Abstract
Purpose
We investigated the effect of Serendipita indica, an endophytic fungus, inoculation of different wheat (Triticum aestivum) cultivars on the rhizosphere physical quality.
Methods
S. indica inoculated and uninoculated seedlings of wheat cultivars (Roshan, Ghods, Kavir and Pishtaz) were grown in rhizoboxes. Plants were harvested and intact samples were taken from the rhizosphere to measure soil organic carbon (SOC), hot-water soluble carbohydrates (HWSC), carbon mineralization rate (CMR), water repellency index (RI) by the sorptivity method, and aggregate stability by the high energy moisture characteristic (HEMC) method. Root mucilages of inoculated and uninoculated seedlings were also collected for measuring total polysaccharides (TPmucilage).
Results
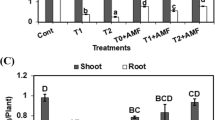
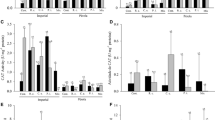
The SOC, HWSC, and RI were increased by 146, 83, and 40% and CMR was decreased by 56% in planted treatments, which consequently increased the HEMC aggregate stability indices. S. indica increased SOC, HWSC, RI, and structural stability, and improved the physical quality especially in soil with Roshan and Ghods, which had more extensive root distributions and higher TPmucilage. The changes of soil-physical and hydraulic properties among different wheat cultivars imply that both quantitative and qualitative properties of root exudates have significant effects on soil quality. Soil with Roshan had the highest SOC, HWSC, and root distribution and the lowest aggregate stability. However, soil with Ghods had almost the same SOC and HWSC, but it had the highest stability indices.
Conclusion
S. indica inoculation of different wheat cultivars, by increasing SOC and inducing water repellency in the rhizosphere, can improve the aggregate stability and soil physical quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- SOC:
-
Soil organic carbon (g kg−1)
- HEMC:
-
High energy moisture characteristic (−)
- RCP:
-
Root colonization percentage (%)
- HWSC:
-
Hot-water soluble carbohydrates (g kg−1)
- CMR:
-
Carbon mineralization rate (μmol C g−1 soil h−1)
- TPmucilage :
-
Total polysaccharides concentration of root mucilage (mg g−1 DW)
- S W :
-
Sorptivity of water (cm s−0.5)
- S E :
-
Sorptivity of ethanol (cm s−0.5)
- RI:
-
Water repellency index ( −)
- β :
-
Soil-water contact angle (°)
- h :
-
Soil matric suction (hPa)
- VDPSW and VDPFW :
-
Volume of drainable pores of slow-wetted and fast-wetted aggregates, respectively (g g−1)
- h modal-SW and h modal-FW :
-
Modal suctions [h at the peak of dθ/dh] of slow-wetted and fast-wetted aggregates, respectively (hPa)
- SI:
-
Structural index (hPa−1)
- SR:
-
Stability ratio (−)
- dθ/dh :
-
Specific water capacity function (hPa−1)
- θ r :
-
Pseudo residual water content (g g−1)
- θ s :
-
Pseudo saturated water content (g g−1)
- α :
-
Scaling parameter of HEMC (hPa−1)
- n :
-
Shape parameter of HEMC (−)
- A, B and C :
-
Quadratic coefficients in the modified van Genuchten model (hPa−2, hPa−1 and g g−1)
- VDPR:
-
Ratio of fast-wetting to slow-wetting VDP values (−)
- S i :
-
Slope at the inflection point of HEMC (hPa−1)
- h i :
-
Matric suction at the inflection point of HEMC (hPa)
- S iR:
-
Ratio of fast-wetting to slow-wetting Si values (−)
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance (−)
References
Ahmed MA, Kroener E, Benard P, Zarebanadkouki M, Kaestner A, Carminati A (2016) Drying of mucilage causes water repellency in the rhizosphere of maize: measurements and modelling. Plant Soil 407:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2749-1
Allison FE (1973) A factor in soil aggregation and root development. In: Allison FE (ed) Soil organic matter and its role in crop production. Elsevier, London, pp 315–345
Aslam MM, Karanja J, Bello SK (2019) Piriformospora indica colonization reprograms plants to improved P-uptake, enhanced crop performance, and biotic/abiotic stress tolerance. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 106:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2019.02.010
Bearden BN (2001) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil structure and soil water characteristics of Vertisols. Plant Soil 229:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004835328943
Carminati A, Moradi AB, Vetterlein D, Vontobel P, Lehmann E, Weller U, Vogel HJ, Oswald SE (2010) Dynamics of soil water content in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 332:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0283-8
Cesarano G, Incerti G, Bonanomi G (2016) The influence of plant litter on soil water repellency: insight from 13C NMR spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 11:e0152565. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152565
