Abstract
Background and aims
Crop diversification usually increase nutrient use efficiency and productivity of crops, but we still lack deeper understandings of the underlying mechanisms. Here we aimed to study the role of root exudates and soil microbial communities in mobilization of soil P during an intercropping system.
Methods
Different barrier treatments were used to separate tomato and potato onion, and different P forms, that makes most of the plant sparingly available P in the soil (i.e., Al-P, Fe-P, Ca-P, Organic P), were applied in a pot experiment. In addition, we studied the effects of monoculture and/or intercropped tomato root exudates in vitro on soil available P and soil microbial community composition using quantitative PCR and high throughput sequencing.
Results
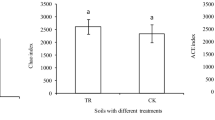
Compared with solid barrier, the 30 μm barrier increased belowground tomato biomass in presence of Ca-P, O-P and no P, soil available P in presence of Al-P, Fe-P and Ca-P, increased abundance of Bacillus spp. in presence of Fe-P, Ca-P and O- P, Pseudomonas spp. in presence of all P forms, and Trichoderma spp. in presence of Al-P, Ca-P and O-P. Compared with control, in vitro root exudates of intercropped tomato activated all P forms examined in this study, and increased soil available P was positively correlated with abundances of Bacillus, Pseudomonas and Trichoderma spp., and relative abundances of Massilia and Planomicrobium. The bacterial community structure and diversity was altered in intercropped tomato root exudates treatment as compared to rest of the treatments.
Conclusions
These findings suggest the key role of root exudates in increased bioavailability of soil P in the intercropping of tomato and potato onion.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Achal V, Savant VV, Reddy MS (2007) Phosphate solubilization by a wild type strain and UV-induced mutants of Aspergillus tubugensis. Soil Biol Biochem 39:695–699
Alaylar B, Güllüce M, Karadayi M, Isaoglu M (2019) Rapid detection of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from agricultural areas in Erzurum. Curr Microbiol 76:804–809
Alori ET, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front Microbiol 8:971
Badri DV, Vivanco JM (2009) Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant Cell Environ 32:666–681
Bharathkumar S, RameshKumar N, Paul D, Prabavathy VR, Nair S (2008) Characterization of the predominant bacterial population of different mangrove rhizosphere soils using 16S rRNA gene-based single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP). World J Microbiol Biot 24:387–394
Bini D, Santos CAD, Silva MCPD, Bonfim JA, Cardoso EJBN (2018) Intercropping Acacia mangium stimulates AMF colonization and soil phosphatase activity in Eucalyptus grandis. Sci Agric 75:102–110
Bononi L, Chiaramonte JB, Pansa CC, Moitinho MA, Melo IS (2020) Phosphorus-solubilizing Trichoderma spp. from Amazon soils improve soybean plant growth. Sci Rep 10:1–13
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencingdata. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chatterjee D, Datta SC, Manjaiah KM (2014) Fractions, uptake and fixation capacity of phosphorus and potassium in three contrasting soil orders. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 14:640–656
Chen S, Zhou X, Yu H, Wu F (2018) Root exudates of potato onion are involved in the suppression of clubroot in a Chinese cabbage-potato onion-Chinese cabbage crop rotation. Eur J Plant Pathol 150(3):765–777
Chen Y, Bonkowski M, Shen Y, Griffiths BS, Jiang Y, Wang X, Sun B (2020) Root ethylene mediates rhizosphere microbial community reconstruction when chemically detecting cyanide produced by neighbouring plants. Microbiome 8:1–17
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Change 19:292–305
Coyte KZ, Schluter J, Foster KR (2015) The ecology of the microbiome: networks, competition, and stability. Science 350:663–666
Crowther TW, Maynard DS, Leff JW, Oldfield EE, McCulley RL, Fierer N, Bradford MA (2014) Predicting the responsiveness of soil biodiversity to deforestation: a cross-biome study. Glob Chang Biol 20:2983–2994
Darch T, Giles CD, Blackwell MS, George TS, Brown LK, Menezes-Blackburn D, Shand CA, Stutter MI, Lumsdon DG, Mezeli MM, Wendler R (2018) Inter-and intra-species intercropping of barley cultivars and legume species, as affected by soil phosphorus availability. Plant Soil 427:125–138
