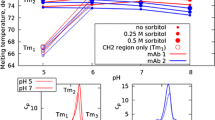
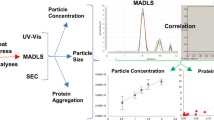
Abstract
Purpose
To develop an analytical platform for the estimation as well as characterization of aggregates over the complete size spectrum (from invisible monomer to visible precipitates).
Methods
Two mAb samples were incubated at 30°C in different buffer systems of protein A chromatography for observing degradation due to aggregation. The aggregation in these samples was quantified by size exclusion chromatography (SEC), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and micro flow imaging (MFI).
Results
The results obtained from various characterization tools were analysed in various size ranges - size exclusion chromatography (SEC) (1 nm - 25 nm), dynamic light scattering (DLS) (10 nm - 5 μm), and micro flow imaging (MFI) (2 μm - 300 μm). Since each characterization tool covers a particular size range, data from multiple tools was collected in the “handover” regions to demonstrate accuracy of the platform.
Conclusions
Based on the observations from the experiments, an analytical platform has been proposed covering the whole size spectrum that would be of utility to those engaged in formulation development as well as other aspects related to stability of biotherapeutic products.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF4:
-
Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation
- AUC:
-
Analytical Ultra Centrifugation
- CC:
-
Coulter Counter
- CD:
-
Circular Dichroism
- CQA:
-
Critical Quality Attributes
- DLS:
-
Dynamic Light Scattering
- EMA:
-
European Medicines Agency
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- FTIR:
-
Fourier Transform Infra-Red Spectroscopy
- HMW:
-
High Molecular Weight
- LO:
-
Light Obscuration
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal Antibody
- MALS:
-
Multi Angle Light Scattering
- MFI:
-
Micro Flow Imaging
- NMR:
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
- NTA:
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
- SEC:
-
Size Exclusion Chromatography
- SEM-EDX:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy – Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
- SLS:
-
Static Light Scattering
- TEM-EDX:
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy – Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
- USP:
-
United States Pharmacopeia
- UV-Visible Spectroscopy:
-
Ultra Violet –Visible Spectroscopy
References
Nicolaides NC, Sass PM, Grasso L. Monoclonal antibodies: a morphing landscape for therapeutics. Drug Dev Res. 2006;67(10):781–9.
Reichert JM, Rosensweig CJ, Faden LB, Dewitz MC. Monoclonal antibody successes in the clinic. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(9):1073–8.
ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline, Specifications: Test procedures and acceptance criteria for biotechnological/biological products Q6B, 1999. Available from: http://www.ich.org/LOB/media/MEDIA4986.pdf https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q6B/Step4/Q6B_Guideline.pdf. Accessed 1 Sept 1999
Rosenberg AS. Effects of protein aggregates: an immunologic perspective. AAPS J. 2006;8(3):E501–7.
Wang W. Protein aggregation and its inhibition in biopharmaceutics. Int J Pharm. 2005;289(1–2):1–30.
Wang W, Roberts CJ, editors. Aggregation of therapeutic proteins. New Jersey: Wiley; 2010.
Joshi V, Shivach T, Kumar V, Yadav N, Rathore AS. Avoiding antibody aggregation during processing: establishing hold times. Biotechnol J. 2014;9(9):1195–205.
Shukla AA, Hubbard B, Tressel T, Guhan S, Low D. Downstream processing of monoclonal antibodies—application of platform approaches. J Chromatogr B. 2007;848(1):28–39.
Ravuluri S, Bansal R, Chhabra N, Rathore AS. Kinetics and characterization of non-enzymatic fragmentation of monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Pharm Res. 2018;35(7):142.
Vázquez-Rey M, Lang DA. Aggregates in monoclonal antibody manufacturing processes. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011;108(7):1494–508.
CMC Biotech Working Group. A-Mab: A case study in bioprocess development. Emeryville: CASSS; 2009.
