Abstract
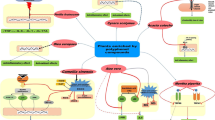
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic digestive illness characterized by symptoms such as bloating, stomach discomfort, diarrhea, irregular bowel motions, and constipation. IBS is caused by genetic predisposition and the gut-brain axis, which affects the brain and psychological health. The gut microbiome may mediate dysbiosis in IBS patients, stress, and psychological comorbidity. Medications for IBS include probiotics, antispasmodics, antibiotics, and several agents acting on central nervous system. However, the disappointing results of conventional treatments are leading many patients to consider complementary and alternative medicines. The current study examines different herbal remedies, their phytoconstituents, the ways in which herbs work, and novel approaches based on nanotechnology to treat IBS. Moreover, with the help of the phytoconstituents discussed in this review, a ligand-based pharmacophore was generated in order to obtain structural knowledge for potential future developments of leads for the treatment of IBS. Potent activity against IBS may be enhanced by structural alterations of these phytoconstituents on hydrophobic, donor, and acceptor regions. In summary, this research could pave the way for the management of IBS through the use of herbal medicinal plants and encourage scientists to explore for novel natural remedies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- IkB-α:
-
Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor-alpha
- NFkB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- cGMP:
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- PPAR:
-
Gamma-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- TLR-4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2
- TRPV1:
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid-1
- TRPA1:
-
Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily A member 1
References
Abbott GW, Redford KE, Yoshimura RF, Manville RW, Moreira L, Tran K, Arena G, Kookootsedes A, Lasky E, Gunnison E (2021) KCNQ and KCNE isoform-dependent pharmacology rationalizes native American dual use of specific plants as both analgesics and gastrointestinal therapeutics. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.777057
Agarwal H, Nakara A, Shanmugam VK (2019) Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 109:2561–2572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.116
Agrahari P (2014) A review on the pharmacological aspects of Carum carvi. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277014638
Ahluwalia B, Magnusson MK, Böhn L, Störsrud S, Larsson F, Savolainen O, Ross A, Simrén M, Öhman L (2020) Randomized clinical trial: effects of Aloe barbadensis Mill extract on symptoms, fecal microbiota and fecal metabolite profiles in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 32(8):e13860. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13860
Ahluwalia B (2022) Aloe barbadensis Mill. as a therapeutic option for irritable bowel syndrome: properties, bioactivity and mode of action
Akkol EK, Karpuz B, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Khan H (2020) A phytopharmacological overview of medicinal plants used for prophylactic and treatment of colitis. Food Chem Toxicol 144:111628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111628
Akter KM, Kim HJ, Khalil AAK, Park WS, Lee MK, Park JH, Ahn MJ (2018) Inner morphological and chemical differentiation of Boehmeria species. J Nat Med 72(2):4–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1164-8
Alam M, Khan H, Samiullah L, Siddique KM (2012) A review on phytochemical and pharmacological studies of Kundur (Boswellia serrata Roxb ex Colebr.)-a Unani drug. J Appl Pharm Sci 148–156
Ali S, Watson MS, Osborne RH (2004) The stimulant cathartic, emodin, contracts the rat isolated ileum by triggering release of endogenous acetylcholine. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol 24(4):103–105
Allan JJ, Raveendra KR, Jayachandra SV, Sushma KR, Goudar KS, Shivaprasad HN, Venkateshwarlu K, Geetharani P, Sushma G, Agarwal A (2012) An extract of Glycyrrhiza glabra (GutGard) alleviates symptoms of functional dyspepsia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/216970
Al-Snafi AE (2020) Constituents and pharmacology of Fumaria officinalis-a review some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: medicinal plants with anticancer effects View project Virtual Learninggggg View project Constituents and Pharmacology of Fumaria Officinalis-A Review. In:IOSR journal of pharmacy, vol 10. www.iosrphr.org
Ammon HPT (2016) Boswellic acids and their role in chronic inflammatory diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 928:291–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_13
Anthoni C, Laukoetter MG, Rijcken E, Vowinkel T, Mennigen R, Müller S, Senninger N, Russell J, Jauch J, Bergmann J, Granger DN, Krieglstein CF (2006) Mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory actions of boswellic acid derivatives in experimental colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290(6):G1131–G1137. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00562.2005
Anurekha J, Gupta VB (2006) Chemistry and pharmacological profile of guggul: a review. Indian J Tradit Knowl 5(4)
Arsul MI, Insanu M, Fidrianny I (2021) Phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of Boehmeria genus: an update review. Pharmacogn J 13(6):1533–1541. https://doi.org/10.5530/PJ.2021.13.195
Awaad AS, El-Meligy RM, Soliman GA (2013) Natural products in treatment of ulcerative colitis and peptic ulcer. J Saudi Chem Soc 17(1):101–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2012.03.002
Barbara G, Feinle-Bisset C, Ghoshal UC et al (2016) The intestinal microenvironment and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology 150:1305–1318. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.028
