Abstract
Background and Aims
Many recent studies examining aluminum (Al) toxicity have failed to consider its complex chemistry, thereby leading to erroneous results.
Methods
Using modelling and experimental approaches, we focussed on the key effects of pH, P, and ionic strength on Al in nutrient solutions and resultant root elongation rate (RER) of soybean (Glycine max).
Results
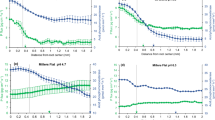
A review of the literature showed that the composition of nutrient solutions (ionic strength =3 to 26 mM) in many studies differs markedly from solutions (mean ionic strength =5 mM) extracted from acid soils. Nutrient solutions should have a pH ≤ 4.5 to ensure that Al remains soluble and that the toxic Al3+ ion is the dominant species. Solutions should contain ≤5 μM P to ensure that Al is not precipitated and should have an ionic strength of < ca. 5 mM. Finally, we have shown that soybean RER is more closely related to the activity of Al3+ at the outer surface of the root-cell plasma membrane than its activity in the bulk solution.
Conclusions
This study has highlighted the crucial consideration of the kinetic and thermodynamic chemistry of Al in experiments designed to study the rhizotoxic effects of Al.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams F (1966) Calcium deficiency as a causal agent of ammonium phosphate injury to cotton seedlings. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 30:485–488
Adams F, Lund ZF (1966) Effect of chemical activity of soil solution aluminum on cotton root penetration of acid subsoils. Soil Sci 101:193–198
Adams ML, Hawke DJ, Nilsson NHS, Powell KJ (2000) The relationship between soil solution pH and Al3+concentrations in a range of South Island (New Zealand) soils. Soil Res 38:141–154
Alvarez E, Martinez A, Calvo R (1992) Geochemical aspects of aluminium in forest soils in Galicia (N.W. Spain). Biogeochemistry 16:167–180
An Y, Zhou P, Xiao Q, Shi D (2014) Effects of foliar application of organic acids on alleviation of aluminum toxicity in alfalfa. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 177:421–430
Asher CJ (1981) Limiting external concentrations of trace elements for plant growth: use of flowing solution culture techniques. J Plant Nutr 3:163–180
Asher CJ, Edwards DG (1983) Modern solution culture techniques. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology: inorganic plant nutrition. Eds. A Lauchli and R L Bieleski. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 94–119
Bertsch PM (1987) Conditions for Al13 polymer formation in partially neutralized aluminum solutions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:825–828
Bertsch PM, Parker DR (1996) Aqueous polynuclear aluminum species. In: Sposito G (ed) In The Environmental Chemistry of Aluminum. CRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, p. 464
Blamey FPC, Hernandez-Soriano MC, Cheng M, Tang C, Paterson DJ, Lombi E, Wang WH, Scheckel KG, Kopittke PM (2015) Synchrotron-based techniques shed light on mechanisms of plant sensitivity and tolerance to high manganese in the root environment. Plant Physiol 169:2006–2020
Bruce RC, Warrell LA, Edwards DG, Bell LC (1988) Effects of aluminium and calcium in the soil solution of acid soils on root elongation of Glycine max cv. Forrest. Aust J Agric Res 39:319–338
Büyükkeskin T, Akinci Ş, Eroğlu AE (2014) Effects of humic acid on root development and nutrient uptake of Vicia faba L. (broad bean) seedlings grown under aluminum toxicity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 46:277–292
Cocker KM, Evans DE, Hodson MJ (1998) The amelioration of aluminium toxicity by silicon in higher plants: solution chemistry or an in planta mechanism? Physiol Plant 104:608–614
Delhaize E, Ryan PR (1995) Aluminum toxicity and tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol 107:315–321
Eswaran H, Reich P, Beinroth F (1997) Global distribution of soils with acidity. In: Plant-soil interactions at low pH. Ed. A C Moniz. Brazilian Soil Science Society, Sao Paulo, pp. 159–164
