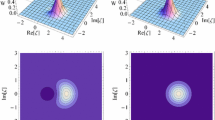
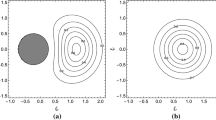
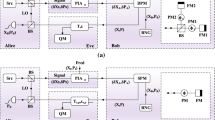
Abstract
In this study, we analyse the efficiency of a protocol with discrete modulation of continuous variable non-Gaussian states, that is, the coherent states having the addition of one photon followed by the subtraction of one photon (PASCS). We calculate lower bounds of the asymptotic key rates against Gaussian collective attacks based on the fact that for sufficiently small modulation variances we remain close to the protocol with Gaussian modulation. We compare the results of a four-state protocol (quadrature phase-shift-keying) using PASCS with the ones using coherent states, and show that under the same environmental conditions, the former always outperforms the latter, allowing to increase the maximum possible distance for secret key generation. Interestingly, we find that for the protocol using discrete-modulated PASCS, the noisier the line, the better will be its performance compared to the protocol using coherent states, showing that continuous variable non-Gaussian states can be considerably more advantageous for performing quantum key distribution in non-ideal situations.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The manuscript has no associated data.
References
Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002)
Silberhorn, Ch., Ralph, T.C., Lütkenhaus, N., Leuchs, G.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography: beating the 3 dB loss limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 167901 (2002)
Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Reverse reconciliation protocols for quantum cryptography with continuous variables. arXiv preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0204127 (2002)
Grosshans, F., et al.: Quantum key distribution using Gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421, 238 (2003)
Christandl, M., Renner, R., Ekert, A.: arXiv:quant-ph/0402131 (2004)
Grosshans, F.: Collective attacks and unconditional security in continuous variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 020504 (2005)
Lodewyck, J., et al.: Quantum key distribution over 25 km with an all-fiber continuous-variable system. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042305 (2007)
Jouguet, P., et al.: Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 7, 378 (2013)
Namiki, R., Hirano, T.: Security of quantum cryptography using balanced homodyne detection. Phys. Rev. A 67, 022308 (2003)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Unconditional security proof of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 180504 (2009)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Erratum: Unconditional security proof of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 259902 (2011)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution protocols with a non-Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 83, 042312 (2011)
Ghorai, S., Grangier, P., Diamanti, E., Leverrier, A.: Asymptotic security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. X 9, 021059 (2019)
Lin, J., Upadhyaya, T., Lütkenhaus, N.: Asymptotic security analysis of discrete-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. X 9, 041064 (2019)
Denys, A., Brown, P., Leverrier, A.: Explicit asymptotic secret key rate of continuous variable quantum key distribution with an arbitrary modulation. Quantum 5, 540 (2021)
Leverrier, A. et al.: Quantum communications with Gaussian and non-Gaussian states of light In: International Conference on Quantum Information, OSA Technical Digest (CD) (Optical Society of America, 2011), paper QMF1. http://www.opticsinfobase.org/abstract.cfm?URI=ICQI-2011-QMF1
Becir, A., Wahiddin, M.R.: Phase coherent states for enhancing the performance of continuous variable quantum key distribution. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 81, 034005 (2012)
Borelli, L.F.M., Aguiar, L.S., Roversi, J.A., Vidiella-Barranco, A.: Quantum key distribution using continuous-variable non-Gaussian states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 893–904 (2016)
Srikara, S., Tapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Continuous variable B92 quantum key distribution protocol using single photon added and subtracted coherent states. Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 371 (2020)
Li, F., Wang, Y., Liao, Q., Guo, Y.: Four-state continuous-variable quantum key distribution with photon subtraction. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 2755 (2018)
Ghalaii, M., Ottaviani, C., Kumar, R., Pirandola, S., Razavi, M.S.: Discrete-modulation continuous-variable quantum key distribution enhanced by quantum scissors. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 38, 506 (2020)
Pariggi, V., Zavatta, A., Kim, M., Bellini, M.: Probing quantum commutation rules by addition and subtraction of single photons to/from a light field. Science 317, 1890 (2007)
Wang, Z., Yuan, H., Fan, H.: Nonclassicality of the photon addition-then-subtraction coherent state and its decoherence in the photon-loss channel. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 28, 1964 (2011)
García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J.: Unconditional optimality of Gaussian attacks against continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190503 (2006)
Navascués, M., Grosshans, F., Acín, A.: Optimality of Gaussian attacks in continuous-variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190502 (2006)
Grosshans, F., et al.: Virtual entanglement and reconciliation protocols for quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Quantum Inf. Comput. 3, 535–552 (2003)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27, 379 (1948)
Zhao, W., et al.: Unidimensional continuous-variable quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Lett. A 384, 126061 (2020)
Wang, X., et al.: Realistic rate-distance limit of continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 27, 13372 (2019)
Zavatta, A., Fiurášek, J., Bellini, M.: A high-fidelity noiseless amplifier for quantum light states. Nat. Photonics 5, 52 (2011)
Blandino, R., Leverrier, A., Barbieri, M., Etesse, J., Grangier, P., Tualle-Brouri, R.: Improving the maximum transmission distance of continuous-variable quantum key distribution using a noiseless amplifier. Phys. Rev. A 86, 012327 (2012)
Walk, N., Ralph, T.C., Symul, T., Lam, P.K.: Security of continuous-variable quantum cryptography with Gaussian postselection. Phys. Rev. A 87, 020303(R) (2013)
Fiurasek, J., Cerf, N.J.: Gaussian postselection and virtual noiseless amplification in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 060302(R) (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, (CNPq) Brazil, via the Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia - Informação quântica (INCT-IQ), grant N\({^{\underline{o}}}\) 465469/2014-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aguiar, L.S., Borelli, L.F.M., Roversi, J.A. et al. Performance analysis of continuous-variable quantum key distribution using non-Gaussian states. Quantum Inf Process 21, 304 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03645-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03645-z