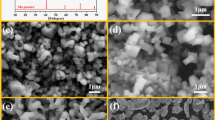
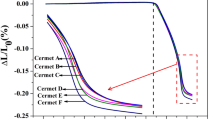
(Ti, W)C–Ni cermets with different contents of Mo2C were produced by the spark plasma sintering (SPS) method. The grain size (GS), composition of ceramic phases, and mechanical properties of the sintered cermets were investigated. The amount of Mo2C had a significant influence on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-prepared cermets. GS and fracture toughness (KIc) were decreased as a result of increasing the amount of Mo2C. By increasing the amount of Mo2C, the transverse rupture strength (TRS) and hardness (HRA) were enhanced. However, above 10 wt.%, the TRS was reduced. The conventional black cores observed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE–SEM) in backscattered electron imaging (BSE) in (Ti, W)C–Ni cermets will be partially turned into some white cores which contain higher Mo, except for Ti and W elements, when content of Mo2C reaches ~15 wt.%. Batch mechanical tests indicate that cermets with some white cores have refined microstructure and higher hardness, but relatively lower transverse rupture strength (TRS) and fracture toughness (KIc) at room temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Ettmayer, H. Kolasks, W. Lengauer, et al., “Ti(C, N) cermets--metallurgy and properties,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. , 13, 343–351(1995).
D. Mari, S. Bolognini, G. Feusier, et al., “TiMoCN based cermets. Part II. Microstructure and room temperature mechanical properties,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 21, 47–53 (2003).
Yuemei Wu, Ji Xiong, Zhixing Guo, et al., “Microstructure and fracture toughness of Ti(C0.7N0.3) –WC– Ni cermets,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 29, 85–89(2011)
W. T. Kwon, J. S. Park, and S. Kang, “Effect of group IV elements on the cutting characteristics of Ti(C, N) cermet tools and reliability analysis,” J. Mater. Proc. Tech., 166, 9–14 (2005).
Y. J. Park, S. W. Kim, and S. Kang, “The formation of a solid solution band at the surface of Ti (CN)-based cermets.,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A291, 198–206 (2000).
Jun Qu, Weihao Xiong, Dameng Ye, et al., “Effect of WC content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti(C0.5 N0.5)–WC–Mo–Ni cermets,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 28, 243–249 (2010).
S. Y. Ahn and S. Kang, “Effect of WC particle size on microstructure and rim composition in the Ti (C0.7 N0.3)–WC–Ni system,” Scripta. Mater., 55, 1015–1018 (2006).
Yan Li, Ning Liu, Xiaobo Zhang, and Chunlan Rong, “Effect of WC content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti, W)(C, N)–Co cermets,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 26, 33–40 (2008).
J. C. LaSalvia, D. K. Kim, and M. A. Meyers, “Effect of Mo on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC–Ni-based cermets produced by combustion synthesis–impact forging technique,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A206, 71–80 (1996).
Yan Li, Ning Liu, Xiaobo Zhang, and Chunlan Rong, “Effect of Mo addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grade TiC–TiN–WC–Mo2C–Co cermets,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 26, 190–196 (2008).
S. Ahn and S. Kang, “Effect of various carbides on the dissolution behavior of Ti (C0.7 N0.3) in a Ti (C0.7 N0.3) –30Ni system,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 19, 539–545 (2001).
S. Park and S. Kang, “Toughened ultrafine (Ti, W) (CN)–Ni cermets,” Scripta Mater., 52, 129–133 (2005).
T. Cutard, T. Viatte, G. Feusier, and W. Benoit, “Microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of TiC0.7 N0.3–Mo2C–Ni cermets,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A209, 218–227 (1996).
Shiquan Zhou, Wei Zhao, and Weihao Xiong, “Microstructure and properties of the cermets based on Ti(C,N),” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 27, 26–32 (2009).
Jong-Ku Park and Seung-Tae Park, “Densification of TiN-Ni cermets by improving wettability of liquid nickel on TiN grain surface with addition of Mo2C,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 17, 295–299 (1999).
Xiaobo Zhang, Ning Liu, and Chunlan Rong, “Effect of molybdenum content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine Ti(C, N) based cermets,” Mater. Characterization, 59, 1690–1696 (2008).
S. Y. Ahn and S. Kang, “Formation of core/rim structures in Ti(C, N)-WC-Ni cermets via a dissolution and precipitation process,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 83, 1489–1494 (2000).
P. Lindahl, P. Guatafson, U. Rolander, et al., “Microstructure of model cermets with high Mo or W content,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 17, 411–421 (1999).
Ma Qian and L. C. Lim , “Microstructural evolution in the phase mixtures of Ti(C, N)-Mo at 1600 degree,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A264, 39–46 (1999)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge with thanks the support of this research by the Natural Science Foundation of Education Department of Anhui Province (No. KJ2012B148), the Natural Science Foundation of Hefei University (No. 13RC09), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51102073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 53, No. 1–2 (495), pp. 73–80, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, C., Tian, C. Effect of Mo2C on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti, W)C–Ni Cermets. Powder Metall Met Ceram 53, 57–63 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-014-9587-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-014-9587-1