de Vries FT, Griffiths RI, Bailey M, Craig H, Girlanda M, Gweon HS, Hallin S, Kaisermann A, Keith AM, Kretzschmar M, Lemanceau P (2018) Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nat Commun 9:3033
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Eisenhauer N, Lanoue A, Strecker T, Scheu S, Steinauer K, Thakur MP, Mommer L (2017) Root biomass and exudates link plant diversity with soil bacterial and fungal biomass. Sci Rep 7:1–8
Fernández L, Agaras B, Zalba P, Wall LG, Valverde C (2012) Pseudomonas spp isolates with high phosphate-mobilizing potential and root colonization properties from agricultural bulk soils under no-till management. Biol Fertil Soils 48:763–773
Gao D, Zhou X, Duan Y, Fu X, Wu F (2017) Wheat cover crop promoted cucumber seedling growth through regulating soil nutrient resources or soil microbial communities? Plant Soil 418:459–475
Garbeva P, Van Veen JA, Van Elsas JD (2003) Predominant Bacillus spp in agricultural soil under different management regimes detected via PCR-DGGE. Microb Ecol 45:302–316
García-López AM, Recena R, Avilés M, Delgado A (2018) Effect of Bacillus subtilis QST713 and Trichoderma asperellum T34 on P uptake by wheat and how it is modulated by soil properties. J Soils Sediments 18:727–738
Gardes M, Bruns TD (1993) ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol Ecol 2:113–118
Hagn A, Wallisch S, Radl V, Munch JC, Schloter M (2007) A new cultivation independent approach to detect and monitor common Trichoderma species in soils. J Microbiol Methods 69:86–92
Hao WY, Ren LX, Ran W, Shen QR (2010) Allelopathic effects of root exudates from watermelon and rice plants on Fusarium oxysporum f sp niveum. Plant Soil 336:485–497
Huang XF, Chaparro JM, Reardon KF, Zhang R, Shen Q, Vivanco JM (2014) Rhizosphere interactions: root exudates, microbes, and microbial communities. Botany 92:267–275
Jin X, Shi Y, Wu F, Pan K, Zhou X (2020) Intercropping of wheat changed cucumber rhizosphere bacterial community composition and inhibited cucumber Fusarium wilt disease. Sci Agric 77:e20190005
Kapri A, Tewari L (2010) Phosphate solubilization potential and phosphatase activity of rhizospheric Trichoderma spp. Braz J Microbiol 41:787–795
Khashi u Rahman M, Zhou X, Wu F (2019) The role of root exudates, CMNs, and VOCs in plant–plant interaction. J Plant Interact 14:630–636
Khosravi A, Zarei M, Ronaghi A (2017) Influence of biofertilizers and phosphate sources on the phosphorus uptake of lettuce and chemical forms of phosphorus in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 48:2701–2714
Kong CH, Zhang SZ, Li YH, Xia ZC, Yang XF, Meiners SJ, Wang P (2018) Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals. Nat Commun 9:1–9
Lambers H, Bishop JG, Hopper SD, Laliberté E, Zúniga-Feest A (2012) Phosphorus-mobilization ecosystem engineering: the roles of cluster roots and carboxylate exudation in young P-limited ecosystems. Ann Bot 110:329–348
Lambers H, Plaxton WC (2015) Phosphorus: back to the roots. Annu Plant Rev 48:3–22
Li C, Tian Q, u Rahman MK, Wu F (2020) Effect of anti-fungal compound phytosphingosine in wheat root exudates on the rhizosphere soil microbial community of watermelon. Plant Soil 456:223–240
Li L, Li SM, Sun JH, Zhou LL, Bao XG, Zhang HG, Zhang FS (2007) Diversity enhances agricultural productivity via rhizosphere phosphorus facilitation on phosphorus-deficient soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:11192–11196
Li XG, Zhang TL, Wang XX, Hua K, Zhao L, Han ZM (2013) The composition of root exudates from two different resistant peanut cultivars and their effects on the growth of soil-borne pathogen. Int J Biol Sci 9:164–173
Li Y, Ran W, Zhang R, Sun S, Xu G (2009) Facilitated legume nodulation, phosphate uptake and nitrogen transfer by arbuscular inoculation in an upland rice and mung bean intercropping system. Plant Soil 315:285–296
Liao D, Zhang C, Li H, Lambers H, Zhang F (2020) Changes in soil phosphorus fractions following sole cropped and intercropped maize and faba bean grown on calcareous soil. Plant Soil 448:587–560
Liu T, Cheng Z, Meng H, Ahmad I, Zhao H (2014) Growth, yield and quality of spring tomato and physicochemical properties of medium in a tomato/garlic intercropping system under plastic tunnel organic medium cultivation. Sci Hort 170:159–168
Lupatini M, Suleiman AK, Jacques RJ, Antoniolli ZI, de Siqueira FA, Kuramae EE, Roesch LF (2014) Network topology reveals high connectance levels and few key microbial genera within soils. Front Environ Sci 2:10
