Abstract
Key message
Alternative translation initiation of the unique Arabidopsis trehalase gene allows for the production of two isoforms with different subcellular localization, providing enzyme access to both intra- and extra-cellular trehalose.
Abstract
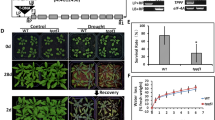
The trehalose-hydrolyzing enzyme trehalase mediates drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana by controlling ABA-induced stomatal closure. We now report the existence of two trehalase isoforms, produced from a single transcript by alternative translation initiation. The longer full-length N-glycosylated isoform (AtTRE1L) localizes in the plasma membrane with the catalytic domain in the apoplast. The shorter isoform (AtTRE1S) lacks the transmembrane domain and localizes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. The two isoforms can physically interact and this interaction affects localization of AtTRE1S. Consistent with their role in plant drought stress tolerance, both isoforms are activated by AtCPK10, a stress-induced calcium-dependent guard cell protein kinase. Transgenic plants expressing either isoform indicate that both can mediate ABA-induced stomatal closure in response to drought stress but that the short (cytoplasmic/nuclear) isoform, enriched in those conditions, is significantly more effective.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials are available upon request to the authors.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aebi M (2013) N-linked protein glycosylation in the ER. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:2430–2437
Besingi RN, Clark PL (2015) Extracellular protease digestion to evaluate membrane protein cell surface localization. Nat Protoc 10:2074–2080
Cheng S-H, Willmann WR, Chen H-C, Sheen J (2002) Calcium signaling through protein kinases. The Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase gene family. Plant Physiol 129:469–485
Corpet F (1988) Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10881–10890
DeFalco TA, Bender KW, Snedden WA (2009) Breaking the code: Ca2+ sensor in plant signaling. Biochem J 425:27–40
Durek P et al (2010) PhosPhAt: the Arabidopsis thaliana phosphorylation site database. An update. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D828–D834
Elbein AD, Pan YT, Pastuszak I, Carroll D (2003) New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology 13:17R-27R
Fichtner F, Lunn JE (2021) The role of trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) in plant metabolism and development. Annu Rev Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-095929
Fichtner F et al (2020) Functional features of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase1, an essential enzyme in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32:1949–1972
Fichtner F et al (2021) Regulation of shoot branching in arabidopsis by trehalose 6-phosphate. New Phytol 229:2135–2151
Frison M, Parrou JL, Guillaumot D, Masqeulier D, François J, Chaumont F, Batoko H (2007) The Arabidopsis thaliana trehalase is a plasma membrane-bound enzyme with extracellular activity. FEBS Lett 581:4010–4016
Garapati P, Feil R, Lunn JE, Van Dijck P, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B (2015) Transcription factor Arabidopsis activating Factor1 integrates carbon starvation responses with trehalose metabolism. Plant Physiol 169:379–390
Gietz RD, Schliestl RH, Willems AR, Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 11:355–360
Gómez LD, Gilday A, Feil R, Lunn JE, Graham IA (2010) AtTPS1-mediated trehalose 6-phosphate synthesis is essential for embryogenic and vegetative growth and responsiveness to ABA in germinating seeds and stomatal guard cells. Plant J 64:1–13
Gupta R, Jung E, Brunak S (2004) Prediction of N-glycosylation sites in human proteins. Available at http://www.cbsdtudk/services/NetNGlyc/
Heazlewood JL, Durek P, Hummel J, Selbig J, Weckwerth W, Walther D, Schulze WX (2008) PhoPhAt: a database of phosphorylation sites in Arabidopsis thaliana and a plant-specific phosphorylation site predictor. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D1015–D1021
Helenius A, Aebi M (2001) Intracellular functions of N-linked glycans. Science 291:2364–2369
Kataya ARA, Elshobaky A, Heidari B, Dugassa NF, Thelen JJ, Lillo C (2020) Multi-targeted trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase I harbors a novel peroxisomal targeting signal 1 and is essential for flowering and development. Planta 251:98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03389-z
Klimecka M, Muszyńska G (2007) Structure and functions of plant calcium-dependent protein kinases. Acta Biochim Pol 54:219–233
Krasensky J, Broyart C, Rabanal FA, Jonak C (2014) The redox-sensitive chloroplast trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase AtTPPD regulates salt stress tolerance. Antioxid Redox Signal 21:1289–1304
Kretzschmar T et al (2015) A trehaloe-6-phosphate phosphatase enhances anaerobic germination tolerance in rice. Nat Plants 1:15124. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.124
Leckie CP, McAinsh MR, Allen GJ, Sanders D, Hetherington AM (1998) Abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure medated by cyclic ADP-ribose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15837–15842
Lin J-R, Mondal AM, Liu R, Hu J (2012) Minimalist ensemble algorithms for genome-wide protein localization prediction. BMC Bioinform 13:157
Lin Q, Wang S, Dao Y, Wang J, Wang K (2020) Arabidopsis thaliana trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene TPPI enhances drought tolerance by regulating stomatal apertures. J Exp Bot 71:4285–4297
Liu KH et al (2017) Discovery of nitrate-CPK-NLP signalling in central nutrient-growth networks. Nature 545:311–316
Lu P-L et al (2007) A novel drought-inducible gene, ATAF1, encodes a NAC family protein that negatively regulates the expression of stress-responsive genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 63:289–305
