Abstract
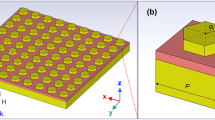
In this work, an ultra-thin plasmonic metamaterial nanostructure absorber is simulated using the finite difference time domain method in the visible and near-infrared regions. A periodic square titanium-silica cap coated with glass medium is mounted on top of a silver substrate. The presence of the glass host enhances the absorption bandwidth by 276%. With an almost perfect metal–insulator-metal absorber, over 90% absorbance has been obtained for wavelengths from 440 to 1850 nm, producing an absorption bandwidth of 1410 nm. The impact of changing dimensions and using different materials on the absorption spectra has been investigated in both visible and near-infrared regimes. The considered metals for the top layer are titanium, nickel, silver, aluminum, and gold; however, the insulators are silica, quartz, vanadium dioxide, methyl methacrylate, and aluminum dioxide. In addition, aluminum, silver, copper, and gold are then simulated as a substrate. The optimum structure, which produces the maximum absorber bandwidth, 1410 nm, with a higher absorption, over 90%, is Glass-Ti–SiO2–Ag. The finding illustrates that the optimum dimensions of the Ti–SiO2 cab and the square base unit cell of the silver substrate are 250 nm and 200 nm, respectively. Finally, the absorption bandwidth is calculated using different polarization angles ranges from 10° to 70° with a step10°.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askari, M.: A near infrared plasmonic perfect absorber as a sensor for hemoglobin concentration detection. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53, 67–81 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02703-z
Askari, M., Hosseini, M.V.: Infrared metamaterial refractive-index-based sensor. JOSA B 37, 2712–2718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.392977
Askari, M., Hosseini, M.V.: A novel metamaterial design for achieving a large group index via classical electromagnetically induced reflectance. Opt. Quant Electron. 52, 191–208 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02302-y
Cui, Y., He, Y., Jin, Y., Ding, F., Yang, L., Ye, Y., Zhong, S., Lin, Y., He, S.: Plasmonic and metamaterial structures as electromagnetic absorbers. Laser Photonics Rev. 8, 495–520 (2014)
Dragoman, M., Dragoman, D.: Plasmonics: applications to nanoscale te rahertz and optical devices . Prog. Quantum. Electron. 32, 1–41 (2008)
Fann, C.H., Zhang, J., ElKabbash, M., Donaldson, W.R., Campbell, E.M., Guo, C.: Broadband infrared plasmonic metamaterial absorber with multipronged absorption mechanisms. Opt. Express 27, 27917–27926 (2019)
Gao, H., Peng, W., Cui, W., Chu, S., Yu, L., Yang, X.: Ultraviolet to near infrared titanium nitride broadband plasmonic absorber. Opt. Mater. 97,109377, (2019).
Hao, J., Zhou, L., Qiu, M.: Nearly total absorption of light and heat generation by plasmonic metamaterials. Phys. Rev. B 83, 165107 (2011)
Hedayati, M.K., Zillohu, A.U., Strunskus, T., Faupel, F., Elbahri, M.: Plasmonic tunable metamaterial absorber as ultraviolet protection film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 , 041103 (2014)
Hedayati, M.K., Faupel, F., Elbahri, M.: Review of plasmonic nanocomposite metamaterial absorber. Materials 7, 1221–1248 (2014)
Landy, N.I., Bingham, C.M., Tyler, T., Jokerst, N., Smith, D.R. Padilla, W.J.: Design, theory, and measurement of a polarization-insensitive absorber for terahertz imaging. Phys. Rev. B 79, 125104 (2009).
Lei, L., Li, S., Huang, H., Tao, K., Xu, P.: Ultra-broadband absorber from visible to near-infrared using plasmonic metamaterial. Opt. Express 26(5), 5686–5693 (2018)
Li, D., Szabó, Z., Qing, X., Li, E.P., Chen, Z.N.: A high gain antenna with an optimized metamaterial inspired superstrate. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60, 6018–6023 (2012)
Liu, J., He, H., Xiao, D., Liu, Y.: Recent advances of plasmonic nanoparticles and their applications. Materials 11, 1833 (2018)
Maier, T., Brueckl, H.: Multispectral microbolometers for the midinfrared. Opt. Lett. 35, 3766–3768 (2010)
Ni, X., Wong, Z.J., Mrejen, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, X.: An ultrathin invisibility skin cloak for visible light. Science 349, 1310–1314 (2015)
Palik, E.: Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids. Academic, New York (1985)
Pradhan, J.K., Achanta, V.G., Agarwal, A.K., Ramakrishna, S.A.: Performance enhancement due to a top dielectric coating on a metamaterial perfect absorber. Appl. Opt. 59, E118–E125 (2020)
Ra’Di, Y., Simovski, C. R., Tretyakov, S.A.: Thin perfect absorbers for electromagnetic waves: theory, design, and realizations. Phys. Rev. Appl. 3, 037001 (2015).
Segovia, P., Marino, G., Krasavin, A.V., Olivier, N., Wurtz, G.A., Belov, P.A., Ginzburg, P., Zayats, A.V.: Hyperbolic metamaterial antenna for second-harmonic generation tomography. Opt. Express 23, 30730–30738 (2015)
Shin, D., Urzhumov, Y., Jung, Y., Kang, G., Baek, S., Choi, M., Park, H., Kim, K., Smith, D.R.: Broadband electromagnetic cloaking with smart metamaterials. Nat. Commun. 3, 1–8 (2012)
Wang, Y., Sun, T., Paudel, T., Zhang, Y., Ren, Z., Kempa, K.: Metamaterial-plasmonic absorber structure for high efficiency amorphous silicon solar cells. Nano Lett. 12, 440–445 (2012)
Watts, C., Liu, X., Padilla, W.: Advanced materials 24, 98 -112 (2012)
Wu, C., Neuner III, B., John, J., Milder, A., Zollars, B., Savoy, S., & Shvets, G.: Metamaterial-based integrated plasmonic absorber/emitter for solar thermo-photovoltaic systems. J. Opt. 14 ,024005 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elrashidi, A., Tharwat, M.M. Broadband absorber using ultra-thin plasmonic metamaterials nanostructure in the visible and near-infrared regions. Opt Quant Electron 53, 426 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03089-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03089-2