Beloqui A, Memvanga PB, Coco R, Reimondez-Troitiño S, Alhouayek M, Muccioli GG, Alonso MJ, Csaba N, de la Fuente M, Préat V (2016) A comparative study of curcumin-loaded lipid-based nanocarriers in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Colloids Surf, B 143:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.03.038
Beubler E, Juan H (1979) Effect of ricinoleic acid and other laxatives on net water flux and prostaglandin E release by the rat colon. J Pharm Pharmacol 31(1):681–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13628.x
Bijkerk CJ, De Wit NJ, Muris JWM, Whorwell PJ, Knottnerus JA, Hoes AW (2009) Soluble or insoluble fibre in irritable bowel syndrome in primary care? Randomised Placebo Controlled Trial BMJ (online) 339(7721):613–615. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b3154
Boudreau MD, Beland FA (2006) An evaluation of the biological and toxicological properties of Aloe barbadensis (Miller), aloe vera. J Environ Sci Health Part C Environ Carcinogenes Ecotoxicol Rev 24(1):103–154. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590500600614303
Brierley SM, Kelber O (2011) Use of natural products in gastrointestinal therapies. Curr Opinion Pharmacol 11(6):604–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2011.09.007
Brinkhaus B, Hentschel C, Von Keudell C, Schindler G, Lindner M, Stützer H, Kohnen R, Willich SN, Lehmacher W, Hahn EG (2005) Herbal medicine with curcuma and fumitory in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Scand J Gastroenterol 40(8):936–943. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520510023134
Briscoe CP, Tadayyon M, Andrews JL, Benson WG, Chambers JK, Eilert MM, Ellis C, Elshourbagy NA, Goetz AS, Minnick DT, Murdock PR, Sauls HR, Shabon U, Spinage LD, Strum JC, Szekeres PG, Tan KB, Way JM, Ignar DM, Muir AI (2003) The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long chain fatty acids. J Biol Chem 278(13):11303–11311. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M211495200
Bundy R, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Booth J (2004) Turmeric extract may improve irritable bowel syndrome symptomology in otherwise healthy adults: a pilot study. J Alternat Complement Med 10(6):1015–1018
Cappello G, Spezzaferro M, Grossi L, Manzoli L, Marzio L (2007) Peppermint oil (Mintoil®) in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective double blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Dig Liver Dis 39(6):530–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2007.02.006
Cash BD, Epstein MS, Shah SM (2016) A novel delivery system of peppermint oil is an effective therapy for irritable bowel syndrome symptoms. Dig Dis Sci 61(2):560–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3858-7
Catanzaro D, Rancan S, Orso G, Dall’acqua S, Brun P, Giron MC, Carrara M, Castagliuolo I, Ragazzi E, Caparrotta L, Montopoli M (2015) Boswellia serrata preserves intestinal epithelial barrier from oxidative and inflammatory damage. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0125375. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125375
Chen G, Zhu L, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Chen H, Yang J (2009) Isoliquiritigenin, a Flavonoid from Licorice, plays a dual role in regulating Gastrointestinal Motility in vitro and in vivo. Phytother Res 23:498–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr
Chen D, Chen G, Sun Y, Zeng X, Ye H (2020) Physiological genetics, chemical composition, health benefits and toxicology of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) flower: a review. Food Res Int 137:109584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109584
Cheon JH, Kim JS, Kim JM, Kim N, Jung HC, Song IS (2006) Plant sterol guggulsterone inhibits nuclear factor-kB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells by blocking IkB kinase and ameliorates acute murine colitis. https://academic.oup.com/ibdjournal/article/12/12/1152/4682864
Choi J, Nguyen QN, Baek JY, Cho DE, Kang KS, Hahm DH, Jang TW, Park JH, Lee AY, Lee S (2022) Beneficial role of Boehmeria nivea in health and phytochemical constituents. J Food Biochem 46(12):e14474. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14474
Chumpitazi BP, Kearns GL, Shulman RJ (2018) the physiological effects and safety of peppermint oil and its efficacy in irritable bowel syndrome and other functional disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 47(6):738–752. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14519
Chung JM, Lee SD, Kang D, Kwon DD, Kim KS, Kim SY, Kim HG, Moon DG, Park KH, Park YH, Pai KS, Suh HJ, Lee JW, Cho WY, Ha TS, Han SW (2010) An epidemiologic study of voiding and bowel habits in Korean children: a nationwide multicenter study. Urology 76(1):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2009.12.022
Cline WS, Lorenzsonn V, Benz L, Bass P, Olsen WA (1976) The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Investig 58(2):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI108482
Cockerell KM, Watkins ASM, Reeves LB, Goddard L, Lomer MCE (2012) Effects of linseeds on the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot randomised controlled trial. J Hum Nutr Diet 25(5):435–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2012.01263.x
Czigle S, Bittner Fialova S, Tóth J, Mučaji P, Nagy M (2022) Treatment of gastrointestinal disorders—plants and potential mechanisms of action of their constituents. Molecules 27(9):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092881
Dar NJ, Hamid A, Ahmad M (2015) Pharmacologic overview of Withania somnifera, the Indian Ginseng. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(23):4445–4460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2012-1
