Abstract
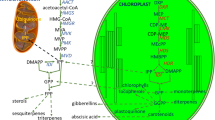
p-Menthanes are among the most valuable groups of monoterpenoids produced by plants. Products such as menthol, carvone, pulegone, and limonene are well-known fragrance compounds that are also used as pesticides or medicines. In flowering plants, they are synthesized and stored in specialized anatomical structures such as glandular trichomes (GT), secretory cavities, and root resin ducts. These metabolites originate through the 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate precursor pathway in the plastids of GT secretory cells but also require the activity of prenyltransferases and modifying enzymes in the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum to complete their functionalization to biologically active forms. (−)-Menthol is the best characterized of these and is pharmacologically active due to its affinity for the Cold and Menthol Receptor 1 and the κ-Opioid Receptor. p-Menthanes are found throughout the plant kingdom, and although their essential oils are still obtained mostly through traditional agriculture, synthetic biology approaches increasingly enable large scale production of economically valuable examples in microbes and cell free systems. Limonene is the model p-menthane monoterpene, and detailed studies of (+)-limonene synthase and (−)-limonene synthase crystal structures have enabled identification of catalytic residues and determinants of stereospecificity, which has implications for the ecological properties of these volatile products in defense and interspecific signaling. This review examines the chemical diversity of the p-menthanes in the plant kingdom, their biosynthetic origins in specialized anatomical structures, and the enzymology of p-menthane biosynthetic enzymes from diverse plant families.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adal AM, Mahmoud SS (2020) Short-chain isoprenyl diphosphate synthases of lavender (Lavandula). Plant Mol Biol 102(4):517–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-020-00962-8
Albino RC, Oliveira PC, Prosdocimi F, Da Silva OF, Bizzo HR, Gama PE, Sakuragui CM, Furtado C, De Oliveira DR (2017) Oxidation of monoterpenes in Protium heptaphyllum oleoresins. Phytochemistry 136:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.01.013
Alonso WR, Rajaonarivony J, Gershenzon J, Croteau R (1992) Purification of 4S-limonene synthase, a monoterpene cyclase from the glandular trichomes of peppermint (Mentha × piperita) and spearmint (Mentha spicata). J Biol Chem 267(11):7582–7587
Alonso-Gutierrez J, Chan R, Batth TS, Adams PD, Keasling JD, Petzold CJ, Lee TS (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for limonene and perillyl alcohol production. Metab Eng 19:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.05.004
Alonso-Gutierrez J, Kim E-M, Batth TS, Cho N, Hu Q, Chan LJG, Petzold CJ, Hillson NJ, Adams PD, Keasling JD, Martin HG, Lee TS (2015) Principal component analysis of proteomics (PCAP) as a tool to direct metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 28:123–133
Andrews TJ, Kane HJ (1991) Pyruvate is a by-product of catalysis by ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. J Biol Chem 266(15):9447–9452
Andriotis VME, Kruger NJ, Pike MJ, Smith AM (2010) Plastidial glycolysis in developing Arabidopsis embryos. New Phytol 185(3):649–662. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03113.x
Asikainen M, Jauhiainen O, Aaltonen O, Harlin A (2013) Continuous catalyst-free aromatization of γ-terpinene using air as an oxidant. Green Chem 15(11):3230. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc41224e
Banerjee A, Sharkey TD (2014) Methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway metabolic regulation. Nat Prod Rep 31(8):1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NP70124G
Başer KHC, Demirci B, Tabanca N, Özek T, Gören N (2001) Composition of the essential oils of Tanacetum armenum (DC.) Schultz Bip., T. balsamita L., T. chiliophyllum (Fisch. & Mey.) Schultz Bip. var. chiliophyllum and T. haradjani (Rech. fil.) Grierson and the enantiomeric distribution of camphor and carvone. Flavour Fragr J 16(3):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.977
Bergman ME, Davis B, Phillips MA (2019) Medically useful plant terpenoids: biosynthesis, occurrence, and mechanism of action. Molecules 24(21):3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213961
Bergman ME, Chávez Á, Ferrer A, Phillips MA (2020) Distinct metabolic pathways drive monoterpenoid biosynthesis in a natural population of Pelargonium graveolens. J Exp Botany 71(1):258–271. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz397
Bertea CM, Schalk M, Karp F, Maffei M, Croteau R (2001) Demonstration that menthofuran synthase of mint (Mentha) is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase: cloning, functional expression, and characterization of the responsible gene. Arch Biochem Biophys 390(2):279–286. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.2001.2378
Bertea C, Schalk M, Mau CJ, Karp F, Wildung MR, Croteau R (2003) Molecular evaluation of a spearmint mutant altered in the expression of limonene hydroxylases that direct essential oil monoterpene biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 64(7):1203–1211
Bicchi C, D’Amato A, Rubiolo P (1999) Cyclodextrin derivatives as chiral selectors for direct gas chromatographic separation of enantiomers in the essential oil, aroma and flavour fields. J Chromatogr A 843(1–2):99–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(99)00202-2
Bick JA, Lange BM (2003) Metabolic cross talk between cytosolic and plastidial pathways of isoprenoid biosynthesis: unidirectional transport of intermediates across the chloroplast envelope membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys 415(2):146–154