Chantigny MH, Angers DA (2007) Carbohydrates. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 653–665
Childs EC (1940) The use of soil moisture characteristics in soil studies. Soil Sci 50:239–252
Collis-George N, Figueroa BS (1984) The use of high energy moisture characteristic to assess soil stability. Aust J Soil Res 22:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9840349
Cosentino D, Hallett PD, Michel JC, Chenu C (2010) Do different methods for measuring the hydrophobicity of soil aggregates give the same trends in soil amended with residue? Geoderma 159:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.07.015
Costa O, Raaijmakers JM, Kuramae EE (2018) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front Microbiol 9:1636. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01636
Cruz BC, Furrer JM, Guo YS, Dougherty D, Hinestroza HF, Hernandez JS, Gage DJ, Cho YK, Shor LM (2017) Pore-scale water dynamics during drying and the impacts of structure and surface wettability. Water Resour Res 53:5585–5600. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR019862
Czarnes S, Hallett PD, Bengough AG, Young IM (2000) Root-and microbial-derived mucilages affect soil structure and water transport. Eur J Soil Sci 51:435–443. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00327.x
Dabral S, Varma A, Choudhary DK, Bahuguna RN, Nath M (2019) Biopriming with Piriformospora indica ameliorates cadmium stress in rice by lowering oxidative stress and cell death in root cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 186:109741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109741
De Gryze S, Jassogne L, Six J, Bossuyt H, Wevers M, Merckx R (2006) Pore structure changes during decomposition of fresh residue: X-ray tomography analyses. Geoderma 134:82–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.09.002
Dexter AR (2004) Soil physical quality: Part I. Theory, effects of soil texture, density, and organic matter, and effects on root growth. Geoderma 120:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.09.004
Dignac M, Derrien D, Barré P (2017) Increasing soil carbon storage: mechanisms, effects of agricultural practices and proxies. A Review Agron Sustain Dev 37:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-017-0421-2
Dijkstra FA, Carrillo Y, Pendall E, Morgan JA (2013) Rhizosphere priming: a nutrient perspective. Front Microbiol 4:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00216
Gill SS, Gill R, Trivedi DK, Anjum NA, Sharma KK, Ansari MW, Ansari AA, Johri AK, Prasad R, Pereira E, Varma A (2016) Piriformospora indica: potential and significance in plant stress tolerance. Front Microbiol 7:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00332
Goebel MO, Bachmann J, Reichstein M, Janssens IA, Guggenberger G (2011) Soil water repellency and its implications for organic matter decomposition–is there a link to extreme climatic events? Glob Chang Biol 17:2640–2656. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02414.x
Haans A (2018) Contrast analysis: A tutorial. Pract Assess Res Eval 23:9. https://doi.org/10.7275/zeyh-j468
Håkansson I (1990) A method for characterizing the state of compactness of the plough layer. Soil Tillage Res 16:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-1987(90)90024-8
Hallett PD, Young IM (1999) Changes to water repellence of soil aggregates caused by substrate-induced microbial activity. Eur J Soil Sci 50:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.1999.00214.x
Hallett PD, Gordon DC, Bengough AG (2003) Plant influence on rhizosphere hydraulic properties: direct measurements using a miniaturized infiltrometer. New Phytol 157:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00690.x
Hallett PD, Feeney DS, Bengough AG, Rillig MC, Scrimgeour CM, Young IM (2009) Disentangling the impact of AM fungi versus roots on soil structure and water transport. Plant Soil 314:183–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9717-y
Hallett PD (2008) A brief overview of the causes, impacts and amelioration of soil water repellency– a review. Soil Water Res 3:S21–S29. https://doi.org/10.17221/1198-SWR
Hill TW, Kafer E (2001) Improved protocols for Aspergillus medium: elements and minimum salt stock solutions trace medium. Fungal Genet Rep 48:20–21
Hinsinger P, Bengough AG, Vetterlein D, Young IM (2009) Rhizosphere: biophysics, biogeochemistry and ecological relevance. Plant Soil 321:117–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9885-9
Holz M, Leue M, Ahmed MA, Benard P, Gerke HH, Carminati A (2018) Spatial distribution of mucilage in the rhizosphere measured with infrared spectroscopy. Front Environ Sci 6:87. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00087
Hopkins, (2007) Carbon mineralization. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 589–598