Carpenter JF, Randolph TW, Jiskoot W, Crommelin DJ, Middaugh CR, Winter G, et al. Overlooking subvisible particles in therapeutic protein products: gaps that may compromise product quality. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(4):1201–5.
Huang CT, Sharma D, Oma P, Krishnamurthy R. Quantitation of protein particles in parenteral solutions using micro-flow imaging. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(9):3058–71.
Ishikawa T, Ito T, Endo R, Nakagawa K, Sawa E, Wakamatsu K. Influence of pH on heat-induced aggregation and degradation of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(8):1413–7.
Rathore AS, Joshi V, Yadav N. Aggregation of monoclonal antibody products: formation and removal. Biopharm International. 2013;26(3):40–5.
Carpenter JF, Randolph TW, Jiskoot W, Crommelin DJ, Middaugh CR, Winter G. Potential inaccurate quantitation and sizing of protein aggregates by size exclusion chromatography: essential need to use orthogonal methods to assure the quality of therapeutic protein products. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(5):2200–8.
Fekete S, Beck A, Veuthey JL, Guillarme D. Theory and practice of size exclusion chromatography for the analysis of protein aggregates. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014;101:161–73.
Cromwell ME, Hilario E, Jacobson F. Protein aggregation and bioprocessing. AAPS J. 2006;8(3):E572–9.
Cao S, Pollastrini J, Jiang Y. Separation and characterization of protein aggregates and particles by field flow fractionation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009;10(4):382–90.
Liu J, Andya JD, Shire SJ. A critical review of analytical ultracentrifugation and field flow fractionation methods for measuring protein aggregation. AAPS J. 2006;8(3):E580–9.
Singh SK, Afonina N, Awwad M, Bechtold-Peters K, Blue JT, Chou D, et al. An industry perspective on the monitoring of subvisible particles as a quality attribute for protein therapeutics. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(8):3302–21.
Narhi LO, Schmit J, Bechtold-Peters K, Sharma D. Classification of protein aggregates. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101(2):493–8.
Mahler HC, Friess W, Grauschopf U, Kiese S. Protein aggregation: pathways, induction factors and analysis. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(9):2909–34.
Bickel F, Herold EM, Signes A, Romeijn S, Jiskoot W, Kiefer H. Reversible NaCl-induced aggregation of a monoclonal antibody at low pH: characterization of aggregates and factors affecting aggregation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;107:310–20.
Mahler HC, Müller R, Friess W, Delille A, Matheus S. Induction and analysis of aggregates in a liquid IgG1-antibody formulation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;59(3):407–17.
Hernandez R. Continuous manufacturing: a changing processing paradigm. Biopharm International. 2015; 28(4).
Joshi V, Shivach T, Yadav N, Rathore AS. Circular dichroism spectroscopy as a tool for monitoring aggregation in monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Anal Chem. 2014;86(23):11606–13.
Den Engelsman J, Garidel P, Smulders R, Koll H, Smith B, Bassarab S, et al. Strategies for the assessment of protein aggregates in pharmaceutical biotech product development. Pharm Res. 2011;28(4):920–33.
He F, Phan DH, Hogan S, Bailey R, Becker GW, Narhi LO, et al. Detection of IgG aggregation by a high throughput method based on extrinsic fluorescence. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(6):2598–608.
Kong J, Yu S. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2007;39(8):549–59.
Wen ZQ. Raman spectroscopy of protein pharmaceuticals. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(11):2861–78.
Philo JS. A critical review of methods for size characterization of non-particulate protein aggregates. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009;10(4):359–72.
Bansal R, Dhawan S, Chattopadhyay S, Maurya GP, Haridas V, Rathore AS. Peptide Dendrons as thermal-stability amplifiers for immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody biotherapeutics. Bioconjug Chem. 2017;28(10):2549–59.
Guttman A, Rathore AS, Krull IS. Bioanalytical tools for the characterization of biologics and biosimilars. LC GC North America. 2012;30(5):1–5.