de Vogel-van den Bosch HM, Bünger M, de Groot PJ, Bosch-Vermeulen H, Hooiveld GJ, Müller M (2008) PPARalpha-mediated effects of dietary lipids on intestinal barrier gene expression. BMC Genom 9:1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-231
Dejban P, Nikravangolsefid N, Chamanara M, Dehpour A, Rashidian A (2021) The role of medicinal products in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) through inhibition of TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Phytother Res 35(2):835–845. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6866
Di Ciaula A, Portincasa P, Maes N, Albert A (2018) Efficacy of bio-optimized extracts of turmeric and essential fenneoil on the quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Ann Gastroenterol 31(6):685–691. https://doi.org/10.20524/aog.2018.0304
Dolatabadi F, Abdolghaffari AH, Farzaei MH, Baeeri M, Ziarani FS, Eslami M, Abdollahi M, Rahimi R (2018) The protective effect of Melissa officinalis l. in visceral hypersensitivity in rat using 2 models of acid-induced colitis and stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome: a possible role of nitric oxide pathway. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 24(3):490–501. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm17035
Doustfatemeh S, Imanieh MH, Mohagheghzade A, Zarshenas MM, Torkamani Z, Yousefi G, Farahangiz S, Salehi A (2017) The effect of black tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) on pediatrics with acute nonbacterial diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial. J Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 22(1):114–119. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587216654600
Ekundayo O, Laakso I, Hiltunen R (1988) Composition of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) volatile oils from Nigeria. Flavour Fragr J 3:85–90
Elbadawi M, Ammar RM, Aziz-Kalbhenn H, Rabini S, Klauck SM, Dawood M, Saeed MEM, Kampf CJ, Efferth T (2021) Anti-inflammatory and tight junction protective activity of the herbal preparation STW 5-II on mouse intestinal organoids. Phytomedicine 88:153589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153589
Elkhishin IA, Awwad IA (2009) A study of the cardiovascular toxic effects of Zingiber officinale (Ginger) in adult male albino rats and its possible mechanisms of action. Mansoura J Forensic Med Clin Toxicol 17(2):109–127
Fan K, Xi J, Fan L, Wang P, Zhu C, Tang Y, Xu X, Liang M, Jiang B, Yan X, Gao L (2018) In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat Commun 9(1):1440. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03903-8
Ferreira-da-Silva FW, da Silva-Alves KS, Alves-Fernandes TA, Coelho-de-Souza AN, Leal-Cardoso JH (2015) Effects of 1,8-cineole on Na+ currents of dissociated superior cervical ganglia neurons. Neurosci Lett 595:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.04.005
Ford AC, Bercik P, Morgan DG, Bolino C, Pintos-Sanchez MI, Moayyedi P (2013) Validation of the Rome III criteria for the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome in secondary care. Gastroenterology 145(6):1262–1270. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.048
Ford AC, Lacy BE, Talley NJ (2017) Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med 376(26):2566–2578. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1607547
Gao CC, Li GW, Wang TT, Gao L, Wang FF, Shang HW, Yang ZJ, Guo YX, Wang BY, Xu JD (2021a) Rhubarb extract relieves constipation by stimulating mucus production in the colon and altering the intestinal flora. Biomed Pharmacother 138:111479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111479
Gao D, Cho CW, Vinh LB, Kim JH, Kim YH, Kang JS (2021b) Phytochemical analysis of trifoliate orange during fermentation by HPLC–DAD–ESI–MS/ MS coupled with multivariate statistical analysis. Acta Chromatogr 33(4):371–377. https://doi.org/10.1556/1326.2020.00818
Gerges SH, Tolba MF, Elsherbiny DA, El-Demerdash E (2020) The natural flavonoid galangin ameliorates dextran sulphate sodium–induced ulcerative colitis in mice: effect on Toll-like receptor 4, inflammation and oxidative stress. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 127(1):10–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13388
Gill S, Chater PI, Wilcox MD, Pearson JP, Brownlee IA (2018) The impact of dietary fibres on the physiological processes of the large intestine. Bioact Carbohydr Diet Fibre 16:62–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2018.06.001
Greeson JM, Sanford B, Monti DA (2001) St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum): a review of the current pharmacological, toxicological, and clinical literature. Psychopharmacology 153(4):402–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000625
Guginski G, Luiz AP, Silva MD, Massaro M, Martins DF, Chaves J, Mattos RW, Silveira D, Ferreira VMM, Calixto JB, Santos ARS (2009) Mechanisms involved in the antinociception caused by ethanolic extract obtained from the leaves of Melissa officinalis (lemon balm) in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93(1):10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2009.03.014
Gupta M, Mishra V, Gulati M, Kapoor B, Kaur A, Gupta R, Tambuwala MM (2022) Natural compounds as safe therapeutic options for ulcerative colitis. Inflammopharmacology 30(2):397–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-00931-1
Hawrelak JA, Wohlmuth H, Pattinson M, Myers SP, Goldenberg JZ, Harnett J, Cooley K, Van De Venter C, Reid R, Whitten DL (2020) Western herbal medicines in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement Therap Med 48:102233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2019.102233
