Abstract
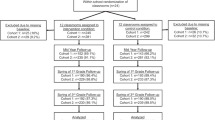
This paper reports a randomized controlled trial of the effects of behavioral parenting skills training, social skills training, and supplemental reading instruction on the social behavior of early elementary school children (K through 3). We selected children based on teacher-rated aggressive behavior or reading-skill deficits, delivered the intervention over a 2-year period, and obtained follow-up data for two additional years. The intervention affected only two of eight measures of child functioning—parent daily reports of antisocial behavior and parent ratings of coercive behavior. There was evidence that parents of boys in the intervention condition displayed significantly greater declines in their rated use of coercive discipline than did parents of boys in the control condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL/4–18, YSR, and TRF profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Adams, G. L., & Engelmann, S. E. (1996). Research on direct instruction: 25 Years beyond DISTAR. Seattle, WA: Educational Achievement Systems.
Adams, M. J. (1990). Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about print. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
August, D., & Hakuta, K. (1997). Improving schooling for language-minority children: A research agenda. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Bachman, J. G., Green, S., & Wirtanen, I. D. (1991). Dropping out—problem or symptom? Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Institute of Social Research.
Barrera, M., Jr., Biglan, A., Taylor, T. K., Gunn, B. K., Smolkowski, K., Black, C. et al. (2002). Early elementary school intervention to reduce conduct problems: A randomized trial with Hispanic and non-Hispanic children. Prevention Science, 3(2), 83–94.
Beauchaine, T. P., Webster-Stratton, C., & Reid, M. J. (in press). Mediators, moderators, and predictors of one-year outcomes among children treated for early-onset conduct problems: A latent growth curve analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology.
Biglan, A., Brennan, P. A., Foster, S. L., Holder, H. D., Miller, T. L., Cunningham, P. B. et al. (2004). Helping adolescents at risk: Prevention of multiple problem behaviors. New York: Guilford.
Camp, B. W., van Doorninck, W. J., Zimet, S. G., & Dahlem, N. W. (1977). Verbal abilities in young aggressive boys. Journal of Educational Psychology, 69(2), 129–135.
Capaldi, D. M., & Patterson, G. R. (1989). Psychometric properties of fourteen latent constructs from the Oregon youth study. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Chamberlain, P., & Reid, J. B. (1987). Parent observation and report of child symptoms. Behavioral Assessment, 9(1), 97–109.
Chamberlain, P. (Submitted). Standardization of a parent report measure.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (1999a). Initial impact of the Fast Track prevention trial for conduct problems: I. The high-risk sample. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67(5), 631–647.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (1999b). Initial impact of the Fast Track prevention trial for conduct problems: II. Classroom effects. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67(5), 648–57.
Cornwall, A., & Bawden, H. N. (1992). Reading disabilities and aggression: A critical review. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 25(5), 281–288.
Feshbach, S., & Price, J. (1984). Cognitive competencies and aggressive behavior: A developmental study. Aggressive Behavior, 10(3), 185–200.
Francis, D. J., Shaywitz, S. E., Stuebing, K. K., Shaywitz, B. A., & Fletcher, J. M. (1996). Developmental lag versus deficit models of reading disability: A longitudinal, individual growth curves analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88(1), 3–17.
Gersten, R., & Baker, S. (2000). What we know about effective instructional practices for English-language learners. Exceptional Children, 66(4), 454–470.
Gunn, B. K., Biglan, A., Smolkowski, K., & Ary, D. V. (2000). The efficacy of supplemental instruction in decoding skills for Hispanic and non-Hispanic students in early elementary school. Journal of Special Education, 34(2), 90–103.
Gunn, B. K., Smolkowski, K., Biglan, A., & Black, C. (2002). Supplemental instruction in decoding skills for Hispanic and non-Hispanic students in early elementary school: A follow-up. Journal of Special Education, 36(2), 69–79.
Gunn, B. K., Smolkowski, K., Biglan, A., Black, C., & Blair, J. (in press). Fostering the development of reading skill through supplemental instruction: Results for Hispanic and non-Hispanic students Journal of Special Education.
Hernandez, L. P., & Lucero, E. (1996). DAYS: La familia community drug and alcohol prevention program: Family-centered model for working with inner-city Hispanic families. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 16(3), 255-272.