Hosseini F, Mosaddeghi MR, Hajabbasi MA, Sabzalian MR (2015a) Aboveground fungal endophyte infection in tall fescue alters rhizosphere chemical, biological, and hydraulic properties in texture–dependent ways. Plant Soil 388:351–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2340-1
Hosseini F, Mosaddeghi MR, Hajabbasi MA, Sabzalian MR (2015b) Influence of tall fescue endophyte infection on structural stability as quantified by high energy moisture characteristic in a range of soils. Geoderma 249:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.03.013
Hosseini F, Mosaddeghi MR, Dexter AR (2017a) Effect of the fungus Piriformospora indica on physiological characteristics and root morphology of wheat under combined drought and mechanical stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 118:107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.06.005
Hosseini F, Mosaddeghi MR, Hajabbasi MA, Mamedov AI (2017b) Effects of endophyte–infected and non–infected tall fescue residues on aggregate stability in four texturally different soils. Geoderma 285:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.10.001
Hosseini F, Mosaddeghi MR, Dexter AR, Sepehri M (2018) Maize water status and physiological traits as affected by root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica under combined drought and mechanical stresses. Planta 247:1229–1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2861-6
Hosseini F, Mosaddeghi MR, Dexter AR, Sepehri M (2019) Effect of endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica and PEG–induced water stress on maximum root growth pressure and elongation rate of maize. Plant Soil 435:423–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-03909-7
Hu X, Li X, Guo L, Liu Y, Wang P, Zhao YD, Cheng YQ, Lyu YL, Liu LY (2019) Influence of shrub roots on soil macropores using X-ray computed tomography in a shrub-encroached grassland in Northern China. J Soils Sediments 19:1970–1980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2218-6
Hua MD, Senthil Kumar R, Shyur L, Cheng YB, Tian Z, Oelmüller R, Yeh KW (2017) Metabolomic compounds identified in Piriformospora indica-colonized Chinese cabbage roots delineate symbiotic functions of the interaction. Sci Rep 7:9291. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08715-2
Huo C, Luo Y, Cheng W (2017) Rhizosphere priming effect: a meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 111:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.04.003
Johnson CM, Strout R, Broyer TC, Carlton AB (1957) Comparative chlorine requirements of different plant species. Plant Soil 8:327–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666323
Jones DL, Hodge A, Kuzyakov Y (2004) Plant and mycorrhizal regulation of rhizodeposition. New Phytol 163:459–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01130.x
Kell DB (2011) Breeding crop plants with deep roots: their role in sustainable carbon, nutrient and water sequestration. Ann Bot 108:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr175
Khayamim F, Khademi H, Sabzalian MR (2011) Effect of Neotyphodium endophyte–tall fescue symbiosis on mineralogical changes in clay–sized phlogopite and muscovite. Plant Soil 341:473–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0659-9
Kirkham MB (2014) Principles of soil and plant water relations. Academic Press, Cambridge
Koo BJ, Adriano DC, Bolan NS, Barton CD (2005) Root exudates and microorganisms. In: Hillel D (ed) Encyclopedia of soils in the environment, vol 3. Elsevier, Oxford, UK, pp 421–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-12-348530-4/00461-6
Kuzyakov Y (2010) Priming effects: interactions between living and dead organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1363–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.04.003
Levy GJ, Mamedov AI (2002) High-energy-moisture-characteristic aggregate stability as a predictor for seal formation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1603–1609. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2002.1603
Lipiec J, Wojciga A, Horn R (2009) Hydraulic properties of soil aggregates as influenced by compaction. Soil Tillage Res 103:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2008.10.021
Luo Y, Xueyong Z, Olof A, Yangchun Z, Wenda H (2014) Artificial root exudates and soil organic carbon mineralization in a degraded sandy grassland in northern China. J Arid Land 6:423–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-014-0063-z
Mainwaring K, Hallin IL, Douglas P, Doerr SH, Morley CP (2013) The role of naturally occurring organic compounds in causing soil water repellency. Eur J Soil Sci 64:667–680. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12078
