Abstract
Background and aims
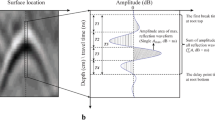
Root zone soil moisture is an important component in water cycling through the soil-plant-atmosphere continuum. However, its measurement in the field remains a challenge, especially non-invasively and repeatedly. Here, we developed a new method that uses ground-penetrating radar (GPR) to quantify root zone soil moisture.
Methods
Coarse roots were chosen as reflectors to collect GPR radargrams. An automatic hyperbola detection algorithm identified coarse root reflections in GPR radargrams and determined the velocity of GPR wave, which then was used to calculate the average soil water content of a soil profile (ASWC) and soil water content in a depth interval (ISWC). In total, GPR reflection data of 55 root samples from three computer simulation scenarios and two field experiments in sandy shrubland, one burying roots at known depths and the other under the undisturbed condition, were used to evaluate the proposed method.
Results
Both the simulated and the field collected data demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method for measuring root zone soil moisture with high accuracy. Even in the two field experiments, the root-mean-square errors of the estimated ASWC and ISWC relative to measurements from soil cores were as low as 0.003 and 0.012 m3·m−3, respectively.
Conclusion
The proposed method offers a new way of quantifying root zone soil moisture non-invasively that allows repeated measurements. This study expands the application of GPR in root and soil study and enhances our ability to monitor plant-soil-water interactions.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GPR:
-
ground-penetrating radar
- ASWC:
-
average soil water content of a soil profile
- ISWC:
-
soil water content of a depth interval
- ROI:
-
region of interest
- RMSE:
-
root-mean-square error
References
Annan P (2003) Ground Penetrating Radar: Principles, Procedures & Applications. Sensors & Software Inc., Mississauga
Butnor JR, Doolittle JA, Johnsen KH, Samuelson L, Stokes T, Kress L (2003) Utility of ground-penetrating radar as a root biomass survey tool in forest systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:1607–1615. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2003.1607
Cao X, Liu Y, Cui X, Chen J, Chen X (2018) Mechanisms, monitoring and modeling of shrub encroachment into grassland: a review. Int J Digital Earth:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2018.1478004
Collins DBG, Bras RL (2007) Plant rooting strategies in water-limited ecosystems. Water Resour Res 43:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006wr005541
Cui X, Chen J, Shen JS, Cao X, Chen XH, Zhu XL (2011) Modeling tree root diameter and biomass by ground-penetrating radar. Sci China Earth Sci 54:711–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-4103-z
Cui X, Guo L, Chen J, Chen X, Zhu X (2013) Estimating tree-root biomass in different depths using ground-penetrating radar: evidence from a controlled experiment. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51:3410–3423. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2012.2224351
Das NN, Mohanty BP (2006) Root zone soil moisture assessment using remote sensing and vadose zone modeling. Vadose Zone J 5:296–307. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2005.0033
Giannopoulos A (2005) Modelling ground penetrating radar by gprmax. Constr Build Mater 19:755–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.06.007
Grote K, Hubbard S, Rubin Y (2002) GPR monitoring of volumetric water content in soils applied to highway construction and maintenance. Lead Edge 21:482–504. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1481259
Guo L, Lin H (2016) Critical zone research and observatories: current status and future perspectives. Vadose Zone J 15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2016
Guo L, Lin H (2018) Addressing two bottlenecks to advance the understanding of preferential flow in soils. Adv Agron 147:61–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2017.10.002
Guo L, Chen J, Cui X, Fan B, Lin H (2013a) Application of ground penetrating radar for coarse root detection and quantification: a review. Plant Soil 362:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1455-5
Guo L, Lin H, Fan B, Cui X, Chen J (2013b) Impact of root water content on root biomass estimation using ground penetrating radar: evidence from forward simulations and field controlled experiments. Plant Soil 371:503–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1710-4
Guo L, Lin H, Fan B, Cui X, Chen J (2013c) Forward simulation of root’s ground penetrating radar signal: simulator development and validation. Plant Soil 372:487–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1751-8