Ludwig AA, Romeis T, Jones JD (2004) CDPK-mediated signalling pathways: specificity and cross-talk. J Exp Bot 55:181–188
Lunn JE et al (2006) Sugar-induced increases in trehalose-6-phosphate are correlated with redox activation of ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase and higher rates of starch synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 397:139–148
Lunn JE, Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Van Dijck P, Stitt M (2014) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J 79:544–567
MacRobbie EAC (2006) Control of volume and turgor in stomatal guard cells. J Membr Biol 210:131–142
Majeran W, Le Caer J-P, Ponnala L, Meinel T, Giglione C (2018) Targeted profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana subproteomes illuminated co- and posttranslationally N-terminally myristoylated proteins. Plant Cell 30:543–562
Miller CA, Martinat MA, Hyman LE (1998) Assessment of aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex interactions using pBEVY plasmids: expression vectors with bi-directional promoters for use in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3577–3583
Müller J, Aeschbacher RA, Wingler A, Boller T, Wiemken A (2001) Trehalose and trehalase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 125:1086–1093
Nagashima Y, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2018) Function of N-glycosylation in plants. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant Biol 274:70–79
Nguyen NC, Hoang XLT, Nguyen QT, Binh NX, Watanabe Y, Thao NP, Tran LP (2019) Ectopic expression of Glycine max GmNAC109 enhances drought tolerance and ABA sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Biomolecules 9:714
Norrander J, Kempe T, Messing J (1983) Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene 26:101–106
Obaidul Islam M, Kato H, Shima S, Tezuka D, Matsui H, Imai R (2019) Functional identification of a rice trehalase gene involved in salt stress tolerance. Gene 685:42–49
Pernambuco MB, Winderickx J, Crauwels M, Griffioen G, Mager WH, Thevelein JM (1996) Glucose-triggered signalling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: different requirements for sugar phosphorylation between cells grown on glucose and those grown on non-fermentable carbon sources. Microbiol 142:1775–1782
Schluepmann H, van Dijken A, Aghdasi M, Wobbes B, Paul M, Smeekens S (2004) Trehalose mediated growth inhibition of Arabidopsis seedlings is due to trehalose-6-phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiol 135:879–890
Schulz P, Herde M, Romeis T (2013) Calcium-dependent protein kinases: hubs in plant stress signaling and development. Plant Physiol 163:523–530
Sheen J (1996) Ca2+-dependent protein kinases and stress signal transduction in plants. Science 274:1900–1902
Shi S, Li S, Asim M, Mao J, Xu D, Ullah Z, Liu G, Wang Q, Liu H (2018) The Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) and their roles in plant growth regulation and abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 19:1900
Shim JS, Oh N, Chung PJ, Kim YS, Choi YD, Kim J-K (2018) Overexpression of OsNAC14 improves drought tolerance in rice. Front Plant Sci 9:310
Van Houtte H, Van Dijck P (2013) Trehalase activity in Arabidopsis thaliana optimized for 96-well plates. Bio Protoc. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.21946
Van Houtte H et al (2013) Overexpression of the trehalase gene AtTRE1 leads to increased drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis and is involved in ABA-induced stomatal closure. Plant Physiol 161:1158–1171
Vandesteene L et al (2012) Expansive evolution of the TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE PHOSPHATASE gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 160:884–896
Veluthambi K, Mahadevan S, Maheshwari R (1981) Trehalose toxicity in Cuscuta reflexa: correlation with low trehalase activity. Plant Physiol 68:1369–1374
Veluthambi K, Mahadevan S, Maheshwari R (1982) Trehalose toxicity in Cuscuta reflexa: sucrose decreases in shoot tips upon trehalose feeding. Plant Physiol 69:1247–1251
Wang W, Chen Q, Xu S, Liu WC, Zhu X, Song CP (2020) Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase E modulates ABA-controlled root growth and stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 62:1518–1534
Wingler A (2002) The function of trehalose biosynthesis in plants. Phytochemistry 60:437–440
Xiang C, Han P, Lutziger I, Wang K, Oliver DJ (1999) A mini binary vector series for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 40:711–717
Yang X, Kim MY, Ha J, Lee SH (2019) Overexpression of the Soybean NAC gene GmNAC109 increases lateral root formation and abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic. Front Plant Sci 10:1036
Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2:1565–1572
Zou J-J, Wei F-J, Wang C, Wu J-J, Ratnasekera D, Liu W-X, Wu W-U (2010) Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK10 functions in abscisic acid- and Ca2+-mediated stomatal regulation in response to drought stress. Plant Physiol 154:1232–1243
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the F.R. lab for helpful discussions and initial training of T.B.P. We would like to thank Nico Van Goethem (VIB-KU Leuven Center for Microbiology) for assistance with preparation of the figures.
Funding
T.B.P. was supported by a grant from Vietnam International Education Development (VIED) as well as by a KU Leuven Global Minds Fellowship. This work was supported by a grant from the Research Fund of KU Leuven (Grant # C14/17/063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TBP and NC conducted the experiments. TBP, FR and PVD designed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Cong Huyen Bao Phan, T., Crepin, N., Rolland, F. et al. Two trehalase isoforms, produced from a single transcript, regulate drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 108, 531–547 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01243-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-022-01243-2