Goldbach HE, Yu Q, Wingender R, Schulz M, Wimmer M, Findeklee P, Baluska F (2001) Rapid response reactions of roots to boron deprivation. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 164:173–181
Hagvall K, Persson P, Karlsson T (2015) Speciation of aluminum in soils and stream waters: the importance of organic matter. Chem Geol 417:32–43
Heinrichs H, Böttcher G, Brumsack H-J, Pohlmann M (1996) Squeezed soil-pore solutes - a comparison to lysimeter samples and percolation experiments. Water Air Soil Pollut 89:189–204
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agricultural Experiment Station Circular 347, University of California, Berkeley, p. 31
Horst WJ, Göppel H (1986) Aluminium-toleranz von ackerbohne (Vicia faba), lupine (Lupinus luteus), gerste (Hordeum vulgare) und roggen (Secale cereale). I. Sproß- und wurzelwachstum in abhängigkeit vom aluminium-angebot. Z Pflanz Bodenkunde 149:83–93
Horst WJ, Wang Y, Eticha D (2010) The role of the root apoplast in aluminium-induced inhibition of root elongation and in aluminium resistance of plants: a review. Ann Bot 106:185–197
Islam AKMS, Edwards DG, Asher CJ (1980) pH optima for crop growth. Plant Soil 54:339–357
Kerven GL, Larsen PL, Blamey FPC (1995) Detrimental sulfate effects on formation of Al-13 tridecameric polycation in synthetic soil solutions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:765–771
Kinraide TB (1991) Identity of the rhizotoxic aluminum species. Plant Soil 134:167–178
Kinraide TB (2006) Plasma membrane surface potential (ψPM) as a determinant of ion bioavailability: a critical analysis of new and published toxicological studies and a simplified method for the computation of plant ψPM. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:3188–3198
Kinraide TB, Parker DR (1987) Non-phytotoxicity of the aluminum sulfate ion, AlSO4 +. Physiol Plant 71:207–212
Kinraide TB, Parker DR (1989) Assessing the phytotoxicity of mononuclear hydroxy-aluminum. Plant Cell Environ 12:479–488
Kinraide TB, Wang P (2010) The surface charge density of plant cell membranes (σ): an attempt to resolve conflicting values for intrinsic σ. J Exp Bot 61:2507–2518
Kinraide TB, Arnold RC, Baligar VC (1985) A rapid assay for aluminium phytotoxicity at submicromolar concentrations. Physiol Plant 65:245–250
Kopittke PM, Blamey FPC, Kinraide TB, Wang P, Reichman SM, Menzies NW (2011) Separating multiple, short-term deleterious effects of saline solutions to the growth of cowpea seedlings. New Phytol 189:1110–1121
Kopittke PM, Wang P, Menzies NW, Naidu R, Kinraide TB (2014) A web-accessible computer program for calculating electrical potentials and ion activities at cell-membrane surfaces. Plant Soil 375:35–46
Kopittke PM, Moore KL, Lombi E, Gianoncelli A, Ferguson BJ, Blamey FPC, Menzies NW, Nicholson TM, McKenna BA, Wang P, Gresshoff PM, Kourousias G, Webb RI, Green K, Tollenaere A (2015) Identification of the primary lesion of toxic aluminum (Al) in plant roots. Plant Physiol 167:1402–1411
Koyama H, Toda T, Yokota S, Dawair Z, Hara T (1995) Effects of aluminum and pH on root growth and cell viability in Arabidopsis thaliana strain landsberg in hydroponic culture. Plant Cell Physiol 36:201–205
Larsen PL, Kerven GL, Bell LC, Edwards DG (1995) Effects of silicic acid on the chemistry of monomeric and polymeric (Al13) aluminium species in solutions. In: Plant-soil interactions at low pH: principles and management. Eds. R a date, N J Grundon, G E Rayment and M E Probert. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, pp. 617–621
Lindsay WL (1979) Chemical equilibria in soils. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA, p. 449
Magistad OC (1925) The aluminum content of the soil solution and its relation to soil reaction and plant growth. Soil Sci 20:181–225
Manoharan V, Loganathan P, Tillman RW, Parfitt RL (2007) Interactive effects of soil acidity and fluoride on soil solution aluminium chemistry and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) root growth. Environ Pollut 145:778–786
Menzies NW, Bell LC, Edwards DG (1994a) Exchange and solution-phase chemistry of acid, highly weathered soils. 2. Investigation of mechanisms controlling Al release into solution. Aust J Soil Res 32:269–283