Mendhe R, Rathore AS, Krull IS. Analytical tools for enabling process analytical technology applications in biotechnology. LC GC North America. 2012;30(1).
Singla A, Bansal R, Joshi V, Rathore AS. Aggregation kinetics for IgG1-based monoclonal antibody therapeutics. AAPS J. 2016;18(3):689–702.
Morris AM, Watzky MA, Finke RG. Protein aggregation kinetics, mechanism, and curve-fitting: a review of the literature. Biochim Biophys Acta Protein Proteomics. 2009;1794(3):375–97.
Roberts CJ. Non-native protein aggregation kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007;98(5):927–38.
Watzky MA, Morris AM, Ross ED, Finke RG. Fitting yeast and mammalian prion aggregation kinetic data with the Finke− Watzky two-step model of nucleation and autocatalytic growth. Biochemistry. 2008;47(40):10790–800.
Li Y, Lubchenko V, Vekilov PG. The use of dynamic light scattering and Brownian microscopy to characterize protein aggregation. Rev Sci Instrum. 2011;82(5):053106.
Ahrer K, Buchacher A, Iberer G, Josic D, Jungbauer A. Analysis of aggregates of human immunoglobulin G using size-exclusion chromatography, static and dynamic light scattering. J Chromatogr A. 2003;1009(1–2):89–96.
USP <788> Particulate Matter in Injections. USP 35; U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, 2012; 339–342. Available from: https://www.uspnf.com/sites/default/files/usp_pdf/EN/USPNF/revisionGeneralChapter788.pdf. Accessed 21 May 2001
Sharma DK, King D, Oma P, Merchant C. Micro-flow imaging: flow microscopy applied to sub-visible particulate analysis in protein formulations. AAPS J. 2010;12(3):455–64.
Rubinstein M, Colby RH. Polymer physics, vol. 23. New York: Oxford university press; 2003.
Van der Kant R, Karow-Zwick AR, Van Durme J, Blech M, Gallardo R, Seeliger D, et al. Prediction and reduction of the aggregation of monoclonal antibodies. J Mol Biol. 2017;429(8):1244–61.
Hamrang Z, Rattray NJ, Pluen A. Proteins behaving badly: emerging technologies in profiling biopharmaceutical aggregation. Trends Biotechnol. 2013;31(8):448–58.
Kameoka D, Masuzaki E, Ueda T, Imoto T. Effect of buffer species on the unfolding and the aggregation of humanized IgG. J Biochem. 2007;142(3):383–91.
Nobbmann U, Connah M, Fish B, Varley P, Gee C, Mulot S, et al. Dynamic light scattering as a relative tool for assessing the molecular integrity and stability of monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2007;24(1):117–28.
Hawe A, Hulse WL, Jiskoot W, Forbes RT. Taylor dispersion analysis compared to dynamic light scattering for the size analysis of therapeutic peptides and proteins and their aggregates. Pharm Res. 2011;28(9):2302–10.
Ye H. Simultaneous determination of protein aggregation, degradation, and absolute molecular weight by size exclusion chromatography–multiangle laser light scattering. Anal Biochem. 2006;356(1):76–85.
Gabrielson JP, Brader ML, Pekar AH, Mathis KB, Winter G, Carpenter JF, et al. Quantitation of aggregate levels in a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody formulation by size-exclusion chromatography, asymmetrical flow field flow fractionation, and sedimentation velocity. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(2):268–79.
Hong P, Koza S, Bouvier ES. A review size-exclusion chromatography for the analysis of protein biotherapeutics and their aggregates. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 2012;35(20):2923–50.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Protein Simple, San Jose, CA, USA, for providing us the access to the MFI for particle size analysis. This work was funded by the Centre of Excellence for Biopharmaceutical Technology grant from Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (number BT/COE/34/SP15097/2015). The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 724 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, R., Gupta, S. & Rathore, A.S. Analytical Platform for Monitoring Aggregation of Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics. Pharm Res 36, 152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2690-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2690-8