Blerot B, Martinelli L, Prunier C, Saint-Marcoux D, Legrand S, Bony A, Sarrabère L, Florence G, Boyer N, Caissard J-C, Baudino S, Jullien F, Gros F, Boyer N, Caissard J-C, Baudino S, Jullien F (2018) Functional analysis of four terpene synthases in rose-scented pelargonium cultivars (Pelargonium × hybridum) and evolution of scent in the Pelargonium Genus. Front Plant Sci 9:1435–1435. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01435
Bohlmann J, Steele CL, Croteau R (1997) Monoterpene synthases from grand fir (Abies grandis). cDNA isolation, characterization, and functional expression of myrcene synthase, (−)-(4S)-limonene synthase, and (−)-(1S,5S)-pinene synthase. J Biol Chem 272(35):21784–21792. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.272.35.21784
Bohlmann J, Meyer-Gauen G, Croteau R (1998) Plant terpenoid synthases: molecular biology and phylogenetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(8):4126–4133
Bohlmann J, Phillips MA, Ramachandiran V, Katoh S, Croteau R (1999) cDNA cloning, characterization, and functional expression of four new monoterpene synthase members of the Tpsd gene family from grand fir (Abies grandis). Arch Biochem Biophys 368(2):232–243
Boukhris M, Ben Nasri-Ayachi M, Mezghani I, Bouaziz M, Boukhris M, Sayadi S (2013) Trichomes morphology, structure and essential oils of Pelargonium graveolens L’Hér. (Geraniaceae). Ind Crops Prod 50:604–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.08.029
Bouvier F, Suire C, d’Harlingue A, Backhaus RA, Camara B (2000) Molecular cloning of geranyl diphosphate synthase and compartmentation of monoterpene synthesis in plant cells. Plant J 24(2):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00875.x
Bouwmeester HJ, Davies JAR, Toxopeus H (1995) Enantiomeric composition of carvone, limonene, and carveols in seeds of dill and annual and biennial caraway varieties. J Agric Food Chem 43(12):3057–3064. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00060a013
Bouwmeester HJ, Gershenzon J, Konings MC, Croteau R (1998) Biosynthesis of the monoterpenes limonene and carvone in the fruit of caraway: I. Demonstration of enzyme activities and their changes with development. Plant Physiol 117(3):901–912
Bouwmeester HJ, Konings MCJM, Gershenzon J, Karp F, Croteau R (1999) Cytochrome P-450 dependent (+)-limonene-6-hydroxylation in fruits of caraway (Carum carvi). Phytochemistry 50(2):243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00516-0
Burke C, Croteau R (2002a) Geranyl diphosphate synthase from Abies grandis: cDNA isolation, functional expression, and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys 405(1):130–136
Burke C, Croteau R (2002b) Interaction with the small subunit of geranyl diphosphate synthase modifies the chain length specificity of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase to produce geranyl diphosphate. J Biol Chem 277(5):3141–3149
Burke CC, Wildung MR, Croteau R (1999) Geranyl diphosphate synthase: cloning, expression, and characterization of this prenyltransferase as a heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(23):13062–13067. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.23.13062
Byun-McKay A, Godard K-A, Toudefallah M, Martin DM, Alfaro R, King J, Bohlmann J, Plant AL (2006) Wound-induced terpene synthase gene expression in sitka spruce that exhibit resistance or susceptibility to attack by the white pine weevil. Plant Physiol 140(3):1009–1021
Calisto BM, Perez-Gil J, Bergua M, Querol-Audi J, Fita I, Imperial S (2007) Biosynthesis of isoprenoids in plants: structure of the 2C-methyl-d-erithrytol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Comparison with the bacterial enzymes. Protein Sci 16(9):2082–2088. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.072972807
Chang T-H, Hsieh F-L, Ko T-P, Teng K-H, Liang P-H, Wang AH-J (2010) Structure of a heterotetrameric geranyl pyrophosphate synthase from mint (Mentha piperita) reveals intersubunit regulation. Plant Cell 22(2):454–467
Chen F, Ro D-K, Petri J, Gershenzon J, Bohlmann J, Pichersky E, Tholl D (2004) Characterization of a root-specific Arabidopsis terpene synthase responsible for the formation of the volatile monoterpene 1, 8-cineole. Plant Physiol 135(4):1956–1966
Chen F, Tholl D, Bohlmann J, Pichersky E (2011) The family of terpene synthases in plants: a mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified throughout the kingdom. Plant J 66(1):212–229
Chen Q, Fan D, Wang G (2015) Heteromeric geranyl (geranyl) diphosphate synthase is involved in monoterpene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis flowers. Mol Plant 8(9):1434–1437
Christianson DW (2017) Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases. Chem Rev 117(17):11570–11648
Colby SM, Alonso WR, Katahira EJ, Mcgarvey DJ, Croteau R (1993) 4S-Limonene synthase from the oil glands of spearmint (Mentha-Spicata)—cDNA isolation, characterization, and bacterial expression of the catalytically active monoterpene cyclase. J Biol Chem 268(31):23016–23024
Crocoll C, Asbach J, Novak J, Gershenzon J, Degenhardt J (2010) Terpene synthases of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) and their roles in the pathway and regulation of terpene biosynthesis. Plant Mol Biol 73(6):587–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9636-1
Croteau R (1977) Site of monoterpene biosynthesis in Majorana hortensis leaves. Plant Physiol 59(3):519–520. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.59.3.519
Croteau R, Purkett PT (1989) Geranyl pyrophosphate synthase: characterization of the enzyme and evidence that this chain-length specific prenyltransferase is associated with monoterpene biosynthesis in sage (Salvia officinalis). Arch Biochem Biophys 271(2):524–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(89)90304-4
Croteau R, Venkatachalam KV (1986) Metabolism of monoterpenes: demonstration that (+)-cis-isopulegone, not piperitenone, is the key intermediate in the conversion of (−)-isopiperitenone to (+)-pulegone in peppermint (Mentha piperita). Arch Biochem Biophys 249(2):306–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(86)90007-X