Menzies NW, Edwards DG, Bell LC (1994b) Effects of calcium and aluminium in the soil solution of acid, surface soils on root elongation of mungbean. Aust J Soil Res 32:721–737
Miyasaka SC, Hue NV, Dunn MA (2006) Aluminum. In: Handbook of plant nutrition. Eds. A barker and D J Pilbeam. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, pp. 439–497
Nordstrom DK, May HM (1996) Aqueous equilibrium data for mononuclear aluminum species. In: Sposito G (ed) The environmental chemistry of aluminum. CRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp. 39–80
Oh M, Roy S, Kamal A, Cho K, Cho S-W, Park C-S, Choi J-S, Komatsu S, Woo S-H (2014) Proteome analysis of roots of wheat seedlings under aluminum stress. Mol Biol Rep 41:671–681
Oulehle F, Hruška J (2005) Tree species (Picea abies and Fagus sylvatica) effects on soil water acidification and aluminium chemistry at sites subjected to long-term acidification in the Ore Mts., Czech Republic. J Inorg Biochem 99:1822–1829
Parker DR, Norvell WA (1999) Advances in solution culture methods for plant mineral nutrition research. Adv Agron 65:151–213
Parkhurst D (2014) PhreeqcI v3.1.7. United States Geological Survey. http://water.usgs.gov/software/ (Accessed December 2014).
Rehmus A, Bigalke M, Valarezo C, Castillo J, Wilcke W (2015) Aluminum toxicity to tropical montane forest tree seedlings in Southern Ecuador. Plant Soil 388:87–97
Reisenauer HM (1966) Mineral nutrients in soil solution. In: Environmental biology. Eds. P L Altman and D S Dittmer. Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Bethesda, MD, pp. 507–508
Schneider C, Doucet F, Strekopytov S, Exley C (2004) The solubility of an hydroxyaluminosilicate. Polyhedron 23:3185–3191
Shaff JE, Schultz BA, Craft EJ, Clark RT, Kochian LV (2010) GEOCHEM-EZ: a chemical speciation program with greater power and flexibility. Plant Soil 330:207–214
Shen X, Xiao X, Dong Z, Chen Y (2014) Silicon effects on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of peanut under aluminum stress. Acta Physiol Plant 36:3063–3069
Sposito G (ed) (1996) The environmental chemistry of aluminum. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, p. 480
Taylor GJ, Stadt KJ, Dale MRT (1991) Modeling the phytotoxicity of aluminum, cadmium, copper, manganese, nickel, and zinc using the Weibull frequency-distribution. Can J Bot 69:359–367
Tokizawa M, Kobayashi Y, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Iuchi S, Nomoto M, Tada Y, Yamamoto YY, Koyama H (2015) Sensitive to proton rhizotoxicity1, calmodulin binding transcription activator2, and other transcription factors are involved in aluminum-activated malate transporter1 expression. Plant Physiol 167:991–1003
Wheeler DM, Edmeades DC (1995) Effect of depth and lime or phosphorus-fertilizer applications on the soil solution chemistry of some New Zealand pastoral soils. Aust J Soil Res 33:461–476
Wheeler DM, Edmeades DC, Christie RA, Gardner R (1992) Effect of aluminium on the growth of 34 plant species: a summary of results obtained in low ionic strength solution culture. Plant Soil 146:61–66
Yang M, Tan L, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Cheng F, Ye S, Jiang W (2015) Effect of low pH and aluminum toxicity on the photosynthetic characteristics of different fast-growing Eucalyptus vegetatively propagated clones. PLoS ONE 10, e0130963.
Zhang HH, Jiang Z, Qin R, Zhang HN, Zou JH, Jiang WS, Liu DH (2014) Accumulation and cellular toxicity of aluminum in seedling of Pinus massoniana. BMC Plant Biol 14
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Australian Research Council (ARC) Future Fellowship (FT120100277 to P.M.K.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Juan Barcelo.
Electronic Supplementary Materials
ESM 1
(PDF 264 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopittke, P.M., Blamey, F.P.C. Theoretical and experimental assessment of nutrient solution composition in short-term studies of aluminium rhizotoxicity. Plant Soil 406, 311–326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2890-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2890-5