Abstract
Background and aims
Drought is predicted to have a profound impact on soil respiration. This study aimed to assess the effects of long-term precipitation decrease on soil respiration in a tropical rainforest.
Methods
A precipitation reduction experiment was conducted in a tropical forest in southwest China at the beginning of 2011. Soil respiration and environmental parameters were measured monthly for three years.
Results
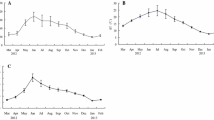
The continuous precipitation reduction treatment did not affect the seasonal patterns of soil respiration, but it significantly increased soil respiration in the study plot during the rainy season, and the relationship between soil respiration and soil moisture differed in the control and reduction treatment in the rainy season. Compared with the net ecosystem exchange of carbon in this system, the increment of annual soil carbon emissions in the reduction treatment was considerable and should not be ignored.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that the responses of soil respiration to precipitation decrease may vary seasonally and the variation of volumetric water content in different seasons may be an important factor leading to the seasonal variation. The variation of soil moisture among different ecosystems as well as in different seasons should be taken into consideration when predicting the future response of soil respiration to drought globally.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balser TC, Wixon DL (2009) Investigating biological control over soil carbon temperature sensitivity. Glob Chang Biol 15:2935–2949
Birch H (1958) The effect of soil drying on humus decomposition and nitrogen availability. Plant Soil 10:9–31
Borken W, Savage K, Davidson EA, Trumbore SE (2006) Effects of experimental drought on soil respiration and radiocarbon efflux from a temperate forest soil. Glob Chang Biol 12:177–193
Bouma TJ, Bryla DR (2000) On the assessment of root and soil respiration for soils of different textures: interactions with soil moisture contents and soil CO2 concentrations. Plant Soil 227:215–221
Bouskill NJ, Lim HC, Borglin S, Salve R, Wood TE, Silver WL, Brodie EL (2013) Pre-exposure to drought increases the resistance of tropical forest soil bacterial communities to extended drought. Isme J 7:384–394
Cao M, Zhang J, Feng Z, Deng J, Deng X (1996) Tree species composition of a seasonal rain forest in Xishuangbanna, southwest China. Trop Ecol 37:183–192
Cattanio JH, Davidson EA, Nepstad DC, Verchot LV, Ackerman IL (2002) Unexpected results of a pilot throughfall exclusion experiment on soil emissions of CO2, CH4, N2O, and NO in eastern Amazonia. Biol Fertil Soils 36:102–108
Chambers JQ, Tribuzy ES, Toledo LC, Crispim BF, Higuchi N, Jd S, Araujo AC, Kruijt B, Nobre AD, Trumbore SE (2004) Respiration from a tropical forest ecosystem: partitioning of sources and low carbon use efficiency. Ecol Appl 14:72–88
Cleveland CC, Wieder WR, Reed SC, Townsend AR (2010) Experimental drought in a tropical rain forest increases soil carbon dioxide losses to the atmosphere. Ecology 91:2313–2323
Cox PM, Betts RA, Jones CD, Spall SA, Totterdell IJ (2000) Acceleration of global warming due to carbon-cycle feedbacks in a coupled climate model. Nature 408:184–187
Davidson EA, Trumbore SE (1995) Gas diffusivity and production of CO2 in deep soils of the eastern Amazon. Tellus Ser B Chem Phys Meteorol 47:550–565
Davidson EA, Belk E, Boone RD (1998) Soil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest. Glob Chang Biol 4:217–227
Davidson EA, Nepstad DC, Ishida FY, Brando PM (2008) Effects of an experimental drought and recovery on soil emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and nitric oxide in a moist tropical forest. Glob Chang Biol 14:2582–2590
Edwards NT (1975) Effects of temperature and moisture on carbon dioxide evolution in a mixed deciduous forest. Soil Sci Soc Am J 39:361–365
Hall SJ, McDowell WH, Silver WL (2013) When wet gets wetter: decoupling of moisture, redox biogeochemistry, and greenhouse gas fluxes in a humid tropical forest soil. Ecosystems 16:576–589
Hanson PJ, Edwards NT, Garten CT, Andrews JA (2000) Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: a review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry 48:115–146
Jassal RS, Black TA, Novak MD, Gaumont-Guay D, Nesic Z (2008) Effect of soil water stress on soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity in an 18-year-old temperate Douglas-fir stand. Glob Chang Biol 14:1305–1318