Croteau RB, Davis EM, Ringer KL, Wildung MR (2005) (−)-Menthol biosynthesis and molecular genetics. Naturwissenschaften 92(12):562–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-005-0055-0
Da Fonseca CO, Landeiro JA, Clark SS, Quirico-Santos T, Da Costa Carvalho MDG, Gattass CR (2006) Recent advances in the molecular genetics of malignant gliomas disclose targets for antitumor agent perillyl alcohol. Surg Neurol 65:S2–S8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.06.030
Davis EM, Ringer KL, McConkey ME, Croteau R (2005) Monoterpene metabolism: cloning, expression, and characterization of menthone reductases from peppermint. Plant Physiol 137(3):873–881. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.053306
De Sousa DP, De Farias Nóbrega FF, De Almeida RN (2007) Influence of the chirality of (R)-(−)- and (S)-(+)-carvone in the central nervous system: a comparative study. Chirality 19(4):264–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.20379
Decarvalho C, Dafonseca M (2006) Carvone: why and how should one bother to produce this terpene. Food Chem 95(3):413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.01.003
Degenhardt J, Köllner TG, Gershenzon J (2009) Monoterpene and sesquiterpene synthases and the origin of terpene skeletal diversity in plants. Phytochemistry 70(15–16):1621–1637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.07.030
Del Terra L, Lonzarich V, Asquini E, Navarini L, Graziosi G, Liverani FS, Pallavicini A (2013) Functional characterization of three Coffea arabica L. monoterpene synthases: insights into the enzymatic machinery of coffee aroma. Phytochemistry 89:6–14
Demissie ZA, Sarker LS, Mahmoud SS (2011) Cloning and functional characterization of β-phellandrene synthase from Lavandula angustifolia. Planta 233(4):685–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1332-5
Dhar MK, Koul A, Kaul S (2013) Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase: a key enzyme in isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway and potential molecular target for drug development. New Biotechnol 30(2):114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2012.07.001
Du F-L, Yu H-L, Xu J-H, Li C-X (2014) Enhanced limonene production by optimizing the expression of limonene biosynthesis and MEP pathway genes in E. coli. Bioresour Bioprocess 1(1):10
Ducluzeau AL, Wamboldt Y, Elowsky CG, Mackenzie SA, Schuurink RC, Basset GJ (2012) Gene network reconstruction identifies the authentic trans-prenyl diphosphate synthase that makes the solanesyl moiety of ubiquinone-9 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69(2):366–375
Dudareva N, Andersson S, Orlova I, Gatto N, Reichelt M, Rhodes D, Boland W, Gershenzon J (2005) The nonmevalonate pathway supports both monoterpene and sesquiterpene formation in snapdragon flowers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(3):933–938
Dudareva N, Negre F, Nagegowda DA, Orlova I (2006) Plant volatiles: recent advances and future perspectives. Crit Rev Plant Sci 25(5):417–440. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680600899973
Erasto P, Viljoen AM (2008) Limonene—a review: biosynthetic, ecological and pharmacological relevance. Nat Prod Commun 3(7):1934578X0800300. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578x0800300728
Evergetis E, Michaelakis A, Haroutounian SA (2013) Exploitation of Apiaceae family essential oils as potent biopesticides and rich source of phellandrenes. Ind Crops Prod 41:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.04.058
Fähnrich A, Krause K, Piechulla B (2011) Product variability of the ‘cineole cassette’ monoterpene synthases of related Nicotiana species. Mol Plant 4(6):965–984. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr021
Fähnrich A, Brosemann A, Teske L, Neumann M, Piechulla B (2012) Synthesis of ‘cineole cassette’ monoterpenes in Nicotiana section Alatae: gene isolation, expression, functional characterization and phylogenetic analysis. Plant Mol Biol 79(6):537–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9933-y
Falk L, Biswas K, Boeckelmann A, Lane A, Mahmoud SS (2009) An effcient method for the micropropagation of lavenders: regeneration of a unique mutant. J Essent Oil Res 21(3):225–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2009.9700154
Frank A, Groll M (2017) The methylerythritol phosphate pathway to isoprenoids. Chem Rev 117(8):5675–5703. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00537
Fujiwara Y, Ito M (2017) Molecular cloning and characterization of a Perilla frutescens cytochrome P450 enzyme that catalyzes the later steps of perillaldehyde biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 134:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.11.009
Gershenzon J, Maffei M, Croteau R (1989) Biochemical and histochemical localization of monoterpene biosynthesis in the glandular trichomes of spearmint (Mentha spicata). Plant Physiol 89(4):1351–1357. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.89.4.1351
Giamakis A, Kretsi O, Chinou I, Spyropoulos CG (2001) Eucalyptus camaldulensis: volatiles from immature flowers and high production of 1,8-cineole and β-pinene by in vitro cultures. Phytochemistry 58(2):351–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(01)00193-5
Gordon WP, Forte AJ, McMurtry RJ, Gal J, Nelson SD (1982) Hepatotoxicity and pulmonary toxicity of pennyroyal oil and its constituent terpenes in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 65(3):413–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008x(82)90387-8
Günnewich N, Page JE, Köllner TG, Degenhardt J, Kutchan TM (2007) Functional expression and characterization of trichome-specific (−)-limonene synthase and (+)-α-pinene synthase from Cannabis sativa. Nat Prod Commun 2(3):1934578X0700200301