Hitomi S, Ono K, Terawaki K, Matsumoto C, Mizuno K, Yamaguchi K, Imai R, Omiya Y, Hattori T, Kase Y, Inenaga K (2017) [6]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol, active ingredients of the traditional Japanese medicine hangeshashinto, relief oral ulcerative mucositis-induced pain via action on Na+ channels. Pharmacol Res 117:288–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.12.026
Huang Y, Xing K, Qiu L, Wu Q, Wei H (2022) Therapeutic implications of functional tea ingredients for ameliorating inflammatory bowel disease: a focused review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62(19):5307–5321. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1884532
Hutchings HA, Wareham K, Baxter JN, Atherton P, Kingham JGC, Duane P, Thomas L, Thomas M, C’hng CL, Williams JG (2011) A randomised, cross-over, placebo-controlled study of aloe vera in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: effects on patient quality of life. ISRN Gastroenterol 2011:1–8. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/206103
Ikarashi N, Ushiki T, Mochizuki T, Toda T, Kudo T, Baba K, Ishii M, Ito K, Ochiai W, Sugiyama K (2011) Effects of magnesium sulphate administration on aquaporin 3 in rat gastrointestinal tract. Biol Pharm Bull 34(2):238–242
Jang Y, Kim EK, Shim WS (2018) Phytotherapeutic effects of the fruits of Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. on cancer, inflammation, and digestive dysfunction. Phytother Res 32(4):616–624. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6008
Jena J, Gupta AK (2012) Ricinus communis Linn: a phytopharmacological review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(4):25–29
Jiang K, Guo S, Yang C, Yang J, Chen Y, Shaukat A, Zhao G, Wu H, Deng G (2018) Barbaloin protects against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 64:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.08.023
Jp L, Liu YM, Ml W, Grimsgaard S (2011) Herbal medicines for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (Review). http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Karakan T, Ozkul C, Küpeli Akkol E, Bilici S, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Capasso R (2021) Gut-brain-microbiota axis: antibiotics and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nutrients 13(2):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020389
Kato M, Takayama Y, Sunagawa M (2021) The calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A is inhibitied by liquiritigenin. Front Pharmacol 12:628968. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.628968
Kaur R, Kaur H, Dhindsa AS (2013) Glycyrrhiza glabra: a phytopharmacological review. Int J Pharm Sci Res 4(7):2470. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.4(7).2470-77
Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y, Pinlaor S, Ma N (2006) Oxidative and nitrative DNA damage in animals and patients with inflammatory diseases in relation to inflammation-related carcinogenesis. Biol Chem 387(4):365–372. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2006.049
Kazemian A, Toghiani A, Shafiei K, Afshar H, Rafiei R, Memari M, Adibi P (2017) Evaluating the efficacy of mixture of Boswellia carterii, Zingiber officinale, and Achillea millefolium on severity of symptoms, anxiety, and depression in irritable bowel syndrome patients. J Res Med Sci 22(11):120. https://doi.org/10.4103/jrms.JRMS_905_16
Kelber O, Bauer R, Kubelka W (2018) Phytotherapy in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Dig Dis 35(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485489
Kim SJ, Kim MC, Um JY, Hong SH (2010) The beneficial effect of vanillic acid on ulcerative colitis. Molecules 15(10):7208–7217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15107208
Kim YS, Hong C, Lee SW, Nam JH, Kim BJ (2016) Effects of ginger and its pungent constituents on transient receptor potential channels. Int J Mol Med 38(6):1905–1914. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2791
Kim JN, Kim HJ, Kim I, Kim YT, Kim BJ (2018) The mechanism of action of zingerone in the pacemaker potentials of interstitial cells of cajal isolated from murine small intestine. Cell Physiol Biochem 46(5):2127–2137. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489453
Kiumarsi F, Derakhshan AR (2022) Gastrointestinal and hepatic effects of fumaria species in traditional Persian medicine and modern medical studies: a narrative review
Kline RM, Kline JJ, Di Palma J, Barbero GJ (2001) Enteric-coated, pH-dependent peppermint oil capsules for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in children. J Pediatr 138(1):125–128. https://doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2001.109606
Kon R, Ikarashi N, Nagoya C, Takayama T, Kusunoki Y, Ishii M, Ueda H, Ochiai W, Machida Y, Sugita K, Sugiyama K (2014) Rheinanthrone, a metabolite of sennoside A, triggers macrophage activation to decrease aquaporin-3 expression in the colon, causing the laxative effect of rhubarb extract. J Ethnopharmacol 152(1):190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.055
Kruis W, Thieme CH, Weinzierl M et al (1984) A diagnostic score for the irritable bowel syndrome: its value in the exclusion of organic disease. Gastroenterology 87:1–7
Küpeli Akkol E, Gürağaç Dereli FT, Taştan H, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Khan H (2020) Effect of Sorbus domestica and its active constituents in an experimental model of colitis rats induced by acetic acid. J Ethnopharmacol 251:112521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112521
Labban L, Nguyen P (2014) Citation: Louay Labban. Medicinal and pharmacological properties of Turmeric (Curcuma longa): a review. Int J Pharm Biomed Sci 5(1):17–23
Lacy BE, Patel NK (2017) Rome criteria and a diagnostic approach to irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Med 6(11):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6110099
