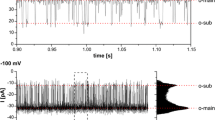
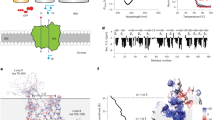
Abstract
The plastid potassium cation efflux antiporters (KEAs) are important for chloroplast function, development, and photosynthesis. To understand their regulation at the protein level is therefore of fundamental importance. Prior studies have focused on the regulatory K+ transport and NAD-binding (KTN) domain in the C-terminus of the thylakoid carrier KEA3 but the localization of this domain remains unclear. While all three plastid KEA members are highly conserved in their transmembrane region and the C-terminal KTN domain, only the inner envelope KEA family members KEA1 and KEA2 carry a long soluble N-terminus. Interestingly, this region is acetylated at lysine 168 by the stromal acetyltransferase enzyme NSI. If an odd number of transmembrane domains existed for inner envelope KEAs, as it was suggested for all three plastid KEA carriers, regulatory domains and consequently protein regulation would occur on opposing sides of the inner envelope. In this study we therefore set out to investigate the topology of inner envelope KEA proteins. Using a newly designed antibody specific to the envelope KEA1 N-terminus and transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing a C-terminal KEA1–YFP fusion protein, we show that both, the N-terminal and C-terminal, regulatory domains of KEA1 reside in the chloroplast stroma and not in the intermembrane space. Considering the high homology between KEA1 and KEA2, we therefore reason that envelope KEAs must consist of an even number of transmembrane domains.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves-Carvalho S, Aubert G, Carrère S, Cruaud C, Brochot A-L, Jacquin F, Klein A, Martin C, Boucherot K, Kreplak J, da Silva C, Moreau S, Gamas P, Wincker P, Gouzy J, Burstin J (2015) Full-length de novo assembly of RNA-seq data in pea (Pisum sativum L.) provides a gene expression atlas and gives insights into root nodulation in this species. Plant J 84:1–19
Aranda-Sicilia MN, Cagnac O, Chanroj S, Sze H, Rodríguez-Rosales MP, Venema K (2012) Arabidopsis KEA2, a homolog of bacterial KefC, encodes a K+/H+ antiporter with a chloroplast transit peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:2362–2371
Aranda-Sicilia MN, Aboukila A, Armbruster U, Cagnac O, Schumann T, Kunz HH, Jahns P, Rodriguez-Rosales MP, Sze H, Venema K (2016) Envelope K+/H+ antiporters AtKEA1 and AtKEA2 function in plastid development. Plant Physiol 172:441–449
Armbruster U, Carrillo LR, Venema K, Pavlovic L, Schmidtmann E, Kornfeld A, Jahns P, Berry JA, Kramer DM, Jonikas MC (2014) Ion antiport accelerates photosynthetic acclimation in fluctuating light environments. Nat Commun 5:5439
Armbruster U, Leonelli L, Correa Galvis V, Strand D, Quinn EH, Jonikas MC, Niyogi KK (2016) Regulation and levels of the thylakoid K+/H+ antiporter KEA3 shape the dynamic response of photosynthesis in fluctuating light. Plant Cell Physiol 57:1557–1567
Armbruster U, Correa Galvis V, Kunz H-H, Strand DD (2017) The regulation of the chloroplast proton motive force plays a key role for photosynthesis in fluctuating light. Curr Opin Plant Biol 37:56–62
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24:1–15
Bölter B, Soll J (2001) Ion channels in the outer membranes of chloroplasts and mitochondria: open doors or regulated gates? EMBO J 20:935–940
Buehl CJ, Deng X, Liu M, McAndrew MJ, Hovde S, Xu X, Kuo M-H (2014) Resolving acetylated and phosphorylated proteins by neutral urea Triton-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: nUT-PAGE. Biotechniques 57:72–80
Caliebe A, Grimm R, Kaiser G, Lubeck J, Soll J, Heins L (1997) The chloroplastic protein import machinery contains a Rieske-type iron-sulfur cluster and a mononuclear iron-binding protein. EMBO J 16:7342–7350
Chanroj S, Wang G, Venema K, Zhang MW, Delwiche CF, Sze H (2012) Conserved and diversified gene families of monovalent cation/H+ antiporters from algae to flowering plants. Front Plant Sci 3:25