Halfmann C, Gu L, Zhou R (2014) Engineering cyanobacteria for the production of a cyclic hydrocarbon fuel from CO2 and H2O. Green Chem 16(6):3175–3185. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc42591f
Hall DE, Robert JA, Keeling CI, Domanski D, Quesada AL, Jancsik S, Kuzyk MA, Hamberger B, Borchers CH, Bohlmann J (2011) An integrated genomic, proteomic and biochemical analysis of (+)-3-carene biosynthesis in Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis) genotypes that are resistant or susceptible to white pine weevil. Plant J 65(6):936–948
Hampel D, Mosandl A, Wust M (2005) Biosynthesis of mono- and sesquiterpenes in carrot roots and leaves (Daucus carota L.): metabolic cross talk of cytosolic mevalonate and plastidial methylerythritol phosphate pathways. Phytochemistry 66(3):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.12.010
Hampel D, Mosandl A, Wüst M (2006) Biosynthesis of mono-and sesquiterpenes in strawberry fruits and foliage: 2H labeling studies. J Agric Food Chem 54(4):1473–1478
Hampel D, Swatski A, Mosandl A, Wüst M (2007) Biosynthesis of monoterpenes and norisoprenoids in raspberry fruits (Rubus idaeus L.): the role of cytosolic mevalonate and plastidial methylerythritol phosphate pathway. J Agric Food Chem 55(22):9296–9304. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf071311x
Hsu C-Y, Huang P-L, Chen C-M, Mao C-T, Chaw S-M (2012) Tangy Scent in Toona sinensis (Meliaceae) leaflets: isolation, functional characterization, and regulation of TsTPS1 and TsTPS2, two key terpene synthase genes in the biosynthesis of the scent compound. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13(15):2721–2732
Huang K-F, Lee Y-R, Tseng Y-H, Wang S-Y, Chu F-H (2015) Cloning and functional characterization of a monoterpene synthase gene from Eleutherococcus trifoliatus. Holzforschung 69(2):163–171
Hyatt DC, Youn BY, Zhao YX, Santhamma B, Coates RM, Croteau RB, Kang CH (2007) Structure of limonene synthase, a simple model for terpenoid cyclase catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(13):5360–5365
Iijima Y, Davidovich-Rikanati R, Fridman E, Gang DR, Bar E, Lewinsohn E, Pichersky E (2004) The biochemical and molecular basis for the divergent patterns in the biosynthesis of terpenes and phenylpropenes in the peltate glands of three cultivars of basil. Plant Physiol 136(3):3724–3736
Jones CG, Keeling CI, Ghisalberti EL, Barbour EL, Plummer JA, Bohlmann J (2008) Isolation of cDNAs and functional characterisation of two multi-product terpene synthase enzymes from sandalwood, Santalum album L. Arch Biochem Biophys 477(1):121–130
Jongedijk E, Müller S, Van Dijk AD, Schijlen E, Champagne A, Boutry M, Levisson M, Van Der Krol S, Bouwmeester H, Beekwilder J (2020) Novel routes towards bioplastics from plants: elucidation of the methylperillate biosynthesis pathway from Salvia dorisiana trichomes. J Exp Bot 71(10):3052–3065
Kamatou GPP, Vermaak I, Viljoen AM, Lawrence BM (2013) Menthol: a simple monoterpene with remarkable biological properties. Phytochemistry 96:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.08.005
Katoh S, Hyatt D, Croteau R (2004) Altering product outcome in Abies grandis (−)-limonene synthase and (−)-limonene/(−)-α-pinene synthase by domain swapping and directed mutagenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 425(1):65–76
Keszei A, Brubaker CL, Carter R, Köllner T, Degenhardt J, Foley WJ (2010) Functional and evolutionary relationships between terpene synthases from Australian Myrtaceae. Phytochemistry 71(8–9):844–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.03.013
Ketoh GK, Koumaglo HK, Glitho IA, Huignard J (2006) Comparative effects of Cymbopogon schoenanthus essential oil and piperitone on Callosobruchus maculatus development. Fitoterapia 77(7–8):506–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2006.05.031
Khojasteh-Bakht SC, Chen W, Koenigs LL, Peter RM, Nelson SD (1999) Metabolism of (R)-(+)-pulegone and (R)-(+)-menthofuran by human liver cytochrome P-450s: evidence for formation of a furan epoxide. Drug Metab Dispos 27(5):574–580
Kim N-S, Lee D-S (2004) Headspace solid-phase microextraction for characterization of fragrances of lemon verbena (Aloysia triphylla) by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 27(1–2):96–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200301603
Kjeldsen F, Christensen LP, Edelenbos M (2003) Changes in volatile compounds of carrots (Daucus carota L.) during refrigerated and frozen storage. J Agric Food Chem 51(18):5400–5407. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030212q
Köllner TG, Schnee C, Li S, Svatoš A, Schneider B, Gershenzon J, Degenhardt J (2008) Protonation of a neutral (S)-β-bisabolene intermediate is involved in (S)-β-macrocarpene formation by the maize sesquiterpene synthases TPS6 and TPS11. J Biol Chem 283(30):20779–20788
Korman TP, Opgenorth PH, Bowie JU (2017) A synthetic biochemistry platform for cell free production of monoterpenes from glucose. Nat Commun 8(1):1–8
Kulkarni R, Pandit S, Chidley H, Nagel R, Schmidt A, Gershenzon J, Pujari K, Giri A, Gupta V (2013) Characterization of three novel isoprenyl diphosphate synthases from the terpenoid rich mango fruit. Plant Physiol Biochem 71:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.07.006
Kumar RP, Morehouse BR, Matos JO, Malik K, Lin H, Krauss IJ, Oprian DD (2017) Structural characterization of early Michaelis complexes in the reaction catalyzed by (+)-limonene synthase from Citrus sinensis using fluorinated substrate analogues. Biochemistry 56(12):1716–1725
Kuzuyama T, Takahashi S, Watanabe H, Seto H (1998) Direct formation of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate from 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate by 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, a new enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway to isopentenyl diphosphate. Tetrahedron Lett 39(25):4509–4512. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-4039(98)00802-8