Jiang H, Deng Q, Zhou G, Hui D, Zhang D, Liu S, Chu G, Li J (2013) Responses of soil respiration and its temperature/moisture sensitivity to precipitation in three subtropical forests in southern China. Biogeosciences 10:3963–3982
Jones CD, Cox P, Huntingford C (2003) Uncertainty in climate-carbon-cycle projections associated with the sensitivity of soil respiration to temperature. Tellus Ser B Chem Phys Meteorol 55:642–648
Keith H, Jacobsen KL, Raison RJ (1997) Effects of soil phosphorus availability, temperature and moisture on soil respiration in Eucalyptus pauciflora forest. Plant Soil 190:127–141
Kirtman B, Power SB, Adedoyin JA, Boer GJ, Bojariu R, Camilloni I, Doblas-Reyes FJ, Fiore AM, Kimoto M, Meehl GA, Prather M, Sarr A, Schär C, Sutton R, van Oldenborgh GJ, Vecchi G, Wang HJ (2013) Near-term climate change: projections and predictability. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 953–1028
Kuzyakov Y (2006) Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods. Soil Biol Biochem 38:425–448
Linn D, Doran J (1984) Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and nontilled soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1267–1272
Liu WH, Zhang YP, Li HM, Liu YH (2005) Fog drip and its relation to groundwater in the tropical seasonal rain forest of Xishuangbanna, Southwest China: a preliminary study. Water Res 39:787–794
Londo AJ, Messina MG, Schoenholtz SH (1999) Forest harvesting effects on soil temperature, moisture, and respiration in a bottomland hardwood forest. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63:637–644
Luo YQ (2007) Terrestrial carbon-cycle feedback to climate warming. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38:683–712
Millingt RJ, Shearer RC (1971) Diffusion in aggregated porous media. Soil Sci 111:372–378
Qi Y, Xu M (2001) Separating the effects of moisture and temperature on soil CO2 efflux in a coniferous forest in the Sierra Nevada mountains. Plant Soil 237:15–23
Raich JW, Potter CS, Bhagawati D (2002) Interannual variability in global soil respiration, 1980–94. Glob Chang Biol 8:800–812
Schimel DS, House JI, Hibbard KA, Bousquet P, Ciais P, Peylin P, Braswell BH, Apps MJ, Baker D, Bondeau A, Canadell J, Churkina G, Cramer W, Denning AS, Field CB, Friedlingstein P, Goodale C, Heimann M, Houghton RA, Melillo JM, Moore B, Murdiyarso D, Noble I, Pacala SW, Prentice IC, Raupach MR, Rayner PJ, Scholes RJ, Steffen WL, Wirth C (2001) Recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon exchange by terrestrial ecosystems. Nature 414:169–172
Schwendenmann L, Veldkamp E (2006) Long-term CO2 production from deeply weathered soils of a tropical rain forest: evidence for a potential positive feedback to climate warming. Glob Chang Biol 12:1878–1893
Schwendenmann L, Veldkamp E, Moser G, Holscher D, Kohler M, Clough Y, Anas I, Djajakirana G, Erasmi S, Hertel D, Leitner D, Leuschner C, Michalzik B, Propastin P, Tjoa A, Tscharntke T, van Straaten O (2010) Effects of an experimental drought on the functioning of a cacao agroforestry system, Sulawesi, Indonesia. Glob Chang Biol 16:1515–1530
Sha LQ, Zheng Z, Tang JW, Wang YH, Zhang YP, Cao M, Wang R, Liu GG, Wang YS, Sun Y (2005) Soil respiration in tropical seasonal rain forest in Xishuangbanna, SW China. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 48:189–197
Silver WL, Lugo AE, Keller M (1999) Soil oxygen availability and biogeochemistry along rainfall and topographic gradients in upland wet tropical forest soils. Biogeochemistry 44:301–328
Singh JS, Gupta SR (1977) Plant decomposition and soil respiration in terrestrial ecosystems. Bot Rev 43:499–528
Skopp J, Jawson MD, Doran JW (1990) Steady-state aerobic microbial activity as a function of soil water content. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:1619–1625
Sotta ED, Veldkamp E, Schwendenmann L, Guimaraes BR, Paixao RK, Ruivo M, Da Costa ACL, Meir P (2007) Effects of an induced drought on soil carbon dioxide (CO2) efflux and soil CO2 production in an Eastern Amazonian rainforest, Brazil. Glob Chang Biol 13:2218–2229
Stevenson I (1956) Some observations on the microbial activity in remoistened air-dried soils. Plant Soil 8:170–182
Suseela V, Dukes JS (2013) The responses of soil and rhizosphere respiration to simulated climatic changes vary by season. Ecology 94:403–413