Mamedov AI, Levy GJ (2013) High energy moisture characteristics: linking between some soil physical processes and structure stability. In: Logsdon S, Berli M, Horn R (eds) Quantifying and modeling soil structure dynamics. Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison, WI, pp 41–74
Mamedov AI, Wagner LE, Huang C, Norton LD, Levy GJ (2010) Polyacrylamide effects on aggregate and structure stability of soils with different clay mineralogy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:1720–1732. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2009.0279
Mao J, Nierop KG, Rietkerk M, Damsté JS, Dekker SC (2016) The influence of vegetation on soil water repellency-markers and soil hydrophobicity. Sci Total Environ 566:608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.077
McNear DH Jr (2013) The rhizosphere- roots, soil and everything in between. Nat Ed Knowl 4:1
Moballegh Z (2017) Symbiotic effect of endophytic fungus, Piriformospora indica, with wheat and maize on soil structural stability indices, and physical and chemical properties. MSc Thesis, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan, Iran. (in Farsi with English abstract)
Mosaddeghi MR, Hosseini F, Hajabbasi MA, Sabzalian MR, Sepehri M (2021) Epichloë spp. and Serendipita indica endophytic fungi: Functions in plant-soil relations. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in Agronomy. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 59–113
Murphy BR, Doohan FM, Hodkinson TR (2014) Yield increase induced by the fungal root endophyte Piriformospora indica in barley grown at low temperature is nutrient limited. Symbiosis 62:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-014-0268-0
Naveed M, Brown LK, Raffan AC, George TS, Bengough AG, Roose T, Sinclair I, Koebernick N, Cooper L, Hacket CA, Hallett PD (2017) Plant exudates may stabilize or weaken soil depending on species, origin and time. Eur J Soil Sci 68:806–816. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12487
Naveed M, Brown LK, Raffan AC, George TS, Bengough AG, Roose T, Sinclair I, Koebernick N, Cooper L, Hallett PD (2018) Rhizosphere-scale quantification of hydraulic and mechanical properties of soil impacted by root and seed exudates. Vadose Zone J 17:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-03939-9
Oades JM, Waters AG (1991) Aggregate hierarchy in soils. Aust J Soil Res 29:815–828. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9910815
Pierson FB, Mulla DJ (1989) An improved method for measuring aggregate stability of a weakly aggregated loessial soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:1825–1831. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300060035x
Qiang X, Zechmann B, Reitz MU, Kogel KH, Schafer P (2012) The mutualistic fungus Piriformospora indica colonizes Arabidopsis roots by inducing an endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered caspase-dependent cell death. Plant Cell 24:794–809. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.093260
Rai M, Acharya D, Singh A, Varma A (2001) Positive growth responses of the medicinal plants Spilanthes calva and Withania somnifera to inoculation by Piriformospora indica in a field trial. Mycorrhiza 11:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720100115
Rasse DP, Rumpel C, Dignac MF (2005) Is soil carbon mostly root carbon? Mechanisms for a specific stabilization. Plant Soil 269:341–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0907-y
Reynolds WD, Topp CG (2007) Soil water desorption and imbibition: tension and pressure techniques. In: Carter MR, Gregorich EG (eds) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 981–997
Rillig MC, Mardatin NF, Leifheit EF, Antunes PM (2010) Mycelium of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increases soil water repellency and is sufficient to maintain water-stable soil aggregates. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1189–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.03.027
Rodriguez RJ, White JF Jr, Arnold AE, Redman ARA (2009) Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytol 182:314–330. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02773.x
Rumpel C, Chabbi A, Marschner B (2012) Carbon storage and sequestration in subsoil horizons: knowledge, gaps and potentials. In: Lal R, Lorenz K, Hüttl R, Schneider B, von Braun J. (eds) Recarbonization of the biosphere. Springer, Dordrecht. pp 445−464. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4159-1_20
Shaver TM, Peterson GA, Ahuja LR, Westfall DG (2013) Soil sorptivity enhancement with crop residue accumulation in semiarid dryland no-till agroecosystems. Geoderma 192:254–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.08.014
Singh BN, Hidangmayum A, Singh A, Shera SS, Dwivedi P (2019) Secondary metabolites of plant growth promoting rhizomicroorganisms. Springer, Berlin