Landmann C, Fink B, Festner M, Dregus M, Engel K-H, Schwab W (2007) Cloning and functional characterization of three terpene synthases from lavender (Lavandula angustifolia). Arch Biochem Biophys 465(2):417–429
Lange BM (2015a) Biosynthesis and biotechnology of high-value p-menthane monoterpenes, including menthol, carvone, and limonene. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 148:319–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2014_289
Lange BM (2015b) The evolution of plant secretory structures and the emergence of terpenoid chemical diversity. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66(1):null. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043014-114639
Lange BM, Srividya N (2019) Enzymology of monoterpene functionalization in glandular trichomes. J Exp Bot 70(4):1095–1108
Lange BM, Mahmoud SS, Wildung MR, Turner GW, Davis EM, Lange I, Baker RC, Boydston RA, Croteau RB (2011) Improving peppermint essential oil yield and composition by metabolic engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(41):16944–16949. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111558108
Laska M, Teubner P (1999) Olfactory discrimination ability of human subjects for ten pairs of enantiomers. Chem Senses 24(2):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/24.2.161
Laule O, Furholz A, Chang HS, Zhu T, Wang X, Heifetz PB, Gruissem W, Lange BM (2003) Crosstalk between cytosolic and plastidial pathways of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(11):6866–6871
Lee S, Chappell J (2008) Biochemical and genomic characterization of terpene synthases in Magnolia grandiflora. Plant Physiol 147(3):1017–1033
Leitereg TJ, Guadagni DG, Harris J, Mon TR, Teranishi R (1971) Evidence for the difference between the odours of the optical isomers (+)- and (−)-carvone. Nature 230(5294):455–456. https://doi.org/10.1038/230455a0
Lewinsohn E, Gijzen M, Croteau RB (1992) Regulation of monoterpene biosynthesis in conifer defense. In: Regulation of isopentenoid metabolism, ACS symposium series, vol 497. American Chemical Society, pp 8–17. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1992-0497.ch002
Li M, Hou F, Wu T, Jiang X, Li F, Liu H, Xian M, Zhang H (2020) Recent advances of metabolic engineering strategies in natural isoprenoid production using cell factories. Nat Prod Rep 37(1):80–99. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NP00016J
Lin R, Tian J, Huang G, Li T, Li F (2002) Analysis of menthol in three traditional Chinese medicinal herbs and their compound formulation by GC–MS. Biomed Chromatogr 16(3):229–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.131
Lin C, Shen B, Xu Z, Köllner TG, Degenhardt J, Dooner HK (2008) Characterization of the monoterpene synthase gene tps26, the ortholog of a gene induced by insect herbivory in maize. Plant Physiol 146(3):940–951
Liu B, Fan L, Balakrishna S, Sui A, Morris JB, Jordt S-E (2013) TRPM8 is the principal mediator of menthol-induced analgesia of acute and inflammatory pain. Pain 154(10):2169–2177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.043
Liu H, Wang Y, Tang Q, Kong W, Chung W-J, Lu T (2014) MEP pathway-mediated isopentenol production in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Factories 13(1):135. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0135-y
Liu C, Srividya N, Parrish AN, Yue W, Shan M, Wu Q, Lange BM (2018) Morphology of glandular trichomes of Japanese catnip (Schizonepeta tenuifolia Briquet) and developmental dynamics of their secretory activity. Phytochemistry 150:23–30
Lota M-L, De Rocca Serra D, Tomi F, Jacquemond C, Casanova J (2002) Volatile components of peel and leaf oils of lemon and lime species. J Agric Food Chem 50(4):796–805. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010924l
Lücker J, El Tamer MK, Schwab W, Verstappen FW, van der Plas LH, Bouwmeester HJ, Verhoeven HA (2002) Monoterpene biosynthesis in lemon (Citrus limon) cDNA isolation and functional analysis of four monoterpene synthases. Eur J Biochem 269(13):3160–3171
Lücker J, Schwab W, Franssen MC, Van Der Plas LH, Bouwmeester HJ, Verhoeven HA (2004) Metabolic engineering of monoterpene biosynthesis: two-step production of (+)-trans-isopiperitenol by tobacco. Plant J 39(1):135–145
Lupien S, Karp F, Wildung M, Croteau R (1999) Regiospecific cytochrome P450 limonene hydroxylases from mint (Mentha) species: cDNA isolation, characterization, and functional expression of (−)-4S-limonene-3-hydroxylase and (−)-4S-limonene-6-hydroxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys 368(1):181–192
Macleod G, Ames JM (1989) Volatile components of celery and celeriac. Phytochemistry 28(7):1817–1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(00)97866-x
Mahmoud SS, Croteau RB (2001) Metabolic engineering of essential oil yield and composition in mint by altering expression of deoxyxylulose phosphate reductoisomerase and menthofuran synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(15):8915–8920
Mahmoud SS, Croteau RB (2003) Menthofuran regulates essential oil biosynthesis in peppermint by controlling a downstream monoterpene reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(24):14481–14486. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2436325100
Maleknia SD, Bell TL, Adams MA (2009) Eucalypt smoke and wildfires: temperature dependent emissions of biogenic volatile organic compounds. Int J Mass Spectrom 279(2–3):126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2008.10.027
Martin DM, Bohlmann J (2004) Identification of Vitis vinifera (−)-α-terpineol synthase by in silico screening of full-length cDNA ESTs and functional characterization of recombinant terpene synthase. Phytochemistry 65(9):1223–1229
Martin DM, Faldt J, Bohlmann J (2004) Functional characterization of nine Norway spruce TPS genes and evolution of gymnosperm terpene synthases of the TPS-d subfamily. Plant Physiol 135(4):1908–1927
