Abstract
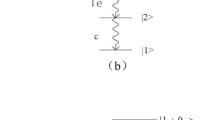
The optical response in a hybrid optomechanical system containing a triple quantum well (TQW) is investigated theoretically. The optomechanical cavity is driven by a strong pump field and a weak probe field. We show that multiple electromagnetically induced transparency windows and optomechanically induced transparency (OMIT) window exist simultaneously for the weak probe field due to the Jaynes–Cummings coupling and optomechanical coupling respectively. Furthermore, the system absorption spectra can be tuned by changing the system coupling strength. Especially, when two external control lasers are applied to the TQW with frequency detuning, multiple transparency windows can be illustrated and adjusted by the external fields. Therefore, via changing the external coupling fields, we can realize manipulating the OMIT transparency window, tunable group delay and switch from fast light to slow light. Such a system may be much practical for the flexibility of TQW in the quantum information processing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram, M.J., Ghafoor, F., Saif, F.: Electromagnetically induced transparency and tunable fano resonances in hybrid optomechanics. J. Phys. B Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 48(6), 065502 (2015)
Akram, M.J., Ghafoor, F., Khan, et al.: Control of Fano resonances and slow light using Bose–Einstein condensates in a nanocavity. Phys. Rev. A 95(2), 023810 (2017)
Aspelmeyer, M., Kippenberg, T.J., Marquardt, F.: Cavity optomechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 86(4), 1391 (2014)
Bayrakli, I.: Electromagnetically induced transparency in natural and artificial molecules. Opt. Laser Technol. 141, 107168 (2021)
Bian, X., Zhang, Y., Zhai, Z., et al.: Enhanced four-wave mixing in P T-symmetric optomechanical systems. Opt. Express 28(7), 9049–9061 (2020)
Černotík, O., Genes, C., Dantan, A.: Interference effects in hybrid cavity optomechanics. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4(2), 024002 (2019)
Chen, H.: Robust four-wave mixing and double second-order optomechanically induced transparency sideband in a hybrid optomechanical system. Photonics 8(7), 234 (2021)
Chen, M., Xiao, Z., Lu, X., et al.: Simulation of dynamically tunable and switchable electromagnetically induced transparency analogue based on metal-graphene hybrid metamaterial. Carbon 159, 273–282 (2020)
Hafeez, A., Abbas, M., Qamar, S.: Optomechanically induced transparency and Fano resonances in a graphene-based nanocavity. JOSA B 36(11), 3070–3078 (2019)
He, Q., Badshah, F., Din, R.U., et al.: Multiple transparency in a multimode quadratic coupling optomechanical system with an ensemble of three-level atoms. JOSA B 35(10), 2550–2561 (2018)
Hsu, H., Cheng, C.Y., Shiu, J.S., et al.: Quantum fidelity of electromagnetically induced transparency: the full quantum theory. Opt. Express 30(2), 2097–2111 (2022)
Hussain, A., Abbas, M.: Double transparency with slow and fast light in an optomechanical system. Opt. Commun. 461, 125284 (2020)
Huy, B.N., Le Van, D., Xuan, K.D.: Controllable optical properties of multiple electromagnetically induced transparency in gaseous atomic media. Commun. Phys. 29(1), 1–1 (2019)
Jing, H., Özdemir, ŞK., Geng, Z., et al.: Optomechanically-induced transparency in parity-time-symmetric microresonators. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 9663 (2015)
Karuza, M., Biancofiore, C., Bawaj, M., et al.: Optomechanically induced transparency in a membrane-in-the-middle setup at room temperature. Phys. Rev. A 88(1), 013804 (2013)
Kong, C., Xiong, H., Wu, Y.: Coulomb-interaction-dependent effect of high-order sideband generation in an optomechanical system. Phys. Rev. A 95(3), 033820 (2017)
Lai, D.G., Wang, X., Qin, W., et al.: Tunable optomechanically induced transparency by controlling the dark-mode effect. Phys. Rev. A 102(2), 023707 (2020)
Lei, X., Ma, L., Yan, J., et al.: Electromagnetically induced transparency quantum memory for non-classical states of light. Adv. Phys. X 7(1), 2060133 (2022)
Li, W., Jiang, Y., Li, C., et al.: Parity-time-symmetry enhanced optomechanically-induced- transparency. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 31095 (2016)
Liao, Q., Xiao, X., Nie, W., et al.: Transparency and tunable slow-fast light in a hybrid cavity optomechanical system. Opt. Express 28(4), 5288–5305 (2020)
Liu, Y., Davanço, M., Aksyuk, V., et al.: Electromagnetically induced transparency and wideband wavelength conversion in silicon nitride microdisk optomechanical resonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(22), 223603 (2013)
Liu, Y.C., Li, B.B., Xiao, Y.F.: Electromagnetically induced transparency in optical microcavities. Nanophotonics 6(5), 789–811 (2017)
Liu, Z.X., Xiong, H., Wu, Y.: Generation and amplification of a high-order sideband induced by two-level atoms in a hybrid optomechanical system. Phys. Rev. A 97(1), 013801 (2018)
Liu, H., Qin, L.G., Tian, L.J., et al.: Opto-electromechanically induced transparency in a hybrid opto-electromechanical system. Chin. Phys. B 28(10), 108502 (2019)
Ma, L., Slattery, O., Tang, X.: Optical quantum memory based on electromagnetically induced transparency. J. Opt. 19(4), 043001 (2017)
Ozturk, O., Ozturk, E., Elagoz, S.: Linear and nonlinear optical absorption coefficient and electronic features of triple GaAlAs/GaAs and GaInAs/GaAs quantum wells depending on barrier widths. Optik 180, 394–405 (2019)