Guo L, Chen J, Lin H (2014) Subsurface lateral flow network on a hillslope revealed by time-lapse ground penetrating radar. Water Resour Res 50:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR014603
Guo L, Wu Y, Chen J, Hirano Y, Tanikawa T, Li W, Cui X (2015) Calibrating the impact of root orientation on root quantification using ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 395:289–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2563-9
Hirano Y, Dannoura M, Aono K, Igarashi T, Ishii M, Yamase K, Makita N, Kanazawa Y (2009) Limiting factors in the detection of tree roots using ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 319:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9845-4
Hruška J, Čermák J, Sustek S (1999) Mapping tree root systems with ground-penetrating radar. Tree Physiol 19:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/19.2.125
Huisman JA, Snepvangers J, Bouten W, Heuvelink G (2002) Mapping spatial variation in surface soil water content: comparison of ground-penetrating radar and time domain reflectometry. J Hydrol 269:194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(02)00239-1
Huisman JA, Hubbard SS, Redman JD, Annan AP (2003) Measuring soil water content with ground penetrating radar. Vadose Zone J 2:476–491. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2003.0476
Klenk P, Jaumann S, Roth K (2015) Quantitative high-resolution observations of soil water dynamics in a complicated architecture using time-lapse ground-penetrating radar. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:1125–1139. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-1125-2015
Kumar SV, Dirmeyer PA, Peters-Lidard CD, Bindlish R, Bolten J (2018) Information theoretic evaluation of satellite soil moisture retrievals. Remote Sens Environ 204:392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.10.016
Li W, Cui X, Guo L, Chen J, Chen X, Cao X (2016) Tree root automatic recognition in ground penetrating radar profiles based on randomized hough transform. Remote Sens (Basel) 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8050430
Liu X, Chen J, Cui X, Liu Q, Cao X, Chen X (2017) Measurement of soil water content using ground-penetrating radar: a review of current methods. Int J Digital Earth:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2017.1412520
Loeffler O, Bano M (2004) Ground penetrating radar measurements in a controlled. Vadose Zone J 3:1082–1092. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2004.1082
Lu Y, Song W, Lu J, Wang X, Tan Y (2017) An examination of soil moisture estimation using ground penetrating radar in desert steppe. Water 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070521
Lunt IA, Hubbard SS, Rubin Y (2005) Soil moisture content estimation using ground-penetrating radar reflection data. J Hydrol 307:254–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.10.014
Norman JM, Anderson MC (2005) Soil-plant-atmosphere continum. In: Hillel D (ed) Encyclopedia of soils in the environment. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-12-348530-4/00416-1
Polak A, Wallach R (2001) Analysis of soil moisture variations in an irrigated orchard root zone. Plant Soil 233:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010351101314
Rial FI, Pereira M, Lorenzo H, Arias P, Novo A (2009) Resolution of GPR bowtie antennas: an experimental approach. J Appl Geophys 67:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.05.003
Robinson DA, Binley A, Crook N, Day-Lewis FD, Ferré TPA, Grauch VJS, Knight R, Knoll M, Lakshmi V, Miller R, Nyquist J, Pellerin L, Singha K, Slater L (2008a) Advancing process-based watershed hydrological research using near-surface geophysics: a vision for, and review of, electrical and magnetic geophysical methods. Hydrol Process 22:3604–3635. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6963
Robinson DA, Campbell CS, Hopmans JW, Hornbuckle BK, Jones SB, Knight R, Ogden F, Selker J, Wendroth O (2008b) Soil moisture measurement for ecological and hydrological watershed-scale observatories: a review. Vadose Zone J 7:358–389. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2007.0143
Romano N (2014) Soil moisture at local scale: measurements and simulations. J Hydrol 516:6–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.01.026
Schenk HJ, Jackson RB (2002) Rooting depths, lateral spreads, and below-ground/above-ground allometries of plants in water-limited ecosystems. J Ecol 90:480–494. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2745.2002.00682.x