Maruyama T, Ito M, Kiuchi F, Honda G (2001) Molecular cloning, functional expression and characterization of d-limonene synthase from Schizonepeta tenuifolia. Biol Pharm Bull 24(4):373–377
Maruyama T, Saeki D, Ito M, Honda G (2002) Molecular cloning, functional expression and characterization of d-limonene synthase from Agastache rugosa. Biol Pharm Bull 25(5):661–665
Matsushima A, Sato Y, Otsuka M, Watanabe T, Yamamoto H, Hirata T (2008) An enone reductase from Nicotiana tabacum: cDNA cloning, expression in Escherichia coli, and reduction of enones with the recombinant proteins. Bioorgan Chem 36(1):23–28
Mau CJD, Karp F, Ito M, Honda G, Croteau RB (2010) A candidate cDNA clone for (−)-limonene-7-hydroxylase from Perilla frutescens. Phytochemistry 71(4):373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.12.002
May B, Lange BM, Wüst M (2013) Biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes in grape berry exocarp of Vitis vinifera L.: evidence for a transport of farnesyl diphosphate precursors from plastids to the cytosol. Phytochemistry 95:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.07.021
McCaskill D, Croteau R (1995) Monoterpene and sesquiterpene biosynthesis in glandular trichomes of peppermint (Mentha × piperita) rely exclusively on plastid-derived isopentenyl diphosphate. Planta 197(1):49–56
McCaskill D, Gershenzon J, Croteau R (1992) Morphology and monoterpene biosynthetic capabilities of secretory cell clusters isolated from glandular trichomes of peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). Planta 187(4):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00199962
McConkey ME, Gershenzon J, Croteau RB (2000) Developmental regulation of monoterpene biosynthesis in the glandular trichomes of peppermint. Plant Physiol 122(1):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.1.215
Miller DR (2007) Limonene: attractant kairomone for white pine cone beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in an eastern white pine seed orchard in western North Carolina. J Econ Entomol 100(3):815–822. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/100.3.815
Mkaddem M, Bouajila J, Ennajar M, Lebrihi A, Mathieu F, Romdhane M (2009) Chemical composition and antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Mentha (longifolia L. and viridis) essential oils. J Food Sci 74(7):M358–M363. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01272.x
Morehouse BR, Kumar RP, Matos JO, Olsen SN, Entova S, Oprian DD (2017) Functional and structural characterization of a (+)-limonene synthase from Citrus sinensis. Biochemistry 56(12):1706–1715
Morehouse BR, Kumar RP, Matos JO, Yu Q, Bannister A, Malik K, Temme JS, Krauss IJ, Oprian DD (2019) Direct evidence of an enzyme-generated LPP intermediate in (+)-limonene synthase using a fluorinated GPP substrate analog. ACS Chem Biol 14(9):2035–2043. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00514
Muñoz-Bertomeu J, Arrillaga I, Ros R, Segura J (2006) Up-regulation of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase enhances production of essential oils in transgenic spike lavender. Plant Physiol 142(3):890–900
Ntalli NG, Ferrari F, Giannakou I, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U (2010) Phytochemistry and nematicidal activity of the essential oils from 8 Greek Lamiaceae aromatic plants and 13 terpene components. J Agric Food Chem 58(13):7856–7863. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf100797m
Obadiah A, Kannan R, Ramesh P, Ramasubbu A, Kumar SV (2012) Isolation of carvone and phellandrene from Murraya koenigii and study of their antioxidant activity. Chem Nat Compd 48(1):149–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-012-0186-4
Paetzold H, Garms S, Bartram S, Wieczorek J, Urós-Gracia E-M, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Boland W, Strack D, Hause B, Walter MH (2010) The isogene 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase 2 controls isoprenoid profiles, precursor pathway allocation, and density of tomato trichomes. Mol Plant 3(5):904–916. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq032
Patel T, Ishiuji Y, Yosipovitch G (2007) Menthol: a refreshing look at this ancient compound. J Am Acad Dermatol 57(5):873–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.04.008
Phillips MA, Croteau RB (1999) Resin-based defenses in conifers. Trends Plant Sci 4(5):184–190
Phillips MA, Savage TJ, Croteau R (1999) Monoterpene synthases of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) produce pinene isomers and enantiomers. Arch Biochem Biophys 372(1):197–204. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1999.1467
Phillips MA, Wildung MR, Williams DC, Hyatt DC, Croteau R (2003) cDNA isolation, functional expression, and characterization of (+)-alpha-pinene synthase and (−)-alpha-pinene synthase from loblolly pine (Pinus taeda): stereocontrol in pinene biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 411(2):267–276
Phillips MA, Walter MH, Ralph S, Dabrowska P, Luck K, Urós EM, Boland W, Strack D, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Bohlmann J, Gershenzon J (2007) Functional identification and differential expression of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase in induced terpenoid resin formation of Norway spruce (Picea abies). Plant Mol Biol 65(3):243–257
Phillips M, Leon P, Boronat A, Rodriguezconcepcion M (2008) The plastidial MEP pathway: unified nomenclature and resources. Trends Plant Sci 13(12):619–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.09.003
Polichuk DR, Zhang Y, Reed DW, Schmidt JF, Covello PS (2010) A glandular trichome-specific monoterpene alcohol dehydrogenase from Artemisia annua. Phytochemistry 71(11–12):1264–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.04.026