Suseela V, Conant RT, Wallenstein MD, Dukes JS (2012) Effects of soil moisture on the temperature sensitivity of heterotrophic respiration vary seasonally in an old-field climate change experiment. Glob Chang Biol 18:336–348
Tan ZH, Zhang YP, Yu GR, Sha LQ, Tang JW, Deng XB, Song QH (2010) Carbon balance of a primary tropical seasonal rain forest. J Geophys Res 115:D00h26. doi:10.1029/2009JD012913
Tian H, Melillo JM, Kicklighter DW, McGuire AD, Helfrich J, Moore B, Vorosmarty CJ (2000) Climatic and biotic controls on annual carbon storage in Amazonian ecosystems. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 9:315–335
Townsend AR, Cleveland CC, Houlton BZ, Alden CB, White JWC (2011) Multi-element regulation of the tropical forest carbon cycle. Front Ecol Environ 9:9–17
Valentini R, Matteucci G, Dolman AJ, Schulze ED, Rebmann C, Moors EJ, Granier A, Gross P, Jensen NO, Pilegaard K, Lindroth A, Grelle A, Bernhofer C, Grunwald T, Aubinet M, Ceulemans R, Kowalski AS, Vesala T, Rannik U, Berbigier P, Loustau D, Guomundsson J, Thorgeirsson H, Ibrom A, Morgenstern K, Clement R, Moncrieff J, Montagnani L, Minerbi S, Jarvis PG (2000) Respiration as the main determinant of carbon balance in European forests. Nature 404:861–865
Van Schreven D (1967) The effect of intermittent drying and wetting of a calcareous soil on carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Plant Soil 26:14–32
van Straaten O, Veldkamp E, Kohler M, Anas I (2010) Spatial and temporal effects of drought on soil CO2 efflux in a cacao agroforestry system in Sulawesi, Indonesia. Biogeosciences 7:1223–1235
van Straaten O, Veldkamp E, Corre MD (2011) Simulated drought reduces soil CO2 efflux and production in a tropical forest in Sulawesi, Indonesia. Ecosphere 2, art119
Wood TE, Silver WL (2012) Strong spatial variability in trace gasdynamics following experimental drought in a humid tropical forest. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 26:12. doi:10.1029/2010gb004014
Wood TE, Cavaleri MA, Reed SC (2012) Tropical forest carbon balance in a warmer world: a critical review spanning microbial- to ecosystem-scale processes. Biol Rev 87:912–927
Wood TE, Detto M, Silver WL (2013) Sensitivity of Soil Respiration to Variability in Soil Moisture and Temperature in a Humid Tropical Forest. Plos One 8:7. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080965
Yan J, Zhang Y, Yu G, Zhou G, Zhang L, Li K, Tan Z, Sha L (2013) Seasonal and inter-annual variations in net ecosystem exchange of two old-growth forests in southern China. Agric For Meteorol 182:257–265
Zhang YP, Tan ZH, Song QH, Yu GR, Sun XM (2010) Respiration controls the unexpected seasonal pattern of carbon flux in an Asian tropical rain forest. Atmos Environ 44:3886–3893
Zhou XH, Xiao ZN (2014) Climate projection over yunnan province and the surrounding regions based on CMIP5 data. Climatic Environ Res 19:601–613 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou XH, Sherry RA, An Y, Wallace LL, Luo YQ (2006) Main and interactive effects of warming, clipping, and doubled precipitation on soil CO2 efflux in a grassland ecosystem. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 20, GB1003
Zhou GY, Wei XH, Wu YP, Liu SG, Huang YH, Yan JH, Zhang DQ, Zhang QM, Liu JX, Meng Z, Wang CL, Chu GW, Liu SZ, Tang XL, Liu XD (2011) Quantifying the hydrological responses to climate change in an intact forested small watershed in Southern China. Glob Chang Biol 17:3736–3746
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers, Wenjun Zhou and Jing Zhu for comments and assistance in improving this manuscript. We also appreciate the members of the Global Change Ecology Group for their assistance with the collection of field data. This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (U1202234, 41271056, 41071071), the “Strategic Priority Research Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA05050601, XDA05050206) and the CAS 135 project (XTBG-F01). This work was also supported by Xishuangbanna Station for Tropical Rain Forest Ecosystem Studies and the Biogeochemistry Laboratory of the Public Technology Service Center of XTBG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eric Paterson.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(PDF 155 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Sha, L. et al. Effects of continuous drought stress on soil respiration in a tropical rainforest in southwest China. Plant Soil 394, 343–353 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2523-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2523-4