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Marschner P (2012) Rhizosphere biology in: Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants academic press, pp 369–388
Mikkelsen BL, Rosendahl S, Jakobsen I (2008) Underground resource allocation between individual networks of mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 180:890–898
Mohamed I, Eid KE, Abbas MH, Salem AA, Ahmed N, Ali M, Shah GM, Fang C (2019) Use of plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and mycorrhizae to improve the growth and nutrient utilization of common bean in a soil infected with white rot fungi. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:539–548
Murphy JAMES, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nassal D, Spohn M, Eltlbany N, Jacquiod S, Smalla K, Marhan S, Kandeler E (2018) Effects of phosphorus-mobilizing bacteria on tomato growth and soil microbial activity. Plant Soil 427:17–37
Neutel AM, Heesterbeek JA, de Ruiter PC (2002) Stability in real food webs: weak links in long loops. Science 296:1120–1123
Newman M, Barabási AL, Watts DJ (2006) The structure and dynamics of networks. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Pan RK, Sinha S (2009) Modularity produces small-world networks with dynamical time-scale separation. Europhys Lett 85:68006
Pierik R, Mommer L, Voesenek LA (2013) Molecular mechanisms of plant competition: neighbour detection and response strategies. Funct Ecol 27:841–853
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene databaseproject: improved data processing and web-based tools. NucleicAcids Res 41:D590–D596
Ragot SA, Kertesz MA, Mészáros É, Frossard E, Bünemann EK (2017) Soil phoD and phoX alkaline phosphatase gene diversity responds to multiple environmental factors. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93:fiw212
Rani U, Sharma S, Kumar V (2019) Bacillus species: a potential plant growth regulator in: slam MT, Rahman MM, Pandey P, Boehme MH, Haesaert G (Eds) bacilli and Agrobiotechnology: Phytostimulation and biocontrol (pp 29-47) springer, Cham
Rawat P, Das S, Shankhdhar D, Shankhdhar SC (2020) Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 30:1–20
Reena D, Tiwary BN (2014) Production of indole acetic acid by a novel bacterial strain of Planomicrobium chinense isolated from diesel oil contaminated site and its impact on the growth of Vigna radiata. Eur J Soil Biol 62:92–100
Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C (2009) Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:305–339
Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (2011) Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol 156:989–996
Saharan K, Schütz L, Kahmen A, Wiemken A, Boller T, Mathimaran N (2018) Finger millet growth and nutrient uptake is improved in intercropping with pigeon pea through “biofertilization” and “bioirrigation” mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Front Environ Sci 6:46
Sakurai M, Wasaki J, Tomizawa Y, Shinano T, Osaki M (2008) Analysis of bacterial communities on alkaline phosphatase genes in soil supplied with organic matter. Soil Sci Plant Nut 54:62–71
Salehi A, Mehdi B, Fallah S, Kaul HP, Neugschwandtner RW (2018) Productivity and nutrient use efficiency with integrated fertilization of buckwheat–fenugreek intercrops. Nut Cycl Agroecosys 110:407–425
Schneider KD, Thiessen Martens JR, Zvomuya F, Reid DK, Fraser TD, Lynch DH, O'Halloran IP, Wilson HF (2019) Options for improved phosphorus cycling and use in agriculture at the field and regional scales. J Environ Qual 48:1247–1264
Schöler A, Jacquiod S, Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schloter M (2017) Analysis of soil microbial communities based on amplicon sequenc-ing of marker genes. Biol Fertil Soils 53:485–489
Semchenko M, Lepik A, Abakumova M, Zobel K (2018) Different sets of belowground traits predict the ability of plant species to suppress and tolerate their competitors. Plant Soil 424:157–169
Seshachala U, Tallapragada P (2012) Phosphate solubilizers from the rhizosphere of piper nigrum l in Karnataka. India Chil J Agric Res 72:397–403
Simpson RJ, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE (2011) Strategies and agronomic interventions to improve the phosphorus-use efficiency of farming systems. Plant Soil 349:89–120
Smith SE, Jakobsen I, Grønlund M, Smith FA (2011) Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant phosphorus nutrition: interactions between pathways of phosphorus uptake in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots have important implications for understanding and manipulating plant phosphorus acquisition. Plant Physiol 156:1050–1057
