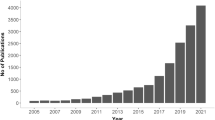
Abstract
Death, injury, conflict, and disorder caused by natural and man-made disasters have resulted in significant challenges to good governance and impeded the goal of achieving the benign development of society. This paper uses a particular method for analyzing the research situation and identifying current trends and focuses. It then proceeds to explore future research needs. The study finds that future researchers will shift their emphasis from the risks caused by natural disasters to those arising from man-made disasters; meanwhile, the study will consider the complex systems of interaction to understand causality. The objectives of management, hence, should change from investigating the impacts of risks to crisis control. Eventually, an evolutionary disaster-based social-risk framework is established, and some suggestions for future research are provided.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadvand, M., Karami, E., Zamani, G.H., Vanclay, F., Ahmadvand, M., Zamani, G.H.: Evaluating the use of social impact assessment in the context of agricultural development projects in Iran. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 29(6), 399–407 (2009)
Austin, W., Park, C., Goble, E.: From interdisciplinary to transdisciplinary research: a case study. Qual. Health Res. 18(4), 557 (2008)
Beck, U.: World Risk Society. Wiley Blackwell, Hoboken (2012)
Becker, H.A.: Social impact assessment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 128(2), 311–321 (2001)
Becker, H.A., Vanclay, F., Becker, H.A., Vanclay, F.: The International Handbook of Social Impact Assessment. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham (2006)
Branch, K.: Guide to Social Assessment. Westview Press, Boulder (1984)
Brown, C., Milke, M., Seville, E.: Disaster waste management: a review article. Waste Manag. (Oxford) 31(6), 1085–1098 (2011)
Burdge, R.J., Vanclay, F., Taylor, C.N.: Social Impact Assessment: An Introduction. Oxford University Press (2000)
Burton, I.: The Environment as Hazard. Guilford Press (1993)
Chen, F.Y., Tong, K., Yang, J.C.: The proposal about constructing the national disaster monitoring, forecast and control system. Acta Astronaut. 28(5), 135–138 (1992)
Clauset, A., Newman, M.E., Moore, C.: Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 70(6–2), 066–111 (2004)
Cutter, S.L.: The vulnerability of science and the science of vulnerability. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 93(1), 1–12 (2003)
Cutter, S.L.: Hazards, Vulnerability and Environmental Justice. Earthscan, London (2006)
Cutter, S.L., Boruff, B.J., Shirley, W.L.: Social vulnerability to environmental hazards. Soc. Sci. Q. 84(2), 242–261 (2003)
Daigle, B., Hall, K., Macdougall, C.: Earthbag housing: structural behaviour and applicability in Sri Lanka. Eng. Sustain. 164(4), 261–273 (2011)
Dibben, C., Chester, D.K.: Human vulnerability in volcanic environments: the case of Furnas, Sao Miguel, Azores. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 92(1–2), 133–150 (1999)
Downs, M., Stoffle, R., Burdge, R.J., Charnley, S., Finsterbusch, K., Freudenburg, B., Fricke, P., Gramling, B., Smith, M., Kragh, B.C.: Principles and guidelines for social impact assessment in the USA: the interorganizational committee on principles and guidelines for social impact assessment. Impact Assess. Project Apprais. 21(3), 231–250 (2003)
Droegemeier, K.K., Smith, J.D., Businger, S., Doswell, C.I., Doyle, J., Duffy, C., Foufoulageorgiou, E., Graziano, T., James, L.D., Krajewski, V.: Hydrological aspects of weather prediction and flood warnings: report of the ninth prospectus development team of the U.S. Weather Research Program. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 2665–2680 (2000)
Garcia, C., Fearnley, C.J.: Evaluating critical links in early warning systems for natural hazards. Environ. Hazards 11(2), 123–137 (2012)
Gilbert, C.: Crisis analysis: between normalization and avoidance. J. Risk Res. 10(7), 925–940 (2007)
Harel, D., Koren, Y.: A fast multi-scale method for drawing large graphs. J. Graph Algorithms Appl. 1984(3), 183–196 (2002)
Hasan, S., Ukkusuri, S.V.: A threshold model of social contagion process for evacuation decision making. Transp. Res. Part B 45(10), 1590–1605 (2011)
Helbing, D.: Globally networked risks and how to respond. Nature 497(7447), 51 (2013)
Hohenemser, C., Kasperson, R.E., K, R.W.: Causal Structure: A Framework for Policy Formulation. Springer, Berlin (1982)
Hunt, J.: Integrated policies for environmental resilience and sustainability. Eng. Sustain. 162(3), 155–167 (2009)
Johansen, W., Aggerholm, H.K., Frandsen, F.: Entering new territory: a study of internal crisis management and crisis communication in organizations. Public Relat. Rev. 38(2), 270–279 (2012)
Jonkman, S.N., Kok, M., Vrijling, J.K.: Flood risk assessment in the Netherlands: a case study for dike ring South Holland. Risk Anal. 28(5), 1357–1374 (2008)
