Abstract
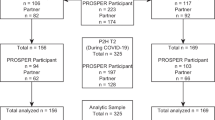
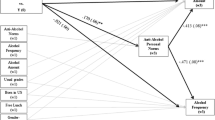
African American couples (N = 139; 67.7 % married; with children between the ages of 9 and 14) were randomly assigned to (a) a culturally sensitive, couple- and parenting-focused program designed to prevent stress-spillover (n = 70) or (b) an information-only control condition in which couples received self-help materials (n = 69). Eight months after baseline, youth whose parents participated in the program, compared with control youth, reported increased parental monitoring, positive racial socialization, and positive self-concept, as well as decreased conduct problems and self-reported substance use. Changes in youth-reported parenting behavior partially mediated the effect of the intervention on conduct problems and fully mediated its impact on positive self-concept, but did not mediate effects on lifetime substance use initiation. Results suggest the potential for a culturally sensitive family-based intervention targeting adults’ couple and parenting processes to enhance multiple parenting behaviors as well as decrease youths’ substance use onset and vulnerability.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton, A. W., Beach, S. R., Kogan, S. M., Stanley, S. M., Fincham, F. D., Hurt, T. R., & Brody, G. H. (2015). Prevention effects on trajectories of African American adolescents’ exposure to interparental conflict and depressive symptoms. Journal of Family Psychology, 29, 171. doi:10.1037/fam0000073.
Beach, S. R., Barton, A. W., Lei, M. K., Brody, G. H., Kogan, S. M., Hurt, T. R., … & Stanley, S. M. (2014). The effect of communication change on long‐term reductions in child exposure to conflict: Impact of the promoting strong African American families (ProSAAF) program. Family Process, 53, 580-595. doi: 10.1111/famp.12085
Bean, R. A., Barber, B. K., & Crane, D. R. (2006). Parental support, behavioral control, and psychological control among African American youth: The relationships to academic grades, delinquency, and depression. Journal of Family Issues, 27, 1335–1355. doi:10.1177/0192513X06289649.
Brody, G. H., Murry, V. M., Gerrard, M., Gibbons, F. X., Molgaard, V., McNair, L., . . . Neubaum-Carlan, E. (2004). The Strong African American Families program: Translating research into prevention programming. Child Development, 75, 900-917. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8634.2004.00713.x
Brody, G. H., Murry, V. M., Kogan, S. M., Gerrard, M., Gibbons, F. X., Molgaard, V., . . . Wills, T. A. (2006). The Strong African American Families program: A cluster-randomized prevention trial of long-term effects and a mediational model. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74, 356-366. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.74.2.356
Brody, G. H., Chen, Y.-F., Kogan, S. M., Murry, V. M., & Brown, A. C. (2010). Long-term effects of the strong African American families program on youths’ alcohol use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 78, 281–285. doi:10.1037/a0018552.
Brody, G. H., Chen, Y., Kogan, S. M., Yu, T., Molgaard, V. K., DiClemente, R. J., & Wingood, G. M. (2012). Family-centered program deters substance use, conduct problems, and depressive symptoms in Black adolescents. Pediatrics, 129, 108–115. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0623.
CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] (2008). Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
Child Trends (2014). Family structure: Indicators on children and youth. Child trends. Retrieved from http://www.childtrends.org/?indicators=family-structure
Coard, S. I., Wallace, S. A., Stevenson, H. C., Jr., & Brotman, L. M. (2004). Towards culturally relevant preventive interventions: The consideration of racial socialization in parent training with African American families. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 13, 277–293. doi:10.1023/b:jcfs.0000022035.07171.f8.
Cummings, E. M., Goeke-Morey, M. C., & Graham, M. A. (2002). Interparental relations as a dimension of parenting. In M. M. Bristol-Power, J. G. Borkowski, & S. L. Landesman (Eds.), Parenting and the child’s world: Influences on academic, intellectual and socio-emotional development (pp. 251–264). Mahwah: Erlbaum. doi:10.4324/9781410603616.
DeGarmo, D. S., Patterson, G. R., & Forgatch, M. S. (2004). How do outcomes in a specified parent training intervention maintain or wane over time? Prevention Science, 5, 73–89. doi:10.1023/b:prev.0000023078.30191.e0.
Dever, B. V., Schulenberg, J. E., Dworkin, J. B., O’Malley, P. M., Kloska, D. D., & Bachman, J. G. (2012). Predicting risk-taking with and without substance use: The effects of parental monitoring, school bonding, and sports participation. Prevention Science, 13, 605–615. doi:10.1007/s11121-012-0288-z.
Elliott, D. S., & Ageton, S. S. (1980). Reconciling race and class differences in self-reported and official estimates of delinquency. American Sociological Review, 45, 95–110. doi:10.2307/2095245.
Epstein, K., Kline Pruett, M., Cowan, P., Cowan, C., Pradhan, L., … & Pruett, K. (2015). More than one way to get there: Pathways of change in coparenting conflict after a preventive intervention. Family Process, 54, 610–618. doi: 10.1111/famp.12138
Gibbons, F. X., Gerrard, M., Cleveland, M. J., Wills, T. A., & Brody, G. H. (2004). Perceived discrimination and substance use in African American parents and their children: A panel study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 86, 517–529. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.86.4.517.
Gonzalez, M., Jones, D., & Parent, J. (2014). Coparenting experiences in African American families: An examination of single mothers and their nonmarital coparents. Family Process, 53, 33–54. doi:10.1111/famp.12063.