Poulose AJ, Croteau R (1978) Biosynthesis of aromatic monoterpenes: conversion of γ-terpinene to p-cymene and thymol in Thymus vulgaris L. Arch Biochem Biophys 187(2):307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(78)90039-5
Qiao Y, Xie B, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Fan G, Yao X, Pan S (2008) Characterization of aroma active compounds in fruit juice and peel oil of Jinchen sweet orange fruit (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) by GC–MS and GC–O. Molecules 13(6):1333–1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13061333
Rai A, Smita SS, Singh AK, Shanker K, Nagegowda DA (2013) Heteromeric and homomeric geranyl diphosphate synthases from Catharanthus roseus and their role in monoterpene indole alkaloid biosynthesis. Mol Plant 6(5):1531–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst058
Rajaonarivony JI, Gershenzon J, Croteau R (1992a) Characterization and mechanism of (4S)-limonene synthase, a monoterpene cyclase from the glandular trichomes of peppermint (Mentha × piperita). Arch Biochem Biophys 296(1):49–57
Rajaonarivony JIM, Gershenzon J, Miyazaki J, Croteau R (1992b) Evidence for an essential histidine residue in 4S-limonene synthase and other terpene cyclases. Arch Biochem Biophys 299(1):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(92)90246-S
Rehman R, Hanif MA, Mushtaq Z, Al-Sadi AM (2016) Biosynthesis of essential oils in aromatic plants: a review. Food Rev Int 32(2):117–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2015.1057841
Riddle JM (1991) Oral contraceptives and early-term abortifacients during classical antiquity and the Middle Ages. Past Present 132(1):3–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/past/132.1.3
Ringer KL, McConkey ME, Davis EM, Rushing GW, Croteau R (2003) Monoterpene double-bond reductases of the (−)-menthol biosynthetic pathway: isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding (−)-isopiperitenone reductase and (+)-pulegone reductase of peppermint. Arch Biochem Biophys 418(1):80–92
Ringer KL, Davis EM, Croteau R (2005) Monoterpene metabolism. Cloning, expression, and characterization of (−)-isopiperitenol/(−)-carveol dehydrogenase of peppermint and spearmint. Plant Physiol 137(3):863–872. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.053298
Roeder S, Hartmann A-M, Effmert U, Piechulla B (2007) Regulation of simultaneous synthesis of floral scent terpenoids by the 1, 8-cineole synthase of Nicotiana suaveolens. Plant Mol Biol 65(1–2):107–124
Rohdich F, Hecht S, Gärtner K, Adam P, Krieger C, Amslinger S, Arigoni D, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2002) Studies on the nonmevalonate terpene biosynthetic pathway: metabolic role of IspH (LytB) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(3):1158–1163. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.032658999
Ruan J-X, Li J-X, Fang X, Wang L-J, Hu W-L, Chen X-Y, Yang C-Q (2016) Isolation and characterization of three new monoterpene synthases from Artemisia annua. Front Plant Sci 7:638. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00638
Ruiz-Sola MÁ, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2012) Carotenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis: a colorful pathway. Arabidopsis Book 10:e0158. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0158
Schilmiller AL, Schauvinhold I, Larson M, Xu R, Charbonneau AL, Schmidt A, Wilkerson C, Last RL, Pichersky E (2009) Monoterpenes in the glandular trichomes of tomato are synthesized from a neryl diphosphate precursor rather than geranyl diphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(26):10865–10870. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904113106
Schmidt A, Gershenzon J (2008) Cloning and characterization of two different types of geranyl diphosphate synthases from Norway spruce (Picea abies). Phytochemistry 69(1):49–57
Seemann M, Wegner P, Schunemann V, Bui BTS, Wolff M, Marquet A, Trautwein AX, Rohmer M (2005) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in chloroplasts via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway: the (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase (GcpE) from Arabidopsis thaliana is a 4Fe–4S protein. J Biol Inorg Chem 10(2):131–137
Seemann M, Bui BTS, Wolff M, Miginlac-Maslow M, Rohmer M (2006) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in plant chloroplasts via the MEP pathway: direct thylakoid/ferredoxin-dependent photoreduction of GcpE/IspG. FEBS Lett 580(6):1547–1552
Sharkey TD, Preiser AL, Weraduwage SM, Gog L (2020) Source of 12C in Calvin–Benson cycle intermediates and isoprene emitted from plant leaves fed with 13CO2. Biochem J 477(17):3237–3252
Shimada T, Endo T, Fujii H, Hara M, Ueda T, Kita M, Omura M (2004) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of four monoterpene synthase genes from Citrus unshiu Marc. Plant Sci 166(1):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2003.07.006
Shimada T, Endo T, Fujii H, Omura M (2005) Isolation and characterization of a new d-limonene synthase gene with a different expression pattern in Citrus unshiu Marc. Sci Hortic 105(4):507–512
Singh AK, Raina VK, Naqvi AA, Patra NK, Kumar B, Ram P, Khanuja SPS (2005) Essential oil composition and chemoarrays of menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L. f. piperascens Malinvaud ex. Holmes) cultivars. Flavour Fragr J 20(3):302–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.1417
Srividya N, Davis EM, Croteau RB, Lange BM (2015) Functional analysis of (4S)-limonene synthase mutants reveals determinants of catalytic outcome in a model monoterpene synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(11):3332–3337
Srividya N, Lange I, Lange BM (2020) Determinants of enantiospecificity in limonene synthases. Biochemistry 59(17):1661–1664. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00206
