Abstract
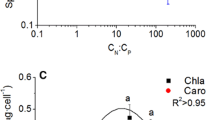
The effects of the atomic ratio of N to P (N:P) on the response of Alexandrium tamarense to UV radiation (UVR) were investigated in this study. Artificial sea water of 5 different N:P ratios for indoor culture and with 3 different N:P ratios for outdoor culture were used for a period of 14 and 9 d, respectively. The short-term response of cells to UVR was analyzed using a fluorometer. Cells that acclimated to nutrient conditions at the Redfield value (16:1) showed the fastest growth rate and highest pigment concentrations in both indoor and outdoor conditions, compared to those acclimated to the non-Redfield conditions. Moreover, these physiological parameters were functions of the N:P ratio according to a two-order equation (y = a + bx + cx2, R2>0.95). The fluorescence data of indoor cultures showed that A. tamarense grown at 16:1 (N:P) exhibited the greatest ratio of repair rate/damage rate (r/k) and minimum level of UVR-induced inhibition. among those grown at all of the N:P ratios following UVR exposure. Outdoor cultures had the same patterns of fluorescence as indoor cultures, but the less UVR-induced inhibitions were detected compared the former with the latter. The following three parameters, the r/k, level of inhibition caused by the two radiation treatments following 60 min of exposure (PAR and PAB, respectively), and level of UVR-induced inhibition, were also functions of the N:P ratio according to the two-order equation (R2>0.96). Further, there was a negative correlation between UVR-induced inhibition and the r/k ratio. In summary, the Redfield value (16:1) was the optimal nutrient stoichiometry for the protection of A. tamarense against the deleterious effects of UVR. Results were not impacted by previous light history experienced by cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASW:
-
artificial sea water
- Car:
-
carotenoids
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- DIN:
-
the dissolved inorganic N
- DIP:
-
the dissolved inorganic P
- k:
-
damage rate constant
- OD:
-
optical density
- P:
-
phosphorus
- PAB:
-
photosynthetically active radiation plus UV-A and UV-B radiation
- PMA:
-
personal measurement assistant
- PSIN:
-
photon system instruments
- r:
-
repair rate constant
- UVabc :
-
ultraviolet absorbing compounds
- UVR:
-
ultraviolet radiation
- Y’:
-
effective photochemical efficiency of PSII
References
Anderson D.M., Glibert P.M., Burkholder J.M.: Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences.–Estuar. Coast. 25: 704–726, 2002.
Beardall J., Sobrino C., Stojkovic S.: Interactions between the impacts of ultraviolet radiation, elevated CO2, and nutrient limitation on marine primary producers. - Photoch. Photobio. Sci. 8: 1257–1265, 2009.
Behrenfeld M.J., Lee H., Small L.F.: Interactions between nutritional status and long-term responses of ultraviolet-B radiation stress in a marine diatom. - Mar. Biol. 118: 523–530, 1994.
Berges J.A., Franklin D.J., Harrison P.J.: Evolution of an artificial seawater medium improvements in enriched seawater, artificial water over the past two decades. - J. Phycol. 37: 1138–1145, 2001.
Brooks A.: Effects of phosphorus nutrition on ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase activation, photosynthetic quantum yield and amounts of Calvin-cycle metabolites in spinach leaves. - Aust. J. Plant. Physiol. 13: 221–237, 1986.
Cabrerizo M., Carrillo P., Villafañe V.E. et al.: Current and predicted global change impacts of UVR, temperature and nutrient inputs on photosynthesis and respiration of key marine phytoplankton groups. - J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 461: 371–380, 2014.
Chai C., Yu Z.M., Song X.X. et al.: The status and characteristics of eutrophication in the Yangtze River (Changjiang) estuary and the adjacent East China Sea, China. - Hydrobiologia 563: 313–328, 2006.
Davies J.P., Grossman A.R.: Responses to deficiencies in macronutrients[M]. - In: Rochaix J.D., Golschmidt-Clermont M., Merchant S. (ed.): The Molecular Biology of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria in Chlamydomonas. Pp 613–633. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht 1998.