Hughes, D., Rodriguez, J., Smith, E. P., Johnson, D. J., Stevenson, H. C., & Spicer, P. (2006). Parents’ ethnic-racial socialization practices: A review of research and directions for future study. Developmental Psychology, 42, 747–770. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.42.5.747.
Hurt, T. R., Beach, S. R. H., Stokes, L. A., Bush, P. L., Sheats, K. J., & Robinson, S. G. (2012). Engaging Black men in empirically based marriage enrichment programs: Lessons from two focus groups on the ProSAAM project. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology, 18, 312–315. doi:10.1037/a0028697.
Knox, V., Cowan, P. A., Pape Cowan, C., & Bildner, E. (2011). Policies that strengthen fatherhood and family relationships: What do we know and what do we need to know? Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 635, 216–239. doi:10.1177/0002716210394769.
Lerner, R., Lerner, J., & Benson, J. B. (2011). Positive youth development (Vol. 41). Waltham: Academic Press.
Lesane-Brown, C. L., Brown, T. N., Caldwell, C. H., & Sellers, R. M. (2005). The comprehensive race socialization inventory. Journal of Black Studies, 36, 163–190. doi:10.1177/0021934704273457.
Lippold, M. A., Greenberg, M. T., Graham, J. W., & Feinberg, M. E. (2014). Unpacking the effect of parental monitoring on early adolescent problem behavior mediation by parental knowledge and moderation by parent-youth warmth. Journal of Family Issues, 35, 1800–1823. doi:10.1177/0192513x13484120.
MacPhee, D., Lunkenheimer, E., & Riggs, N. R. (2015). Resilience as regulation of developmental and family processes. Family Relations, 64, 153–175. doi:10.1111/fare.12100.
Mandara, J. (2006). The impact of family functioning on African American males’ academic achievement: A review and clarification of the empirical literature. Teachers College Record, 108, 206–223. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9620.2006.00648.x.
Markman, H. J., Stanley, S. M., Blumberg, S. L., Jenkins, N. H., & Whiteley, C. (2004). 12 hours to a great marriage: A step-by-step guide for making love last. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
McHale, J. P., Salman-Engin, S., & Coovert, M. D. (2015). Improvements in unmarried African American parents’ rapport, communication, and problem-solving following a prenatal coparenting intervention. Family Process, 54, 619–629. doi:10.1111/famp.12147.
Murry, V. M., Berkel, C., Brody, G. H., Gibbons, M., & Gibbons, F. X. (2007). The strong African American families program: Longitudinal pathways to sexual risk reduction. Journal of Adolescent Health, 41, 333–342. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.04.003.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2010). Mplus version 6: Base program and combination add-on. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Neblett, E. W., Jr., White, R. W., Ford, K. R., Philip, C. L., Nguyen, H. X., & Sellers, R. M. (2008). Patterns of racial socialization and psychological adjustment: Can parental communications about race reduce the impact of racial discrimination? Journal of Research on Adolescence, 18, 477–515. doi:10.1111/j.1532-7795.2008.00568.x.
Neblett, E. W., Jr., Terzian, M., & Harriott, V. (2010). From racial discrimination to substance use: The buffering effects of racial socialization. Child Development Perspectives, 4, 131–137. doi:10.1111/j.1750-8606.2010.00131.x.
Neff, L. A., & Karney, B. R. (2009). Stress and reactivity to daily relationship experiences: How stress hinders adaptive processes in marriage. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 97, 435–450. doi:10.1037/a0015663.
Nelson, J. A., O’Brien, M., Blankson, A. N., Calkins, S. D., & Keane, S. P. (2009). Family stress and parental responses to children’s negative emotions: Tests of the spillover, crossover, and compensatory hypotheses. Journal of Family Psychology, 23, 671–679. doi:10.1037/a0015977.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40, 879–891. doi:10.3758/brm.40.3.879.
Proctor, B. D., & Dalaker, J. (2003). Poverty in the United States: 2002. Washington: US Census Bureau.
Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement, 1, 385–401. doi:10.1177/014662167700100306.
Sellers, R. M., Rowley, S. A., Chavous, T. M., Shelton, J. N., & Smith, M. A. (1997). Multidimensional inventory of black identity: A preliminary investigation of reliability and constuct validity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73, 805. doi:10.1037//0022-3514.73.4.805.
Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. Sociological Methodology, 13, 290–312. doi:10.2307/270723.
Swendsen, J., Burstein, M., Case, B., Conway, K. P., Dierker, L., He, J., & Merikangas, K. R. (2012). Use and abuse of alcohol and illicit drugs in US adolescents: Results of the National Comorbidity Survey—Adolescent Supplement. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69, 390–398. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1503.
Windle, M., & Windle, R. C. (2012). Early onset problem behaviors and alcohol, tobacco, and other substance use disorders in young adulthood. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 121, 152–158. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.08.024.
Zapolski, T. C., Pedersen, S. L., McCarthy, D. M., & Smith, G. T. (2014). Less drinking, yet more problems: Understanding African American drinking and related problems. Psychological Bulletin, 140, 188. doi:10.1037/a0032113.
Acknowledgments
This article was supported in part by grant R01 HD069439 awarded to Steven R. H. Beach and grant P30 DA027827 awarded to Gene H. Brody. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This article was supported in part by grant R01 HD069439 awarded to Steven R. H. Beach and grant P30 DA027827 awarded to Gene H. Brody.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beach, S.R.H., Barton, A.W., Lei, M.K. et al. Decreasing Substance use Risk among African American Youth: Parent-based Mechanisms of Change. Prev Sci 17, 572–583 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0651-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0651-6