Tamura H, Fukuda Y, Padrayuttawat A (1996) Characterization of citrus aroma quality by odor threshold values. In: Biotechnology for improved foods and flavors, ACS symposium series, vol 637. American Chemical Society, pp 282–294. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1996-0637.ch027
Trapp SC, Croteau RB (2001) Genomic organization of plant terpene synthases and molecular evolutionary implications. Genetics 158(2):811–832
Turner GW, Croteau R (2004) Organization of monoterpene biosynthesis in Mentha. Immunocytochemical localizations of geranyl diphosphate synthase, limonene-6-hydroxylase, isopiperitenol dehydrogenase, and pulegone reductase. Plant Physiol 136(4):4215–4227
Turner G, Gershenzon J, Nielson EE, Froehlich JE, Croteau R (1999) Limonene synthase, the enzyme responsible for monoterpene biosynthesis in peppermint, is localized to leucoplasts of oil gland secretory cells. Plant Physiol 120(3):879–886
Turner GW, Gershenzon J, Croteau RB (2000) Distribution of peltate glandular trichomes on developing leaves of peppermint. Plant Physiol 124(2):655. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.124.2.655
Ueoka H, Sasaki K, Miyawaki T, Ichino T, Tatsumi K, Suzuki S, Yamamoto H, Sakurai N, Suzuki H, Shibata D, Yazaki K (2020) A cytosol-localized geranyl diphosphate synthase from Lithospermum erythrorhizon and its molecular evolution. Plant Physiol 182(4):1933. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00999
Van Schie CCN, Ament K, Schmidt A, Lange T, Haring MA, Schuurink RC (2007) Geranyl diphosphate synthase is required for biosynthesis of gibberellins. Plant J 52(4):752–762. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03273.x
Vanek T, Valterova I, Vaisar T (1999) Biotransformation of (S)-(−)- and (R)-(+)-limonene using Solanum aviculare and Dioscorea deltoidea plant cells. Phytochemistry 50(8):1347–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00659-1
Walter MH, Hans J, Strack D (2002) Two distantly related genes encoding 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthases: differential regulation in shoots and apocarotenoid-accumulating mycorrhizal roots. Plant J 31(3):243–254. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01352.x
Wang G, Dixon RA (2009) Heterodimeric geranyl(geranyl)diphosphate synthase from hop (Humulus lupulus) and the evolution of monoterpene biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(24):9914–9919. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904069106
Wang X, Jia C, Wan H (1995) The direct chiral separation of some optically active compounds in essential oils by multidimensional gas chromatography. J Chromatogr Sci 33(1):22–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/33.1.22
Williams DC, McGarvey DJ, Katahira EJ, Croteau R (1998) Truncation of limonene synthase preprotein provides a fully active ‘pseudomature’ form of this monoterpene cyclase and reveals the function of the amino-terminal arginine pair. Biochemistry 37(35):12213–12220
Wise ML, Savage TJ, Katahira E, Croteau R (1998) Monoterpene synthases from common sage (Salvia officinalis)—cDNA isolation, characterization, and functional expression of (+)-sabinene synthase, 1,8-cineole synthase, and (+)-bornyl diphosphate synthase. J Biol Chem 273(24):14891–14899
Wright LP, Rohwer JM, Ghirardo A, Hammerbacher A, Ortiz-Alcaide M, Raguschke B, Schnitzler J-P, Gershenzon J, Phillips MA (2014) Deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate synthase controls flux through the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 165(4):1488–1504. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.245191
Xu J, Ai Y, Wang J, Xu J, Zhang Y, Yang D (2017) Converting S-limonene synthase to pinene or phellandrene synthases reveals the plasticity of the active site. Phytochemistry 137:34–41
Yan Z, Qin Y, Zheng J, Leng P, Hu Z (2018) Gene cloning and expression analysis of limonene synthase in Syringa oblata and S. oblata var. alba. J For Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0697-3
Yuba A, Yazaki K, Tabata M, Honda G, Croteau R (1996) cDNA cloning, characterization, and functional expression of 4S-(−)-limonene synthase from Perilla frutescens. Arch Biochem Biophys 332(2):280–287. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1996.0343
Zebec Z, Wilkes J, Jervis AJ, Scrutton NS, Takano E, Breitling R (2016) Towards synthesis of monoterpenes and derivatives using synthetic biology. Curr Opin Chem Biol 34:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.06.002
Zhang C, Hong K (2020) Production of terpenoids by synthetic biology approaches. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00347
Zheljazkov VD, Cantrell CL, Astatkie T, Hristov A (2010) Yield, content, and composition of peppermint and spearmints as a function of harvesting time and drying. J Agric Food Chem 58(21):11400–11407. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1022077
Zoghbi MDGB, Andrade EHA, Santos AS, Silva MHL, Maia JGS (1998) Essential oils of Lippia alba (Mill.) N. E. Br growing wild in the Brazilian Amazon. Flavour Fragr J 13(1):47–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1099-1026(199801/02)13:1<47:aid-ffj690>3.0.co;2-0
Zulak KG, Bohlmann J (2010) Terpenoid biosynthesis and specialized vascular cells of conifer defense. J Integr Plant Biol 52(1):86–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00910.x
Funding
This work was supported by a Discovery grant provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (RGPIN-2017-06400) to M.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MB and MP wrote drafts of the manuscript, MP revised the manuscript, and MB and MP designed figures. All photographs constitute original work by the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergman, M.E., Phillips, M.A. Structural diversity and biosynthesis of plant derived p-menthane monoterpenes. Phytochem Rev 20, 433–459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-020-09726-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-020-09726-0