Strehmel N, Mönchgesang S, Herklotz S, Krüger S, Ziegler J, Scheel D (2016) Piriformospora indica stimulates root metabolism of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 17:1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071091
Süli E, Mayers DF (2003) An introduction to numerical analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sun C, Shao Y, Vahabi K, Lu J, Bhattacharya S, Dong S, Yeh KW, Sherameti I, Lou B, Baldwin IT, Oelmüller R (2014) The beneficial fungus Piriformospora indica protects Arabidopsis from Verticillium dahliae infection by down-regulation plant defense responses. BMC Plant Biol 14:268. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0268-5
Tillman RW, Scotter DR, Wallis MG, Clothier BE (1989) Water repellency and its measurement by using intrinsic sorptivity. Aust J Soil Res 27:637–644. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9890637
van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:892–898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
van Hees PAW, Jones DL, Finlay R, Godbold DL, Lundström US (2005) The carbon we do not see–the impact of low molecular weight compounds on carbon dynamics and respiration in forest soils: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.06.010
van Hecke MM, Treonis AM, Kaufman JR (2005) How does the fungal endophyte Epichloë coenophiala affect tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) rhizodeposition and soil microorganisms? Plant Soil 275:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-0380-2
Vierheilig H, Schweiger P, Brundrett M (2005) An overview of methods for the detection and observation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in roots. Physiol Plant 125:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00564.x
Vogelmann ES, Reichert JM, Reinert DJ, Mentges MI, Vieira DA, de Barros CA, Fasinmirin JT (2010) Water repellency in soils of humid subtropical climate of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Soil Tillage Res 110:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2010.07.006
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Weiss M, Waller F, Zuccaro A, Selosse MA (2016) Sebacinales: one thousand and one interactions with land plants. New Phytol 211:20–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13977
White I, Sully MJ (1987) Macroscopic and microscopic capillary length and time scales from field infiltration. Water Resour Res 23:1514–1522. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR023i008p01514
Woche SK, Goebel MO, Kirkham MB, Horton R, van der Ploeg RR, Bachmann J (2005) Contact angle of soils as affected by depth, texture, and land management. Eur J Soil Sci 56:239–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2004.00664.x
Yang T, Du W, Zhou J, Wang XX, Dai CC (2013) Effects of the symbiosis between fungal endophytes and Atractylodes lancea on rhizosphere and phyllosphere microbial communities. Symbiosis 61:23–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-013-0254-y
Zhang HS, Zhou MX, Zai XM, Zhao FG, Qin P (2020) Spatio-temporal dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil organic carbon in coastal saline soil of China. Sci Rep 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66976-w
Zheng W, Morris EK, Rillig MC (2014) Ectomycorrhizal fungi in association with Pinus sylvestris seedlings promote soil aggregation and soil water repellency. Soil Biol Biochem 78:326–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.07.015
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Bahram Sharifnabi of Department of Plant Protection, College of Agriculture, Isfahan University of Technology, for providing the S. indica inoculum. We greatly acknowledge the kindness of Prof. Mary Beth Kirkham (Department of Agronomy, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas, USA) for reading the manuscript and English improvement.
Funding
This project was funded by Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) and Isfahan University of Technology as a postdoctoral research fellowship (proposal No. 97005904) to the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Fatemeh Hosseini conducted experiments and wrote the draft of the manuscript. Prof. Mohammad Reza Mosaddeghi supervised the work and contributed to the paper writing. Both authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Andrea Schnepf
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, F., Mosaddeghi, M.R. Effects of Serendipita indica inoculation of four wheat cultivars on hydraulic properties and aggregate stability of a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 469, 347–367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05142-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05142-1