Simi A, Bracciali S, Manacorda G (2008) Hough transform based automatic pipe detection for array GPR: Algorithm development and on-site tests. In: Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome Italy pp:1545–1550. https://doi.org/10.1109/radar.2008.4720763
Steelman CM, Endres AL (2011) Comparison of petrophysical relationships for soil moisture estimation using GPR ground waves. Vadose Zone J 10:270–285. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2010.0040
Steelman CM, Endres AL (2012) Assessing vertical soil moisture dynamics using multi-frequency GPR common-midpoint soundings. J Hydrol 436:51–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.041
Stoffregen H, Zenker T, Wessolek G (2002) Accuracy of soil water content measurements using ground penetrating radar: comparison of ground penetrating radar and lysimeter data. J Hydrol 267:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00150-6
Teuling AJ, Uijlenhoet R, Hupet F, van Loon EE, Troch PA (2006) Estimating spatial mean root-zone soil moisture from point-scale observations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 10:755–767. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-10-755-2006
Topp GC, Davis JL, Annan AP (1980) Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour Res 16:574–582. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR016i003p00574
Tran AP, Bogaert P, Wiaux F, Vanclooster M, Lambot S (2015) High-resolution space-time quantification of soil moisture along a hillslope using joint analysis of ground penetrating radar and frequency domain reflectometry data. J Hydrol 523:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.065
Tzanis A (2010) matGPR release 2: a freeware MATLAB® package for the analysis & interpretation of common and single offset GPR data. FastTimes 15:17–43
Van Auken OW (2009) Causes and consequences of woody plant encroachment into western north American grasslands. J Environ Manag 90:2931–2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.023
van Overmeeren RA, Sariowan SV, Gehrels JC (1997) Ground penetrating radar for determining volumetric soil water content: results of comparative measurements at two test sites. J Hydrol 197:316–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(96)03244-1
Vereecken H, Huisman JA, Bogena H, Vanderborght J, Vrugt JA, Hopmans JW (2008) On the value of soil moisture measurements in vadose zone hydrology: a review. Water Resour Res 44:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR006829
Vereecken H, Huisman JA, Pachepsky Y, Montzka C, van der Kruk J, Bogena H, Weihermüller L, Herbst M, Martinez G, Vanderborght J (2014) On the spatio-temporal dynamics of soil moisture at the field scale. J Hydrol 516:76–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.061
Weiler KW, Steenhuis TS, Boll J, Kung K (1998) Comparison of ground penetrating radar and time-domain reflectometry as soil water sensors. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:1237–1239. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1998.03615995006200050013x
Windsor CG, Capineri L, Falorni P (2005) The estimation of buried pipe diameters by generalized hough transform of radar data. Piers Online 1:345–349. https://doi.org/10.2529/PIERS041117130829
Wollschläger U, Roth K (2005) Estimation of temporal changes of volumetric soil water content from ground-penetrating radar reflections. Subsurf Sens Technol Appl 6:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11220-005-0007-y
Wu Y, Guo L, Cui X, Chen J, Lin H (2014) Ground-penetrating radar-based automatic reconstruction of three-dimensional coarse root system architecture. Plant Soil 383:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2139-0
Xu L (2005) A5 problem solving paradigm: a unified perspective and new results on RHT computing, mixture based learning, and evidence combination. In: IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing, Beijing China, pp 70–77
Xu L, Oja E (1993) Randomized Hough transform (RHT): basic mechanisms, algorithms, and complexities. CVGIP Image Underst 57:131–154. https://doi.org/10.1006/cviu.1993.1009
Xu L, Oja E, Kultanen P (1990) A new curve detection method randomized Hough transform (RHT). Pattern Recogn Lett 11:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8655(90)90042-Z
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41571404) on project of State Key Laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Peter J. Gregory.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 128 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Cui, X., Guo, L. et al. Non-invasive estimation of root zone soil moisture from coarse root reflections in ground-penetrating radar images. Plant Soil 436, 623–639 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-03919-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-03919-5