Latif A, Rehman S, Siddiqui N (2012) Physico-chemical and phytochemical evaluation of a Fumaria officinalis L.(Shahtra) Linn.-an important medicinal herbal drug view project pharmacognostical and phytochemical studies of sankhaholi & sahdevi Lesser known plants view project. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228096232
Lauche R, Janzen A, Lüdtke R, Cramer H, Dobos G, Langhorst J (2015) Efficacy of caraway oil poultices in treating irritable Bowel syndrome-a randomized controlled cross-over trial. Digestion 92(1):22–31. https://doi.org/10.1159/000398790
Lee J-H, Lee S-H, Kim YS, Jeong CS (2009) Protective effects of neohesperidin and poncirin isolated from the fruits of poncirus trifoliata on potential Gastric disease. Phytother Res 23:1748–1753. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr
Lee W, Kim TH, Ku SK, Min KJ, Lee HS, Kwon TK, Bae JS (2012) Barrier protective effects of withaferin A in HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in both cellular and animal models. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 262(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.04.025
Lee AY, Wang X, Lee DG, Kim YM, Jung YS, Kim HB, Kim HY, Cho EJ, Lee S (2014) Various biological activities of ramie (Boehmeria nivea). J Appl Biol Chem 57(3):279–286. https://doi.org/10.3839/jabc.2014.044
Leite CDS, Bonafé GA, Santos JC, Martinez CAR, Ortega MM, Ribeiro ML (2022) The anti-inflammatory properties of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra)-derived compounds in intestinal disorders. Int J Mol Sci 23(8):4121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084121
Levy EI, De Geyter C, Ouald Chaib A, Aman BA, Hegar B, Vandenplas Y (2022) How to manage irritable bowel syndrome in children. Acta Paediatr, Int J Paediatr 111(1):24–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.16107
Li CY, Suzuki K, Hung YL, Yang MS, Yu CP, Lin SP, Hou YC, Fang SH (2017) Aloe metabolites prevent LPS-induced sepsis and inflammatory response by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Am J Chin Med 45(4):847–861. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X17500458
Li L, Cui H, Li T, Qi J, Chen H, Gao F, Tian X, Mu Y, He R, Lv S, Chu F, Xu B, Wang P, Lei H, Xu H, Wang C (2020) Synergistic effect of berberine-based Chinese medicine assembled nanostructures on diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome in vivo. Front Pharmacol 11:1210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01210
Liu L, Welch JM, Erickson RP, Reinhart PH, Simon SA (2000) Different responses to repeated applications of zingerone in behavioral studies, recordings from intact and cultured TG neurons, and from VR1 receptors. Physiol Behav 69:177–186
Liu Z, Wang P, Lu S, Guo R, Gao W, Tong H, Yin Y, Han X, Liu T, Chen X, Zhu MX, Yang Z (2020) Liquiritin, a novel inhibitor of TRPV1 and TRPA1, protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury. Cell Calcium 88:102198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102198
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC (2006) Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 130(5):1480–1491. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.061
Macmillan AK, Merrie AEH, Marshall RJ, Parry BR (2008) Design and validation of a comprehensive fecal incontinence questionnaire. Dis Colon Rectum 51(10):1502–1522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-008-9301-9
Maia MBDS, Franco EDS, De Aquino CMF, Medeiros PLD, Evêncio LB, Góes AJDS (2012) Effect of a semisolid formulation of Linum usitatissimum L. (linseed) oil on the repair of skin wounds. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/270752
Malekmohammad K, Rafieian-Kopaei M, Sardari S, Sewell RDE (2021) Toxicological effects of Mentha x piperita (peppermint): a review. Toxin Rev 40(4):445–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2019.1647545
Manning AP, Thompson WG, Heaton KW, Morris AF (1978) Towards positive diagnosis of the irritable bowel. Br Med J 2
Martínez V, Iriondo De-Hond A, Borrelli F, Capasso R, Del Castillo MD, Abalo R (2020) Cannabidiol and other non-psychoactive cannabinoids for prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders: useful nutraceuticals? Int J Mol Sci 21(9):3067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093067
Mawe GM, Hoffman JM (2013) Serotonin signalling in the gut-functions, dysfunctions and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(8):473–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.105
Melzig MF, Böttger S (2020) Tormentillae rhizoma-review for an underestimated European herbal drug. Planta Med 86(15):1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1129-7214
Mencarelli A, Renga B, Palladino G, Distrutti E, Fiorucci S (2009) The plant sterol guggulsterone attenuates inflammation and immune dysfunction in murine models of inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem Pharmacol 78(9):1214–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.026
Meselhy MR (2003) Inhibition of LPS-induced NO production by the oleogum resin of Commiphora wightii and its constituents. Phytochemistry 62(2):213–218
Mihara S, Shibamoto T (2015) The role of flavor and fragrance chemicals in TRPA1 (transient receptor potential cation channel, member A1) activity associated with allergies. Allergy, Asthma Clin Immunol 11(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-015-0074-0
Milutinović M, Dimitrijević-Branković S, Rajilić-Stojanović M (2021) Plant extracts rich in polyphenols as potent modulators in the growth of probiotic and pathogenic intestinal microorganisms. Front Nutr 8:688843. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.688843
Miraj S, Kiani S (2016) Pharmacological activities of Carum carvi L. Pharm Lett 8(6):135–138
Moradi MT, Rafieian-Koupaei M, Imani-Rastabi R, Nasiri J, Shahrani M, Rabiei Z, Alibabaei Z (2013) Antispasmodic effects of yarrow (Achillea millefolium L.) extract in the isolated ileum of rat. Afr J Tradit, Complement, Alternat Med AJTCAM/Afr Netw Ethnomed 10(6):499–503. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajtcam.v10i6.19ui-9