Hops, H., & Walker, H. M. (1988). CLASS. Contingencies for Learning Academic and Social Skills: A classroom behavior management program for children with acting-out behaviors. Delray Beach, FL: Educational Achievement Systems.
Hops, H., Walker, H. M., & Greenwood, C. R. (1987). CLASS (Contingencies for Learning Academic and Social Skills). Delray Beach, FL: Educational Achievement Systems.
Juel, C. (1988). Learning to read and write: A longitudinal study of 54 children from first through fourth grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 80(4), 437–447.
Kazdin, A. E. (1995). Conduct disorders in childhood and adolescence, 2nd edn., Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Kazdin, A. E., & Crowley, M. J. (1997). Moderators of treatment outcome in cognitively based treatment of antisocial children. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 21(2), 185–207.
Kellam, S. G., Ling, X., Merisca, R., Brown, C. H., & Ialongo, N. (1998a). The effect of the level of aggression in the first grade classroom on the course and malleability of aggressive behavior into middle school. Development and Psychology, 10, 165–85.
Kellam, S. G., Mayer, L. S., Rebok, G. W., & Hawkins, W. E. (1998b). Effects of improving achievement on aggressive behavior and of improving aggressive behavior on achievement through two preventive interventions: An investigation of causal paths. In B.P. Dohrenwend (Ed.), Adversity, stress, & psychopathology (pp. 486–505). New York: Oxford University Press.
Kellam, S. G., Rebok, G. W., Mayer, L. S., Ialongo, N., & Kalodner, C. R. (1994). Depressive symptoms over first grade and their response to a developmental epidemiologically based preventive trial aimed at improving achievement. Development and Psychopathology, 6(3), 463–481.
Kumpfer, K. L., Alvarado, R., Smith, P., & Bellamy, N. (2002). Cultural sensitivity and adaptation in family-based prevention interventions. Prevention Science, 3(3), 241–246.
Littell, R. C., Milliken, G. A., Stroup, W. W., & Wolfinger, R. D. (1996). SAS system for mixed models. Cary, NC: SAS Institute, Inc.
Lowenstein, L. F. (1997). Who is the bully? Home and School, 11, 3–4.
Maccoby, E. E., & Jacklin, C. N. (1974). The psychology of sex differences. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Murray, D. (1998). Design and analysis of group-randomized trials. New York: Oxford University Press.
Muthén, B. O., & Curran, P. J. (1997). General longitudinal modeling of individual differences in experimental designs: A latent variable framework for analysis and power estimation. Psychological Methods, 2(4), 371–402.
National Reading Panel (2000). Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction. On line at http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/nrp/smallbook.htm.
Nich, C., & Carroll, K. M. (1997). Now you see it, now you don’t: A comparison of traditional versus random-effects regression models in the analysis of longitudinal follow-up data from a clinical trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65(2), 252–261.
Pantin, H., Coatsworth, J. D., Feaster, D. J., Newman, F. L., Briones, E., Prado, G., et al. (2003). Familias Unidas: The efficacy of an intervention to promote parental investment in Hispanic immigrant families. Prevention Science, 4(3), 189–201.
Reid, J. B., Eddy, J. M., Fetrow, R. A., & Stoolmiller, M. (1999). Description and immediate impacts of a preventive intervention for conduct problems. American Journal of Community Psychology, 27(4), 483–517.
Reid, J. B., Patterson, G. R., & Snyder, J.(Eds.). (2002). Antisocial behavior in children and adolescents: A developmental analysis and model for intervention. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Reid, M. J., Webster-Stratton, C., & Baydar, N. (2004). Halting the development of conduct problems in Head Start children: The effects of parent training. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33(2), 279–291.
Reid, M. J., Webster-Stratton, C., & Beauchaine, T. P. (2001). Parent training in head start: A comparison of program response among African American, Asian American, Caucasian, and Hispanic mothers. Prevention Science, 2(4), 209-227.
SAS Institute. (2002). SAS/STAT 9 User’s Guide, Volumes 1, 2, & 3. Cary, NC: Author. Retrieved May 15, 2003, from SAS Online Doc 9 website: http://v9doc.sas.com/sasdoc/.
