Abstract
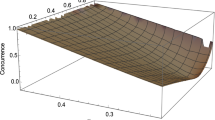
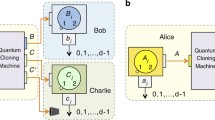
Coherence, being at the heart of interference phenomena, is found to be an useful resource in quantum information theory. Here we want to understand quantum coherence under the combination of two fundamentally dual processes, viz., cloning and deleting. We found the role of quantum cloning and deletion machines with the consumption and generation of quantum coherence. We establish cloning as a cohering process and deletion as a decohering process. Fidelity of the process will be shown to have connection with coherence generation and consumption of the processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802–803 (1982)
Buzek, V., Hillery, M.: Quantum copying: beyond the no-cloning theorem. Phys. Rev. A 54, 1844–1852 (1996)
Bruss, D., DiVincenzo, D.P., Ekert, A., Fuchs, C.A., Macchiavello, C., Smolin, J.A.: Optimal universal and state-dependent quantum cloning. Phys. Rev. A 57, 2368–2378 (1998)
Bruss, D., Cinchetti, M., D’Ariano, G.M., Macchiavello, C.: Phase-covariant quantum cloning. Phys. Rev. A 62, 012302 (2000)
Pati, A.K., Braunstein, S.L.: Impossibility of deleting an unknown quantum state. Nature 404, 164–165 (2000)
Pati, A.K.: Quantum superposition of multiple clones and the novel cloning machine. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 2849–2852 (1999)
Baumgratz, T., Cramer, M., Plenio, M.B.: Quantifying coherence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 140401 (2014)
Lloyd, S.: Quantum coherence in biological systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 302, 012037 (2011)
Li, C.-M., Lambert, N., Chen, Y.-N., Chen, G.-Y., Nori, F.: Witnessing quantum coherence: from solid-state to biological systems. Sci. Rep. 2, 885 (2012)
Huelga, S.F., Plenio, M.B.: Vibrations, quanta and biology. Contemp. Phys. 54, 181–207 (2013)
Skrzypczyk, P., Short, A.J., Popescu, S.: Work extraction and thermodynamics for individual quantum systems. Nat. Commun. 5, 4185 (2014)
Åberg, J.: Catalytic coherence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 150402 (2014)
Lostaglio, M., Jennings, D., Rudolph, T.: Description of quantum coherence in thermodynamic processes requires constraints beyond free energy. Nat. Commun. 6, 6383 (2015)
Lostaglio, M., Korzekwa, K., Jennings, D., Rudolph, T.: Quantum coherence, time-translation symmetry, and thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. X 5, 021001 (2015)
Korzekwa, K., Lostaglio, M., Oppenheim, J., Jennings, D.: The extraction of work from quantum coherence. New J. Phys. 18, 023045 (2016)
Girolami, D.: Observable measure of quantum coherence in finite dimensional systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 170401 (2014)
Gisin, N., Massar, S.: Optimal quantum cloning machine. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 2153–2156 (1997)
Bruss, D., Ekert, A., Macchiavello, C.: Optimal universal quantum cloning and state estimation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2598–2601 (1998)
Bae, J., Acin, A.: Asymptotic quantum cloning is state estimation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 030402 (2006)
Berta, M., Christandl, M., Colbeck, R., Renes, J.M., Renner, R.: The uncertainty principle in the presence of quantum memory. Nat. Phys. 6, 659–662 (2010)
Tomamichel, M., Renner, R.: Uncertainty relation for smooth entropies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 110506 (2011)
Tomamichel, M., Lim, C.C.W., Gisin, N., Renner, R.: Tight finite-key analysis for quantum cryptography. Nat. Commun. 3, 634 (2012)
Sazim, S., Chakrabarty, I., Datta, A., Pati, A.K.: Complementarity of quantum correlations in cloning and deleting of quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 91, 062311 (2015)
Shao, L.-H., Xi, Z., Fan, H., Li, Y.: Fidelity and trace-norm distances for quantifying coherence. Phys. Rev. A 91, 042120 (2015)
Rana, S., Parashar, P., Lewenstein, M.: Trace-distance measure of coherence. Phys. Rev. A 93, 012110 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The author S. Karmakar acknowledges the financial support from UGC, India. The author A.Sen acknowledges NBHM, DAE, India, and the author D. Sarkar acknowledges SERB, DST, India, and DSA-SAP for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix A: Explicit expressions
Appendix A: Explicit expressions
Explicit expression of the coefficients of the cloned state \(\rho _{ab}^{\mathrm{clone}}\) given in Eq. (8):
where \(|u_1\rangle =\alpha \hat{a}|A\rangle +\beta \tilde{c}|\tilde{C}\rangle \), \(|u_2\rangle =\alpha c|C\rangle +\beta \tilde{\hat{a}}|\tilde{A}\rangle \), \(|v_1\rangle =\alpha b_1|B_1\rangle +\beta \tilde{b_2}|\tilde{B_2}\rangle \), \(|v_2\rangle =\alpha b_2|B_2\rangle +\beta \tilde{b_1}|\tilde{B_1}\rangle \)
Explicit expression of the coefficients of the state \(\rho _{ab}^{c\rightarrow d}\) given in Eq. (14):
Explicit expression of the coefficients of the state \(\rho _{aa'}^{d\rightarrow c}\) given in Eq. (23):
Explicit expression of the coefficients of the state \(\rho _{bb'}^{d\rightarrow c}\) given in Eq. (23) are same as \(m_i\)’s, just replacing \(\alpha ^2\) by \(1-\alpha ^2\beta ^2\) and \(\beta ^2\) by \(\alpha ^2\beta ^2\) in Eq. (A3).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karmakar, S., Sen, A. & Sarkar, D. Performance of quantum cloning and deleting machines over coherence. Quantum Inf Process 16, 251 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1691-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1691-y