Dortch Q., Whitledge T.E.: Does nitrogen or silicon limit plankton production in the Mississippi river Plume and nearby regions. - Cont. Shelf Res. 12: 1293–1309, 1992.
Garcia-Pichel F.: A model for internal self-shading in planktonic organisms and its implications for the usefulness of ultraviolet sunscreens. - Limnol. Oceanogr. 39: 1704–1717, 1994.
Geider R.J., La Roche J., Greene R.M. et al.: Response of the photosynthetic apparatus of Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae) to nitrate, phosphate and iron starvation. - J. Phycol. 29: 755–766, 1993.
Geider R.J., Macintyre H.L., Graziano L.M. et al.: Responses of the photosynthetic apparatus of Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) to nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. - Eur. J. Phycol. 33: 315–332, 1998.
Genty B.E., Harbinson J., Baker N.R.: Relative quantum efficiencies of the two photosystems of leaves in photorespiratory and non-photorespiratory conditions. - Plant Physiol. Bioch. 28:1–10, 1989.
Giordano M., Hell R.: Mineral nutrition in photolithotrophs: cellular mechanisms controlling growth in terrestrial and aquatic habitats.–In: Pandalai S.G. (ed.): Recent Research Developments in Plant Physiology 2. Pp. 95–123. Research Signpost, Trivandrum 2001.
Glibert P.M., Burkholder J.M.: The complex relationships between increasing fertilization of the earth, coastal eutrophication and proliferation of harmful algal blooms. - In: Graneli E., Turner J. (ed.): Ecology of Harmful Algae. Pp 34–354, Springer-Verlag, Berlin 2006.
Guan W.C., Gao K.S.: Impacts of UV radiation on photosynthesis and growth of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyceae). - Environ. Exp. Bot. 67: 502–508, 2010.
Guan W.C., Li P., Jian J.B. et al.: Effects of solar ultraviolet radiation on photochemical efficiency of Chaetoceros curvisetus (Bacillariophyceae). - Acta Physiol. Plant. 33: 979–986, 2011.
Guan W.C., Lu S.H.: The short-and long-term response of Scrippsiella trochoidea (Pyrrophyta) to solar ultraviolet radiation. - Photosythetica 48: 287–293, 2010.
Guillard R.R., Ryther J.H.: Studies on marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana (Hustedt) and Detonula confervaceae (Cleve). - Can. J Microbiol. 8: 229–239, 1962.
Heraud P., Beardall J.: Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence during exposure of Dunaliella tertiolecta to UV radiation indicate a dynamic interaction between damage and repair processes. - Photosynth. Res. 63: 123–134, 2000.
Hodgkiss I.J., Ho K.C.: Are changes in N:P ratios in coastal waters the key to increased red tide blooms. - Hydrobiologia 352: 141–147, 1997.
Jaworski G.H.M., Talling J.F., Heaney S.I.: Potassium dependence and phytoplankton ecology: an experimental study. - Freshwater Biol. 48: 833–840, 2003.
John E.H., Flynn K.J.: Growth dynamics and toxicity of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceac): the Effects of changing N:P supply ratios on internal toxin and nutrient levels. - Eur. J. Phyco1. 35: 11–23, 2000.
Justic D., Rabalais N.N., Turner R.E.: Stoichiometric nutrient balance and origin of coastal eutrophication.–Mar. Pollut. Bull. 30: 41–46, 1995.
Lagus A., Suomela J., Weithoff G. et al.: Species-specific differences in phytoplankton responses to N and P enrichments and the N:P ratio in the Archipelago Sea, northern Baltic Sea. - J. Plankton Res. 26: 779–798, 2004.
Lesser M.P., Cullen J.J., Neale P.J.: Carbon uptake in a marine diatom during acute exposure to ultraviolet B radiation: Relative importance of damage and repair. - J. Phycol. 30: 183–192, 1994.
Lippemeier S., Hintze R., Vanselow K.H. et al.: In-line recording of PAM fluorescence of phytoplankton cultures as a new tool for studying effects of fluctuating nutrient supply of photosynthesis. - Eur. J. Phycol. 36: 89–100, 2001.
Litchman E., Neale P.J., Banaszak A.T.: Increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation in nitrogen-limited dinoflagellates: photoprotection and repair. - Limnol. Oceanogr. 47: 86–94, 2002.