Pan, G., Xiao, R., Chen, H., et al.: Multicolor optomechanically induced transparency in a distant nano-electro-optomechanical system assisted by two-level atomic ensemble. Laser Phys. 31(6), 065202 (2021)
Qian, L.B., Yan, X.B.: Perfect optomechanically induced transparency in two-cavity optomechanics. Front. Phys. 18(5), 52301 (2023)
Qin, H., Ding, M., Yin, Y.: Induced transparency with optical cavities. Adv. Photon. Res. 1(1), 2000009 (2020)
Qu, K., Agarwal, G.S.: Fano resonances and their control in optomechanics. Phys. Rev. A 87(6), 063813 (2013)
Qu, Y., Shen, S., Li, J.: Phase-dependent Fano-shape optomechanically induced transparency. Appl. Opt. 57(26), 7444–7454 (2018)
Sayrac, M., Kaynar, E., Ungan, F.: The effect of structure parameters and static electric field on the nonlinear optical properties of triple InGaAs/GaAs quantum well. J. Mol. Struct. 1273, 134252 (2023)
Sete, E.A., Eleuch, H.: Controllable nonlinear effects in an optomechanical resonator containing a quantum well. Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 043824 (2012)
Sohail, A., Zhang, Y., Bary, G., et al.: Tunable optomechanically induced transparency and fano resonance in optomechanical system with levitated nanosphere. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 2814–2827 (2018)
Tang, C., Lan, Y., Dutta, M., et al.: AlGaAs/GaAs triple quantum well photodetector at 5µm wavelength—a simulation study. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 52(11), 1–8 (2016)
Tuzemen, A.T., Dakhlaoui, H., Mora-Ramos, M.E., et al.: The nonlinear optical properties of GaAs/GaAlAs triple quantum well: role of the electromagnetic fields and structural parameters. Physica B 646, 414286 (2022)
Ullah, K.: Control of electromagnetically induced transparency and Fano resonances in a hybrid optomechanical system. Eur. Phys. J. D 73, 1–9 (2019)
Wang, X.F., Chen, B.: Four-wave mixing response in a hybrid atom-optomechanical system. JOSA B 36(2), 162–167 (2019)
Wang, T., Zheng, M.H., Bai, C.H., et al.: Normal-mode splitting and optomechanically induced absorption, amplification, and transparency in a hybrid optomechanical system. Ann. Phys. 530(10), 1800228 (2018)
Wang, C., Jiang, X., Zhao, G., et al.: Electromagnetically induced transparency at a chiral exceptional point. Nat. Phys. 16(3), 334–340 (2020)
Weis, S., Rivière, R., Deléglise, S., et al.: Optomechanically induced transparency. Science 330(6010), 1520–1523 (2010)
Wu, S.C., Qin, L.G., Lu, J., et al.: Phase-dependent double optomechanically induced transparency in a hybrid optomechanical cavity system with coherently mechanical driving. Chin. Phys. B 28(7), 074204 (2019)
Xiong, H., Wu, Y.: Fundamentals and applications of optomechanically induced transparency. Appl. Phys. Rev. 5(3), 031305 (2018)
Xiong, H., Fan, Y.W., Yang, X., et al.: Radiation pressure induced difference-sideband generation beyond linearized description. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109(6), 061108 (2016a)
Xiong, H., Si, L.G., Lü, X.Y., et al.: Optomechanically induced sum sideband generation. Opt. Express 24(6), 5773–5783 (2016b)
Yadav, S., Bhattacherjee, A.B.: Nonlinear optical response in coupled quantum wells optomechanical microcavity. Phys. Scr. 97(1), 015102 (2022)
Yan, X.B.: Optomechanically induced transparency and gain. Phys. Rev. A 101(4), 043820 (2020)
Yan, X.B.: Optomechanically induced optical responses with non-rotating wave approximation. J. Phys. B Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 54(3), 035401 (2021a)
Yan, X.B.: Optomechanically induced ultraslow and ultrafast light. Physica E 131, 114759 (2021b)
Yan, X.B., Jia, W.Z., et al.: Optomechanically induced amplification and perfect transparency in double-cavity optomechanics. Front. Phys. 10, 351–357 (2015)
Yang, Q., Hou, B.P., Lai, D.G.: Local modulation of double optomechanically induced transparency and amplification. Opt. Express 25(9), 9697–9711 (2017)
Yu, C., Yang, W., Sun, L., et al.: Controllable transparency and slow light in a hybrid optomechanical system with quantum dot molecules. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52, 1–11 (2020)
Zhu, Y.J., Bai, C.H., Wang, T., et al.: Optomechanically induced transparency, amplification, and fast–slow light transitions in an optomechanical system with multiple mechanical driving phases. JOSA B 37(3), 888–893 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11447182 and 11647122), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant Nos. 2022CFB475 and 2018CFB672), the Project of the Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. B2021215), and the Natural Science Foundation of Xiaogan City (Grant No. XGKJ2021010002).
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11447182 and 11647122), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant Nos. 2022CFB475 and 2018CFB672), the Project of the Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. B2021215), and the Natural Science Foundation of Xiaogan City (Grant No. XGKJ2021010002).
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Guan, X., Yang, W. et al. Controllable transparency and slow–fast light in an optomechanical system with a triple quantum well. Opt Quant Electron 56, 41 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05631-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05631-w