward a more credible understanding of post-traumatic growth. Journal of Personality, 89(1), 5–8.
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants for their enthusiastic participation in the study. We thank all physicians and nurses in the First and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University and Professor Jian-Hua Xu for her guidance and help.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82373657, 81872683), the Scientific Research Promotion Plan of Anhui Medical University (2022xkjT005), the Key Laboratory of Dermatology, Anhui Medical University, Ministry of Education, China (AYPYS2022-6), and the Peak Discipline Construction Project of Anhui Medical University (2022080009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y-FZ conceived, designed, and supervised the study. Y-HW wrote the manuscript. JC, ML, and Y-FC collected the demographic and clinical data. Y-HW, H-YS, Y-QL, X-YG, and YX conducted data entry and analysis. Y-HW, H-YS, Y-QL, X-YG, YX, Q-QZ, G-HY, W-QH, C-XZ, L-LW, Z-YY, and T-YZ were responsible for the questionnaire survey. All authors contributed to the interpretation of data. FW, JC, ML, and Y-FC revised the manuscript. All authors critically revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YH., Sun, HY., Liu, YQ. et al. Health-related quality of life in Chinese SLE patients: evidence from 1568 SLE patients and 2610 healthy controls. Qual Life Res 33, 207–218 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-023-03516-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-023-03516-9