Mozaffari S, Esmaily H, Rahimi R, Baeeri M, Sanei Y, Asadi-Shahmirzadi A, Salehi-Surmaghi MH, Abdollahi M (2011) Effects of Hypericum perforatum extract on rat irritable bowel syndrome. Pharmacogn Mag 7(27):213–223. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.84235
Nalli M, Ortar G, Schiano Moriello A, Di Marzo V, De Petrocellis L (2017) Effects of curcumin and curcumin analogues on TRP channels. Fitoterapia 122:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2017.09.007
Namkung W, Thiagarajah JR, Phuan P, Verkman AS (2010) Inhibition of Ca 2+ -activated Cl−channels by gallotannins as a possible molecular basis for health benefits of red wine and green tea. FASEB J 24(11):4178–4186. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.10-160648
Nazari S, Rameshrad M, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Toxicological effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra (Licorice): a review. Phytother Res 31(11):1635–1650. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5893
Niu XF, Zhou P, Li WF, Xu HB (2011) Effects of chelerythrine, a specific inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2, on acute inflammation in mice. Fitoterapia 82(4):620–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2011.01.020
Nizamutdinova IT, Jeong JJ, Xu GH, Lee SH, Kang SS, Kim YS, Chang KC, Kim HJ (2008) Hesperidin, hesperidin methyl chalone and phellopterin from Poncirus trifoliata (Rutaceae) differentially regulate the expression of adhesion molecules in tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol 8(5):670–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2008.01.011
Novilla A, Djamhuri DS, Nurhayati B, Rihibiha DD, Afifah E, Widowati W (2017) Anti-inflammatory properties of oolong tea (Camellia sinensis) ethanol extract and epigallocatechin gallate in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 7(11):1005–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.10.002
Okahira M, Kubota M, Iguchi K, Usui S, Hirano K (2008) Regulation of aquaporin 3 expression by magnesium ion. Eur J Pharmacol 588(1):26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.03.063
Park JM, Choi MG, Cho YK, Lee IS, Kim JI, Kim SW, Chung IS (2011) Functional gastrointestinal disorders diagnosed by Rome III questionnaire in Korea. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 17(3):279–286. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2011.17.3.279
Parker S, May B, Zhang C, Zhang AL, Lu C, Xue CC (2016) A pharmacological review of bioactive constituents of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas and Paeonia veitchii Lynch. Phytother Res 30:1445–1473. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5653
Parlar A, Arslan SO, Çam SA (2020) Glabridin alleviates inflammation and nociception in rodents by activating BKCa channels and reducing NO levels. Biol Pharm Bull 43(5):884–897
Pathak DV, Sagar SR, Bhatt HG, Patel PK (2022) A search for potential anti-HIV phytoconstituents from the natural product repository. Adv Tradit Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-022-00646-2
Pawar P, Gilda S, Sharma S, Jagtap S, Paradkar A, Mahadik K, Ranjekar P, Harsulkar A (2011) Rectal gel application of Withania somnifera root extract expounds anti-inflammatory and muco-restorative activity in TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Complement Altern Med 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-11-34
Priya SS, Jha A, Satish Kumar RC, Sabarathinam S (2022) The role of guggulsterone on the NF-κB pathway in inflammatory bowel disease: preclinical evidence. Future Sci OA 8(6):FSO803. https://doi.org/10.2144/fsoa-2022-0020
Punukollu RS, Chadalawada AK, Siddabattuni K, Gogineni NT (2024) A blend of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal root and Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench fruit extracts relieves constipation and improves bowel function: a proof-of-concept clinical investigation. J Ethnopharmacol 318:116997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.116997
Qi J, Cui J, Mi B, Yan X, Xu W, Ma H, Zhang Q, Xu F (2020) Isoliquiritigenin inhibits atherosclerosis by blocking TRPC5 channel expression. Cardiovasc Ther. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1926249
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Abdollahi M (2009) Efficacy and tolerability of Hypericum perforatum in major depressive disorder in comparison with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33(1):118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.10.018
Redford KE, Abbott GW (2020) The ubiquitous flavonoid quercetin is an atypical KCNQ potassium channel activator. Commun Biol 3(1):356. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-1089-8
Riva A, Giacomelli L, Togni S, Franceschi F, Eggenhoffner R, Zuccarini MC, Belcaro G (2019) Oral administration of a lecithin-based delivery form of boswellic acids (Casperome®) for the prevention of symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized clinical study. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 65(1):30–35
Şahin TÖ, Yılmaz B, Yeşilyurt N, Cicia D, Szymanowska A, Amero P, Ağagündüz D, Capasso R (2023) Recent insights into the nutritional immunomodulation of cancer-related microRNAs. Phytother Res 37(10):4375–4397. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7937
Saito YA, Rey E, Almazar-Elder AE, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Locke GR, Talley NJ (2010) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of st john’s wort for treating irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 105(1):170–177. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.577
