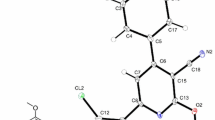
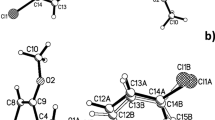
An unknown impurity was identified using the HPLC technique at relative retention time ~1.07 with a peak area of 0.45% during the commercial synthesis of atomoxetine. The profile of the new impurity was established using 1H NMR and LCMS spectroscopy and found to be N,N-dimethyl-3-phenyl-2,3-dichloropropylamine. Adetailed analysis was made using different experimental techniques to find the cause of dichloro impurity. It has been recognized that thionyl chloride (SOCl2) was the potential cause of the formation of the dichloro impurity. The mechanism of the formation of the impurity using retrosynthetic analysis and synthetic strategy was also discussed. The synthesized impurity was compared with the formed impurity by employing LCMS, IR, and NMR spectroscopy. Astrategy for minimizing this potential dichloro impurity was discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Ye, E. Altena, C. Nombela, et al., Biol. Psychiatry, 77(8), 740–748 (2015); https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.01.024.
J. M. Sauer, B. J. Ring, J. W. Witcher, Clin. Pharmacokinetics, 44(6), 571–590 (2005); https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200544060-00002.
F. Bymaster, Neuropsychopharmacology, 27(5), 699–711 (2002); https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00346-9.
J. H. Heiligenstein, D. Gary, J. Urology, et al., Patent US 5,658,590 (1997).
B. M. Bryan, K. K. Schmiegel, Patent US 4,314,081 (1982).
B. M Bryan, K. K. Schmiegel, Eli Lilly and Company, Patent US 4003160A (1977).
R. Saputra, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 53, 1689–1699 (1984).
I. Khairoun, R. Z. Legeros, G. Daculsi, et al., European Patent 1761472B1 (2007).
E. Castelli, A. Vailati, Patent US 7378553B2 (2008).
J. M. Krasniewski, M. W. Mosher, J. Org. Chem., 39(9), 1303–1306 (2002); https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00923a030.
Srinivasan, Chidambaram, Venkateswaran, et al., International Publication No. WO 2009/141833 A2 (2009).
N. Lopez, J. Gomez-Segura, R. P. Marin, J. Perez-Ramirez, J. Catal., 255(1), 29–39 (2008); https://doi.org/10.1016/.jcat.2008.01.020.
L. Friedman, W. P. Wetter, J. Chem. Soc. A: Inorg., Phys. Theor., 36 – 37 (1967); https://doi.org/10.1039/j19670000036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pinninti, S.K., Tene, S., T, S.R. et al. Identification, Synthesis, and Characterization of Potential Dichloro Impurity: N,N-Dimethyl-3-Phenyl-2, 3-Dichloropropylamine in the Synthesis of Atomoxetine. Pharm Chem J 57, 1304–1313 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-024-03039-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-024-03039-8