Marcoval M.A., Villafañe V.E., Helbling E.W.: Combined effects of solar ultraviolet radiation and nutrients addition on growth, biomass and taxonomic composition of coastal marine phytoplankton communities of Patagonia. - J. Photoch. Photobio. B 91: 157–166, 2008.
Marcoval M.A., Villafañe V.E., Helbling E.W.: Interactive effects of ultraviolet radiation and nutrient addition on growth and photosynthesis performance of four species of marine phytoplankton. - J. Photoch. Photobio. B 89: 78–87, 2007.
Porra R.J.: The chequered history of the development and use of simultaneous equations for the accurate determination of chlorophylls a and b. - Photosynth. Res. 73: 149–156, 2002.
Redfield A.C.: The biologycal control of chemical factors in the environment.–Am. Sci. 46: 205–221, 1958.
Reynolds C.S.: Ecology of Phytoplankton. Pp.172. Cambridge University Press, New York 2006.
Rhee G.Y.: Effects of N:P atomic ratios and nitrate limitation on algal growth, cell composition, and nitrate uptake. - Limnol. Oceanogr. 23: 10–25, 1978.
Ryther J.K., Dunstan W.M.: Nitrogen, phosphorus and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. - Science 171: 1008–1013, 1971.
Shelly K., Heraud P., Beardall J.: Nitrogen limitation in Dunaliella tertiolecta Butcher (Chlorophyceae) leads to increased susceptibility to damage by ultraviolet-B radiation but also increased repair capacity. - J. Phycol. 38: 713–720, 2002.
Shelly K., Roberts S., Heraud P., Beardall J.: Interactions between UVB exposure and phosphorus nutrition. 1. Effects on growth, phosphorus uptake, and chlorophyll fluorescence. - J. Phycol. 41: 1204–1211, 2005.
Shen Z.L., Liu Q., Zhang S.M. et al.: A nitrogen budget of the Changjiang river catchment. - Ambio 32: 65–69, 2003.
Strickland J.D.H., Parsons T.R.: A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis, Pigment Analysis. Pp. 185–190. Fisheries Research Board of Canada Bulletin No. 167, Ottawa 1972.
Tang D.L., Di B.P., Wei G.F. et al.: Spatial, seasonal and species variations of harmful algal blooms in the South Yellow Sea and East China Sea. - Hydrobiologia 568: 245–253, 2006.
Veen A., Reuvers M., Ronçak P. Effects of acute and chronic UV-B exposure on a green alga: a continuous culture study using a computer-control dynamic light regime. - Plant Ecol. 128: 28–40, 1997.
Villafañe V.E., Sundbäck K., Figueroa F.L. et al.: Photosynthesis in the aquatic environment as affected by ultraviolet radiation, -In Helbling E.W., Zagarese H. (ed.): UV Effects in Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystems. Pp. 357–397. Roy. Soc. Chemistry, Cambridge 2003.
Weers P.M.M., Gulati R.D.: Growth and reproduction of Daphnia galeata in response to changes in fatty acids, phosphorus, and nitrogen in Chlamydomonasreinhardtii. - Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 1584–1589, 1997.
Yan W.J., Zhang S.: The composition and bioavailability of phosphorus transport through the Changjiang (Yangtze) River during the 1998 flood. - Biogeochemistry 65: 179–194, 2003.
Zhang J., Liu S.M., Ren J.L. et al.: Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and reevaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf. - Prog. Oceanogr. 74: 449–478, 2007.
Zhao D.L., Oosterhuis D.M., Bednarz C.W.: Influence of potassium deficiency on photosynthesis, chlorophyll content, and chloroplast ultrastructure of cotton plants. - Photosynthetica 39: 103–109, 2001.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation for Young Scholars of China (No. 41306106), the Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation (No. LY16D060005), and the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2014F10005). We also thank the comments and suggestions of anonymous reviewers that helped us to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, W., Li, L. Atomic ratio of N to P influences the impact of UV irradiance on photosynthesis and growth in a marine dinoflagellate, Alexandrium tamarense . Photosynthetica 55, 501–509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-016-0670-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-016-0670-3