Chou ML, Fitzpatrick LM, Tu SL, Budziszewski G, Potter-Lewis S, Akita M, Levin JZ, Keegstra K, Li HM (2003) Tic40, a membrane-anchored co-chaperone homolog in the chloroplast protein translocon. EMBO J 22:2970–2980
Fischer K (2011) The import and export business in plastids: transport processes across the inner envelope membrane. Plant Physiol 155:1511–1519
Froehlich J (2011) Studying arabidopsis envelope protein localization and topology using thermolysin and trypsin proteases. In: Jarvis RP (ed) Chloroplast research in arabidopsis: methods and protocols, vol I. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 351–367
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud Se, Wilki MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM (ed) The proteomics protocols handbook. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 571–607
Gutierrez-Carbonell E, Takahashi D, Lattanzio G, Rodriguez-Celma J, Kehr J, Soll J, Philippar K, Uemura M, Abadia J, Lopez-Millan AF (2014) The distinct functional roles of the inner and outer chloroplast envelope of pea (Pisum sativum) as revealed by proteomic approaches. J Proteome Res 13:2941–2953
Höhner R, Aboukila A, Kunz HH, Venema K (2016) Proton gradients and proton-dependent transport processes in the chloroplast. Front Plant Sci 7:218
Höhner R, Galvis VC, Strand DD, Völkner C, Krämer M, Messer M, Dinc F, Sjuts I, Bölter B, Kramer DM, Armbruster U, Kunz H-H (2019) Photosynthesis in arabidopsis is unaffected by the function of the vacuolar K+ channel TPK3. Plant Physiol 180:1322–1335
Hubbart S, Smillie IRA, Heatley M, Swarup R, Foo CC, Zhao L, Murchie EH (2018) Enhanced thylakoid photoprotection can increase yield and canopy radiation use efficiency in rice. Commun Biol 1:22
Jackson DT, Froehlich JE, Keegstra K (1998) The hydrophilic domain of tic110, an inner envelope membrane component of the chloroplastic protein translocation apparatus, faces the stromal compartment. J Biol Chem 273:16583–16588
Johnson HA, Hampton E, Lesley SA (2009) The Thermotoga maritima Trk potassium transporter—from frameshift to function. J Bacteriol 191:2276–2284
Kahsay RY, Gao G, Liao L (2005) An improved hidden Markov model for transmembrane protein detection and topology prediction and its applications to complete genomes. Bioinformatics 21:1853–1858
Keegstra K, Yousif AE (1986) Isolation and characterization of chloroplast envelope membranes. Methods Enzymol 118C:316–325
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJE (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc 10:845
Koskela MM, Brünje A, Ivanauskaite A, Grabsztunowicz M, Lassowskat I, Neumann U, Dinh TV, Sindlinger J, Schwarzer D, Wirtz M, Tyystjärvi E, Finkemeier I, Mulo P (2018) Chloroplast acetyltransferase NSI is required for state transitions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 30:1695–1709
Kromdijk J, Głowacka K, Leonelli L, Gabilly ST, Iwai M, Niyogi KK, Long SP (2016) Improving photosynthesis and crop productivity by accelerating recovery from photoprotection. Science 354:857–861
Kröning N, Willenborg M, Tholema N, Hänelt I, Schmid R, Bakker EP (2007) ATP binding to the KTN/RCK subunit KtrA from the K+ -uptake system KtrAB of Vibrio alginolyticus: its role in the formation of the KtrAB complex and its requirement in vivo. J Biol Chem 282:14018–14027
Kunz HH, Gierth M, Herdean A, Satoh-Cruz M, Kramer DM, Spetea C, Schroeder JI (2014) Plastidial transporters KEA1, -2, and -3 are essential for chloroplast osmoregulation, integrity, and pH regulation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:7480–7485
Liu S, Yu F, Yang Z, Wang T, Xiong H, Chang C, Yu W, Li N (2018) Establishment of dimethyl labeling-based quantitative acetylproteomics in arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 17:1010–1027
Luo R, Jiang H, Lv Y, Hu S, Sheng Z, Shao G, Tang S, Hu P, Wei X (2018) Chlorophyll deficient 3, encoding a putative potassium efflux antiporter, affects chloroplast development under high temperature conditions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Report 36:675–684