Salehi B, Selamoglu Z, Sevindik M, Fahmy NM, Al-Sayed E, El-Shazly M, Csupor-Löffler B, Csupor D, Yazdi SE, Sharifi-Rad J, Arserim-Uçar DK, Arserim EH, Karazhan N, Jahani A, Dey A, Azadi H, Vakili SA, Sharopov F, Martins N, Büsselberg D (2020) Achillea spp.: a comprehensive review on its ethnobotany, phytochemistry, phytopharmacology and industrial applications. Cell Mol Biol 66(4):78–103. https://doi.org/10.14715/cmb/2020.66.4.13
Sánchez M, González-Burgos E, Iglesias I, Gómez-Serranillos MP (2020) Pharmacological update properties of aloe vera and its major active constituents. Molecules 25(6):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061324
Sanechika S, Shimobori C, Ohbuchi K (2021) Identification of herbal components as TRPA1 agonists and TRPM8 antagonists. J Nat Med 75(3):717–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-021-01515-z
Scarpa A, Guerci A (1982) Various uses of the castor oil plant (Ricinus communis L.) a review. J Ethnopharmacol 5:117–137
Selamoglu Z (2018) Pharmacy & pharmacology international journal Aloe vera: a miracle plant with its wide-ranging applications effects of propolis on tyrosine hydroxylase activity on hypertensive rats view project aloe vera: a miracle plant with its wide-ranging applications. Int Congr Biol Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.15406/ppij.2017.06.00144
Serreli G, Naitza MR, Zodio S, Leoni VP, Spada M, Melis MP, Boronat A, Deiana M (2021) Ferulic acid metabolites attenuate lps-induced inflammatory response in enterocyte-like cells. Nutrients 13(9):3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093152
Shakeri A, Sahebkar A, Javadi B (2016) Melissa officinalis L.-a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol 188:204–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.010
Singh BB, Dagenais S, Assistant B-R, Mishra L-C (2000) Scientific basis for the therapeutic use of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha): a review. Altern Med Rev 5(334):346
Singh N, Savanur MA, Srivastava S, D’Silva P, Mugesh G (2017) A redox modulatory Mn3O4 nanozyme with multi-enzyme activity provides efficient cytoprotection to human cells in a Parkinson’s disease model. Angew Chem Int Edn 56(45):14267–14271. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708573
Singh N, Rao AS, Nandal A, Kumar S, Yadav SS, Ganaie SA, Narasimhan B (2021) Phytochemical and pharmacological review of Cinnamomum verum J. Presl-a versatile spice used in food and nutrition. Food Chem 338:127773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127773
Spiller RC, Brown ML, Phillips SF (1986) Decreased fluid tolerance, accelerated transit, and abnormal motility of the human colon induced by oleic acid. Gastroenterology 91:100–107
Stompor-Gorący M, Machaczka M (2021) Recent advances in biological activity, new formulations and prodrugs of ferulic acid. Int J Mol Sci 22(23):12889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312889
Subhash A, Suneela S, Anuradha Ch, Bhavani SN, Minor Babu MS (2014) The role of Aloe vera in various fields of medicine and dentistry. J Orofac Sci 6(1):5. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-8844.132564
Sung MJ, Davaatseren M, Kim SH, Kim MJ, Hwang JT (2013) Boehmeria nivea attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory markers by inhibiting p38 and JNK phosphorylations in RAW264.7 macrophages. Pharm Biol 51(9):1131–1136. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2013.781196
Sybyl-X 2.1, Tripos international, a ceratra company, 63144, USA
Termentzi A, Kefalas P, Kokkalou E (2008) LC-DAD-MS (ESI+) analysis of the phenolic content of Sorbus domestica fruits in relation to their maturity stage. Food Chem 106(3):1234–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.07.021
Thompson WG, Longstreth GF, Drossman DA, Heaton KW, Irvine EJ, Müller-Lissner SA (1999) Functional bowel disorders and functional abdominal pain
Tibble JA, Sigthorsson G, Foster R, Forgacs I, Bjarnason I (2002) Use of surrogate markers of inflammation and Rome criteria to distinguish organic from nonorganic intestinal disease. Gastroenterology 123(2):450–460. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.34755
Tireki S (2021) Herbal nootropics: Crocus sativus, Ginkgo biloba and Melissa officinalis. Open Access J Biomed Sci. https://doi.org/10.38125/oajbs.000300
Treichel AJ, Finholm I, Knutson KR, Alcaino C, Whiteman ST, Brown MR, Matveyenko A, Wegner A, Kacmaz H, Mercado-Perez A, Gajdos GB, Ordog T, Grover M, Szurszewski J, Linden DR, Farrugia G, Beyder A (2022) Specialized mechanosensory epithelial cells in mouse gut intrinsic tactile sensitivity. Gastroenterology 162(2):535-547.e13. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.026
Trute A, Gross J, Mutschler E, Nahrstedt A (1997) In vitro antispasmodic compounds of the dry extract obtained from hedera helix. Planta Med 63(02):125–129
Ullah MA, Hassan A (2022) Medicinal benefits of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) for human health. World J Chem Pharm Sci 1(1):028–033. https://doi.org/10.53346/wjcps.2022.1.1.0025
Van Tilburg MAL, Palsson OS, Ringel Y, Whitehead WE (2014) Is ginger effective for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome? A double blind randomized controlled pilot trial. Complement Ther Med 22(1):17–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2013.12.015
Vejdani R, Shalmani HRM, Mir-Fattahi M, Sajed-Nia F, Abdollahi M, Zali MR, Alizadeh AHM, Bahari A, Amin G (2006) The efficacy of an herbal medicine, carmint, on the relief of abdominal pain and bloating in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study. Dig Dis Sci 51(8):1501–1507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9079-3
Verhaeren EHC, Lemli J (1986) The effect of gallotannins and (+)-catechin on the stimulated fluid secretion on the colon, following a rhein perfusion in guinea pigs. Planta Med 52(04):269–272