Slavin, R. E., Karweit, N. L., & Wasik, B. A. (1994). Preventing early school failure: Research, policy, and practice. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Slavin, R. E., Madden, N. A., Dolan, L. J., Wasik, B. A., Ross, S., Smith, L. et al. (1996). Success for All: A summary of research. Journal of Education for Students Placed at Risk, 1(1), 41-76.
Szapocznik, J., Santisteban, D., Rio, A., Perez-Vidal, A., Santisteban, D., & Kurtines, W. M. (1989). Family effectiveness training: An intervention to prevent drug abuse and problem behaviors in Hispanic adolescents. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 11(1), 4–27.
Taylor, T. K., Eddy, J. M., & Biglan, A. (1999). Interpersonal skills training to reduce aggression and delinquent behavior: Limited evidence and the need for an evidence-based system of care. Journal of Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 2, 169–182.
Taylor, T. K., Schmidt, F., Pepler, D., & Hodgins, C. (1998). A comparison of eclectic treatment with Webster-Stratton’s parents and children series in a children’s mental health center: A randomized controlled trial. Behavior Therapy, 29(2), 221–40.
Thomas, W. P., & Collier, V. P. (1997). Two languages are better than one. Educational Leadership, 55(4), 23–26.
Torgesen, J. K., Wagner, R. K., Rashotte, C. A., Rose, E., Lindamood, P., Conway, T., et al. (1999). Preventing reading failure in young children with phonological processing disabilities: Group and individual responses to instruction. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(4), 579–593.
Walker, H. M. (1995). The acting-out child: Coping with classroom disruption. Longmont, CO: Sopris West.
Walker, H. M., & Hops, H. (1979). The CLASS Program for acting out children: R & D procedures, program outcomes and implementation issues. School Psychology Review, 8, 370-381.
Walker, H., & McConnell, S. (1988). The Walker-McConnell scale of social competence and school adjustment. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed, Inc.
Walker, H., & McConnell, S. (1993). Technical Manual for the Walker-McConnell scale of social competence and school adjustment. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Walker, H. M., Severson, H. H., Nicholson, F., & Kehle, T. (1994). Replication of the Systematic Screening of Behavior Disorders (SSBD) procedure for the identification of at-risk children. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 2(2), 66–77.
Walker, H. M., Severson, H. H., Todis, B. J., Block-Pedego, A. E., Williams, G. J., Haring, N. G., et al. (1990). Systematic screening for behavior disorders (SSBD): Further validation, replication, and normative data. RASE, 11(2), 32–46.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1984). Randomized trial of two parent-training programs for families with conduct-disordered children. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology, 52(4), 666–678.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1992a). The parents and children videotape series: Programs 1–10. Seattle, WA: Seth Enterprises.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1992b). The incredible years. A trouble-shooting guide for parents of children aged 3–8. Toronto: Umbrella Press.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1992c). The teachers and children’s videotape series: Dina dinosaur’s social skills and problem-solving curriculum. Seattle: Seth Enterprises.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1998). Parent training with low-income families: Promoting parental engagement through a collaborative approach. Handbook of child abuse research & treatment (pp. 183–210). New York: Plenum.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Hammond, M. (1997). Treating children with early-onset conduct problems: A comparison of child and parent training interventions. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology, 65(1), 93–109.
Webster-Stratton, C., Kolpacoff, M., & Hollinsworth, T. (1988). Self-administered videotape therapy for families with conduct-problem children: Comparison with two cost-effective treatments and a control group. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56(4), 558–566.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Reid, M. J. (2003). Treating conduct problems and strengthening social and emotional competence in young children: The Dina Dinosaur treatment program. Journal of Emotional & Behavioral Disorders, 11(3), 130–143.
Webster-Stratton, C., Reid, M. J., & Hammond, M. (2001). Preventing conduct problems, promoting social competence: A parent and teacher training partnership in head start. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 30(3), 283–302.
Webster-Stratton, C., Reid, M. J., & Hammond, M. (2004). Treating children with early-onset conduct problems: Intervention outcomes for parent, child, and teacher training. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 33(1), 105–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smolkowski, K., Biglan, A., Barrera, M. et al. Schools and Homes in Partnership (SHIP): Long-Term Effects of a Preventive Intervention Focused on Social Behavior and Reading Skill in Early Elementary School. Prev Sci 6, 113–125 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-005-3410-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-005-3410-7