Lupas A, Van Dyke M, Stock J (1991) Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science 252:1162–1164
Mäser P, Thomine S, Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Hirschi K, Sze H, Talke IN, Amtmann A, Maathuis FJM, Sanders D, Harper JF, Tchieu J, Gribskov M, Persans MW, Salt DE, Kim SA, Guerinot ML (2001) Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:1646–1667
Nowack ECM, Melkonian M (2010) Endosymbiotic associations within protists. Philos Trans R Soc B 365:699–712
Pliotas C, Grayer SC, Ekkerman S, Chan AKN, Healy J, Marius P, Bartlett W, Khan A, Cortopassi WA, Chandler SA, Rasmussen T, Benesch JLP, Paton RS, Claridge TDW, Miller S, Booth IR, Naismith JH, Conway SJ (2017) Adenosine monophosphate binding stabilizes the KTN domain of the Shewanella denitrificans Kef potassium efflux system. Biochemistry 56:4219–42334
Reiland S, Messerli G, Baerenfaller K, Gerrits B, Endler A, Grossmann J, Gruissem W, Baginsky S (2009) Large-scale arabidopsis phosphoproteome profiling reveals novel chloroplast kinase substrates and phosphorylation networks. Plant Physiol 150:889–903
Roosild TP, Miller S, Booth IR, Choe S (2002) A mechanism of regulating transmembrane potassium flux through a ligand-mediated conformational switch. Cell 109:781–791
Roosild TP, Castronovo S, Miller S, Li C, Rasmussen T, Bartlett W, Gunasekera B, Choe S, Booth IR (2009) KTN (RCK) domains regulate K+ channels and transporters by controlling the Dimer-Hinge conformation. Structure 17:893–8903
Roston RL, Gao JP, Murcha MW, Whelan J, Benning C (2012) TGD1,-2, and-3 proteins involved in lipid trafficking form ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter with multiple substrate-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 287:21406–21415
Schneider D, Lopez LS, Li M, Crawford JD, Kirchhoff H, Kunz H-H (2019) Dynamic light experiments and semi-automated plant phenotyping enabled by self-built growth racks and simple upgrades to the IMAGING-PAM. Plant Methods. https://doi.org/10.1101/795476
Sheng PK, Tan JJ, Jin MN, Wu FQ, Zhou KN, Ma WW, Heng YQ, Wang JL, Guo XP, Zhang X, Cheng ZJ, Liu LL, Wang CM, Liu XM, Wan JM (2014) Albino midrib 1, encoding a putative potassium efflux antiporter, affects chloroplast development and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Rep 33:1581–1594
Sohrt K, Soll J (2000) Toc64, a new component of the protein translocon of chloroplasts. J Cell Biol 148:1213–1222
Stahl T, Glockmann C, Soll J, Heins L (1999) Tic40, a new “old” subunit of the chloroplast protein import translocon. J Biol Chem 274:37467–37472
Sun Q, Zybailov B, Majeran W, Friso G, Olinares PDB, van Wijk KJ (2009) PPDB, the plant proteomics database at Cornell. Nucl Acids Res 37:D969–D974
Tsujii M, Kera K, Hamamoto S, Kuromori T, Shikanai T, Uozumi N (2019) Evidence for potassium transport activity of Arabidopsis KEA1-KEA6. Sci Rep 9:10040
Waegemann K, Soll J (1995) Chapter 18 characterization and isolation of the chloroplast protein import machinery. In: Galbraith DW, Bourque DP, Bohnert HJ (eds) Methods in cell biology. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 255–267
Wang C, Yamamoto H, Narumiya F, Munekage YN, Finazzi G, Szabo I, Shikanai T (2017) Fine-tuned regulation of the K+/H+ antiporter KEA3 is required to optimize photosynthesis during induction. Plant J 89:540–553
Acknowledgements
Funding: BB DFG, CRC TR175 (B06), SS DFG, CRC 1035 (A04), H-HK NSF Career Award (IOS-1553506), 3rd call ERA-CAPS funding from NSF (IOS-1847382), and (#DE-SC0017160) from DOE. We thank Professor Dr. Jürgen Soll from LMU for supporting this project by initiating the production of α-KEA1(2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bölter, B., Mitterreiter, M.J., Schwenkert, S. et al. The topology of plastid inner envelope potassium cation efflux antiporter KEA1 provides new insights into its regulatory features. Photosynth Res 145, 43–54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-019-00700-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-019-00700-2