Vion E, Page G, Bourdeaud E, Paccalin M, Guillard J, Rioux Bilan A (2018) Trans ε-viniferin is an amyloid-β disaggregating and anti-inflammatory drug in a mouse primary cellular model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 88:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2017.12.003
Wang D, Wang XH, Yu X, Cao F, Cai X, Chen P, Li M, Feng Y, Li H, Wang X (2021a) Pharmacokinetics of anthraquinones from medicinal plants. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.638993
Wang Z, Cheng Y, Su W, Zhang H, Li C, Routledge MN, Gong Y, Qiao B (2021b) Organ specific differences in alteration of aquaporin expression in rats treated with sennoside a, senna anthraquinones and rhubarb anthraquinones. Int J Mol Sci 22(15):8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158026
Wei H, Wang E (2013) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42(14):6060–6093. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35486e
WFO (2024) World Flora Online. https://www.worldfloraonline.org. Accessed 5 April 2024
World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines (2015) Irritable bowel syndrome: a global perspective
Woźniak M, Fabisiak A, Talar-Wojnarowska R, Małecka-Wojciesko E (2022) The effect of curcumin on symptoms and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Postepy Higieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej 76(1):345–350. https://doi.org/10.2478/ahem-2022-0048
Xu Y, Sun J, Li W, Zhang S, Yang L, Teng Y, Lv K, Liu Y, Su Y, Zhang J, Zhao M (2021) Analgesic effect of the main components of Corydalis yanhusuo (yanhusuo in Chinese) is caused by inhibition of voltage gated sodium channels. J Ethnopharmacol 280:114457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114457
Yan L, Wei L, Zheng W, Liu S, Yin L, Liu C, Zheng L (2021) Oral delivery of chitosan derivative-based nanoparticles encapsulating quercetin to attenuate intestinal injury and regulate gut microbiota dysbiosis in mucositis treatment. ACS Food Sci Technol 1(3):399–409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsfoodscitech.0c00121
Yang H, Xu LN, He CY, Liu X, Fang RY, Ma TH (2011) CFTR chloride channel as a molecular target of anthraquinone compounds in herbal laxatives. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32(6):834–839. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.46
Yde J, Keely SJ, Moeller HB (2021) Expression, regulation and function of Aquaporin-3 in colonic epithelial cells. BBA-Biomembranes. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183619
Yu B, Xie R, Jin L, Tian X, Niu Y, Ma T, Yang H (2019) trans-δ-Viniferin inhibits Ca2+-activated Cl− channels and improves diarrhea symptoms. Fitoterapia 139:104367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104367
Yuk HJ, Ryu HW, Jeong SH, Curtis-Long MJ, Kim HJ, Wang Y, Song YH, Park KH (2013) Profiling of neuraminidase inhibitory polyphenols from the seeds of Paeonia lactiflora. Food Chem Toxicol 55:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.053
Zhang XJ, Li Z, Leung WM, Liu L, Xu HX, Bian ZX (2008) The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin on neonatal maternal separation–induced visceral hyperalgesia in rats. J Pain 9(6):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2007.12.009
Zhao J, Cai X, Gao W, Zhang L, Zou D, Zheng Y, Li Z, Chen H (2018a) Prussian blue nanozyme with multienzyme activity reduces colitis in mice. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(31):26108–26117. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b10345
Zhao L, Huang Y, Lu L, Yang W, Huang T, Lin Z, Lin C, Kwan H, Wong HLX, Chen Y, Sun S, Xie X, Fang X, Yang H, Wang J, Zhu L, Bian Z (2018b) Saturated long-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria contribute to enhanced colonic motility in rats. Microbiome 6(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0492-6
Zheng YF, Liu CF, Lai WF, Xiang Q, Li ZF, Wang H, Lin N (2014) The laxative effect of emodin is attributable to increased aquaporin 3 expression in the colon of mice and HT-29 cells. Fitoterapia 96:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.04.002
Zhi L, Dong L, Kong D, Sun B, Sun Q, Grundy D, Zhang G, Rong W (2013) Curcumin acts via transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 receptors to inhibit gut nociception and reverses visceral hyperalgesia. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25(6):e429–e440. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12145
Zhu H, Li YR (2012) Oxidative stress and redox signaling mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease: updated experimental and clinical evidence. Exp Biol Med 237(5):474–480. https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2011.011358
Zhu X, Luo F, Zheng Y, Zhang J, Huang J, Sun C, Li X, Chen K (2013) Characterization, purification of poncirin from edible citrus ougan (Citrus reticulate cv. Suavissima) and its growth inhibitory effect on human gastric cancer cells SGC-7901. Int J Mol Sci 14(5):8684–8697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058684
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to L.J. Institute of Pharmacy, L J University, Ahmedabad, India for providing necessary support.
Funding
No funding source has been utilized in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DG, JT, PKP and SRS carried out literature search, compilation of data and preparation of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gajjar, D., Thakkar, J., Patel, P.K. et al. Phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology and novel formulations based approaches for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a comprehensive review. Phytochem Rev (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-024-09970-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-024-09970-8