Song YY, Simard SW, Carroll A, Mohn WW, Zeng RS (2015) Defoliation of interior Douglas-fir elicits carbon transfer and stress signalling to ponderosa pine neighbors through ectomycorrhizal networks. Sci Rep 5:1–9
Tang X, Placella SA, Daydé F, Bernard L, Robin A, Journet EP, Justes E, Hinsinger P (2016) Phosphorus availability and microbial community in the rhizosphere of intercropped cereal and legume along a P-fertilizer gradient. Plant Soil 407:119–134
Tian H, Wang H, Hui X, Wang Z, Drijber RA, Liu J (2017) Changes in soil microbial communities after 10 years of winter wheat cultivation versus fallow in an organic-poor soil in the loess plateau of China. PLoS One 12:e0184223
Tringovska I, Yankova V, Markova D, Mihov M (2015) Effect of companion plants on tomato greenhouse production. Sci Hort 186:31–37
Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schöler A, Schloter M (2017) Making big datasmart—how to use metagenomics to understand soil quality. Biol Fertil Soils 53:479–484
Vranova V, Rejsek K, Skene KR, Janous D, Formanek P (2013) Methods of collection of plant root exudates in relation to plant metabolism and purpose: a review. J Plant Nut Soil Sci 176:175–199
Wakelin S, Mander C, Gerard E, Jansa J, Erb A, Young S, Condron L, O’Callaghan M (2012) Response of soil microbial communities to contrasted histories of phosphorus fertilisation in pastures. App Soil Ecol 61:40–48
Wang P, Chen B, Zhang H (2017) High throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial communities in soils of a typical Poyang Lake wetland. Acta Ecol Sin 37:1650–1658
Widmer TL, Graham JH, Mitchell DJ (1998) Histological comparison of fibrous root infection of disease-tolerant and susceptible citrus hosts by Phytophthora nicotianae and P palmivora. Phytopathology 88:389–395
Wu X, Wu F, Zhou X, Fu X, Tao Y, Xu W, Pan K, Liu S (2016) Effects of intercropping with potato onion on the growth of tomato and rhizosphere alkaline phosphatase genes diversity. Front Plant Sci 7:846
Xue L, Ren H, Li S, Leng X, Yao X (2017) Soil bacterial community structure and co-occurrence pattern during vegetation restoration in karst rocky desertification area. Front Microbiol 8:2377
Yu H, Chen S, Zhang X, Zhou X, Wu F (2019) Rhizosphere bacterial community in watermelon-wheat intercropping was more stable than in watermelon monoculture system under Fusarium oxysporum f sp niveum invasion. Plant Soil 445:369–381
Yuan J, Tan X, Ye S, Zhou N, Shi B (2013) The organic acids in root exudates of oiltea and its role in mobilization of sparingly soluble phosphate in red soil. J Chem Pharm Res 5:572–577
Zhang D, Zhang C, Tang X, Li H, Zhang F, Rengel Z, Davies WJ, Shen J (2016) Increased soil phosphorus availability induced by faba bean root exudation stimulates root growth and phosphorus uptake in neighbouring maize. New Phytol 209:823–831
Zhang NN, Sun YM, Wang ET, Yang JS, Yuan HL, Scow KM (2015) Effects of intercropping and Rhizobial inoculation on the ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in rhizospheres of maize and faba bean plants. Appl Soil Ecol 85:76–85
Zhao R, Feng J, Yin X, Liu J, Fu W, Berendonk TU, Zhang T, Li X, Li B (2018) Antibiotic resistome in landfill leachate from different cities of China deciphered by metagenomic analysis. Water Res 134:126–139
Zhao K, Penttinen P, Zhang X, Ao X, Liu M, Yu X, Chen Q (2014) Maize rhizosphere in Sichuan, China, hosts plant growth promoting Burkholderia cepacia with phosphate solubilizing and antifungal abilities. Microbiol Res 169:76–82
Zhou X, Liu J, Wu F (2017) Soil microbial communities in cucumber monoculture and rotation systems and their feedback effects on cucumber seedling growth. Plan Soil 415:50–520
Zhou X, Wu F (2018) Vanillic acid changed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L) seedling rhizosphere total bacterial, Pseudomonas and Bacillus spp communities. Sci Rep 8:1–11
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD1000800) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072655).
Code availability
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not Applicable.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Andrea Schnepf
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khashi u Rahman, M., Wang, X., Gao, D. et al. Root exudates increase phosphorus availability in the tomato/potato onion intercropping system. Plant Soil 464, 45–62 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04935-8