Abstract
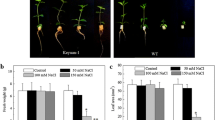
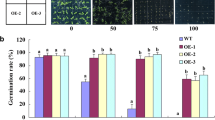
Vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multi-subunit endomembrane proton pump, plays an important role in plant growth and response to environmental stresses. In the present study, transgenic tobacco that overexpressed the V-ATPase c subunit gene from Iris lactea (IrlVHA-c) was used to determine the function of IrlVHA-c. Quantitative PCR analysis showed that IrlVHA-c expression was induced by salt stress in I. lactea roots and leaves. Subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein (GFP) as marker combined with FM4-64 staining showed that the IrlVHA-c-GFP was localized to the endosomal compartment in tobacco cells. Compared with the wild-type, the IrlVHA-c transgenic tobacco plants exhibited greater seed germination rates, root length, fresh weight, and higher relative water content (RWC) of leaves under salt stress. Furthermore, the IrlVHA-c transgenic tobacco leaves have lower stomatal densities and larger stomatal apertures than wild-type. Under salt stress, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the transgenic tobacco was significantly enhanced. Moreover, the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the transgenic tobacco was significantly lower than that in wild-type plants under salt stress. Taken together, these results suggested that the IrlVHA-c plays an important role in salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by influencing stomatal movement and physiological changes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GJ, Chu SP, Schumacher K, Shimazaki CT, Vafeados D, Kemper A, Hawke SD, Tallman G, Tsien RY, Harper JF, Chory J, Schroeder JI (2000) Alteration of stimulus-specific guard cell calcium oscillations and stomatal closing in Arabidopsis det3 mutant. Science 289:2338–2342
Baisakh N, RamanaRao MV, Rajasekaran K, Subudhi P, Janda J, Galbraith D, Vanier C, Pereira A (2012) Enhanced salt stress tolerance of rice plants expressing a vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit c1 (SaVHAc1) gene from the halophyte grass Spartina alterniflora Löisel. Plant Biotechnol J 10:453–464
Begcy K, Mariano ED, Gentile A, Lembke CG, Zingaretti SM, Souza GM, Menossi M (2012) A novel stress-induced sugarcane gene confers tolerance to drought, salt and oxidative stress in transgenic tobacco plants. PLoS One 7:e44697
Dettmer J, Hong-Hermesdorf A, Stierhof YD, Schumacher K (2006) Vacuolar H+-ATPase activity is required for endocytic and secretory trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:715–730
Forgac M (2007) Vacuolar ATPases: rotary proton pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 8:917–929
Gao C, Wang Y, Jiang B, Liu G, Yu L, Wei Z, Yang C (2011) A novel vacuolar membrane H+-ATPase c subunit gene (ThVHAc1) from Tamarix hispida confers tolerance to several abiotic stresses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Rep 38:957–63
Gaxiola RA, Palmgren MG, Schumacher K (2007) Plant proton pumps. FEBS Lett 581:2204–2214
Herman EM, Li X, Su RT, Larsen P, Hsu H, Sze H (1994) Vacuolar-type H+-ATPases are associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and provacuoles of root tip cells. Plant Physiol 106(4):1313–1324
Hetherington AM, Woodward FI (2003) The role of stomata in sensing and driving environmental change. Nature 424:901–908
Hirata T, Iwamoto-Kihara A, Sun-Wada GH, Okajima T, Wada Y, Futai M (2003) Subunit rotation of vacuolar-type proton pumping ATPase: relative rotation of the G and C subunits. The Journal of biological chemistry 278:23714–23719
Kluge C, Lahr J, Hanitzsch M, Bolte S, Golldack D, Dietz KJ (2003) New insight into the structure and regulation of the plant vacuolar H+-ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomembr 35:377–388
Krebs M, Beyhl D, Gorlich E, Al-Rasheid KA, Marten I, Stierhof YD, Hedrich R, Schumacher K (2010) Arabidopsis V-ATPase activity at the tonoplast is required for efficient nutrient storage but not for sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:3251–3256
Leshem Y, Seri L, Levine A (2007) Induction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated endocytosis by salt stress leads to intracellular production of reactive oxygen species and salt tolerance. Plant J 51:185–197
Matsuoka K, Higuchi T, Maeshima M, Nakamura K (1997) A vacuolar-type H+-ATPase in a nonvacuolar organelle is required for the sorting of soluble vacuolar protein precursors in tobacco cells. Plant Cell 9:533–546
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Nishi T, Forgac M (2002) The vacuolar (H+)-ATPases—nature’s most versatile proton pumps. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 3:94–103
Padmanaban S, Lin X, Perera I, Kawamura Y, Sze H (2004) Differential expression of vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit c genes in tissues active in membrane trafficking and their roles in plant growth as revealed by RNAi. Plant Physiol 134:1514–1526
Perera IY, Li X, Sze H (1995) Several distinct genes encode nearly identical to 16 kDa proteolipids of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 29:227–244
Ratajczak R (2000) Structure, function and regulation of the plant vacuolar H(+)-translocating ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:17–36
Schumacher K (2014) pH in the plant endomembrane system—an import and export business. Curr Opin Plant Biol 22:71–76
Schumacher K, Krebs M (2010) The V-ATPase: small cargo, large effects. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:724–730
Seidel T, Kluge C, Hanitzsch M, Ross J, Sauer M, Dietz KJ, Golldack D (2004) Colocalization and FRET-analysis of subunits c and a of the vacuolar H+-ATPase in living plant cells. J Biotechnol 112:165–175
Sunkar R, Bartels D, Kirch HH (2003) Overexpression of a stress-inducible aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana in transgenic plants improves stress tolerance. Plant J 35:452–464
Sze H, Schumacher K, Muller ML, Padmanaban S, Taiz L (2002) A simple nomenclature for a complex proton pump: VHA genes encode the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Trends Plant Sci 7:157–161
Tsiantis MS, Bartholomew DM, Smith JA (1996) Salt regulation of transcript levels for the c subunit of a leaf vacuolar H(+)-ATPase in the halophyte Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant J 9:729–736
Wang Y, Noguchi K, Ono N, Inoue S, Terashima I, Kinoshita T (2014) Overexpression of plasma membrane H+-ATPase in guard cells promotes light-induced stomatal opening and enhances plant growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(1):533–538
Xu CX, Zheng L, Gao CQ, Wang C, Liu GF, Jiang J, Wang YC (2011) Ovexpression of a vacuolar H+-ATPase c subunit gene mediates physiological changes leading to enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:424–430
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhang XZ, Yin LL, Wu T, Xu XF, Jia WS, Han ZH (2012) Cloning and characterization of MxVHA-c, a vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit c gene related to Fe efficiency from Malus xiaojinensis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:1149–1157
Zhang H, Niu X, Liu J, Xiao F, Cao S et al (2013) RNAi-directed downregulation of vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit A results in enhanced stomatal aperture and density in rice. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69046
Zhou A, Bu Y, Takano T, Zhang X, Liu S (2015) Conserved V-ATPase c subunit plays a role in plant growth by influencing V-ATPase-dependent endosomal trafficking. Plant biotechnology journal. Apr 28: [Epub ahead of print].
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (C201112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jingang Wang and Aimin Zhou are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhou, A., Li, Y. et al. Overexpression of IrlVHA-c, A Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase c Subunit Gene from Iris lactea, Enhances Salt Tolerance in Tobacco. Plant Mol Biol Rep 34, 877–885 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-015-0969-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-015-0969-4