Kang, X., Shaohong, E., Yang, Q., Yang, Z., Zhao, P.: Pre-assessment on the loss and impact caused by large-scale flood disasters. Chin. Sci. Bull. 51(B11), 186–196 (2006)
Kasperson, R.E., Renn, O., Slovic, P., Brown, H.S., Emel, J., Goble, R., Kasperson, J.X., Ratick, S.: The social amplification of risk: a conceptual framework. Risk Anal. 8(2), 177–187 (1988)
Kasperson, R.E., Golding, D., Tuler, S.: Toward a Conceptual Framework for Guiding Future OCS Research. Port Ludlow, Washington (1989)
Kasperson, J.X., Kasperson, R.E., Pidgeon, N., Slovic, P.: The social amplification of risk: Assessing fifteen years of research and theory. Soc. Amplif. Risk 1, 13–46 (2003)
Lazarescu, M.: The Floods on the River Danube in 2006: Social Impact and Remedial Processes. Springer, Dordrecht (2009)
Li, Y., Erickson, T.A.: Application of spatial visualization for probabilistic hurricanes risk assessment to build environment. In: Winter Simulation Conference, pp. 1314–1319 (2008)
Lindell, M.K., Prater, C.S.: Assessing community impacts of natural disasters. Nat. Hazards Rev. 4(4), 176–185 (2003)
Luo, Z.S., Xi, Y.C., Wang, H.C.: Research on comprehensive quantitative risk-assessment of urban nature gas pipeline. In: International Conference on Management Science and Engineering, pp. 2196–2202 (2013)
Mahmoudi, H., Renn, O., Vanclay, F., Hoffmann, V., Karami, E.: A framework for combining social impact assessment and risk assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 43(4), 1–8 (2013)
Mei, G.D., Wu, Z.Z.: Study on social risk evaluation index system for tailings pond dam-break based on the vulnerability theory. Adv. Mater. Res. 594–597, 2301–2308 (2012)
Okrent, D.: Comment on societal risk. Science 208(4442), 372–5 (1980)
Omelicheva, M.Y.: Natural disasters: triggers of political instability? Int. Interact. 37(4), 441–465 (2011)
Panteleev, V.A.: Quantitative Risk Assessment of Aircraft Impact on a High-Rise Building and Collapse. Springer, Dordrecht (2008)
Prior, T., Hagmann, J.: Measuring resilience: methodological and political challenges of a trend security concept. J. Risk Res. 17(3), 281–298 (2014)
Renn, O.: Global Risk Governance: Concept and Practice Using the IRGC Framework. Dordrecht (2008a)
Renn, O.: Risk Governance: Coping with Uncertainty in a Complex World. Earthscan, London (2008b)
Sen, C.K., Gordillo, G.M., Roy, S., Kirsner, R., Lambert, L., Hunt, T.K., Gottrup, F., Gurtner, G.C., Longaker, M.T.: Human skin wounds: a major and snowballing threat to public health and the economy. Wound Repair Regener. 17(6), 763 (2009)
Slovic, P.: Trust, emotion, sex, politics, and science: surveying the risk-assessment battlefield. Risk Anal. 19(4), 689–701 (1999)
Smit, B., Wandel, J.: Adaptation, adaptive capacity and vulnerability. Glob. Environ. Change 16(3), 282–292 (2006)
Smith, W., Davies-Colley, C., Mackay, A., Bankoff, G.: Social impact of the 2004 manawatu floods and the ‘hollowing out’ of rural New Zealand. Disasters 35(3), 540–53 (2011)
Tierney, K.J.: The Social Roots of Risk: Producing Disasters, Promoting Resilience. Stanford University Press (2014)
Turner, B.L.I., Clark, W.C., Kates, R.W., Richards, J.T., Meyer, W.B.: The Earth as Transformed by Human Action: Global and Regional Changes in the Biosphere Over the Past 300 Years. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1993)
Vanclay, F.: International principles for social impact assessment: their evolution. Impact Assess. Project Apprais. 21(1), 5–12 (2003)
Wearne, S.H.: Management of urgent emergency engineering projects. IEEE Eng. Manage. Rev. 33(3), 21–21 (2002)
Webler, T., Lord, F.: Planning for the human dimensions of oil spills and spill response. Environ. Manag. 45(4), 723–738 (2010)
Whlberg, A.E.A.: The theoretical features of some current approaches to risk perception. J. Risk Res. 4(3), 237–250 (2001)
Wijkman, A., Timberlake, L.: Natural disasters. Acts of god or acts of man? Developed Nations, p. 150 (1984)
Xu, J., Wang, Z., Shen, F., Ouyang, C., Tu, Y.: Natural disasters and social conflict: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Disaster Reduct. 17, 38–48 (2016)
Zhang, W., Chen, H., Wang, M.: A forecast model of agricultural and livestock products price. In: Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture, pp. 40–48 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 71771157, 71301109), Soft Science Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2017ZR0154), Funding of Sichuan University (Grant No. skqx201726), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (Grant No. 2017M610609) and the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 16YJC630089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Z., Yao, L. Earthquake triggered networked risk and response: based on relevant literature. Qual Quant 52, 2645–2666 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-018-0681-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-018-0681-1