Abstract
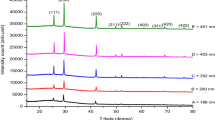
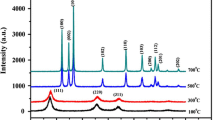
The pH of reaction solutions played a vital role and determines the nature of the final product formed. According to our experimental findings, we were able to control energy band gap, size and configuration of cobalt selenide thin films from aqueous solutions by suitable control of last solution pH. We present a simple solution processed synthesis route for cobalt selenide nanostructure thin films using chemical bath deposition method. The films were characterized by X-ray diffraction, UV–visible spectroscopy for energy band gap estimation and scanning electron microscopy to surface morphology investigation. In this work, the size of the nanosphers and other nanoparticles are relatively easy to control by pH controlling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auf der Maur, M., Lorenz, K., Di Carlo, A.: Band gap engineering approaches to increase InGaN/GaN LED efficiency. Opt. Quant. Electron. 44, 83–88 (2012)
Brus, L.E.: J. Phys. Chem. 90, 2555 (1986)
Brus, L.E.: Appl. Phys. A. 53, 465–474 (1991)
Burda, C., Chen, X., Narayanan, R., El-Sayed, M.A.: Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Rev. 105, 1025–1102 (2005)
Efros, A.L., Rosen, M.: Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 30, 475–521 (2000)
Joshi, R.K.: Solid State Commun. 139, 201–204 (2006)
Kaleji, K.: B: influence of co-doping of Sn/W on the structural and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for MB degradation. Opt. Quant. Electron. 47, 2075–2086 (2014)
Mane, R.S., Lokhande, S.D.: Chemical deposition method for metal chalcogenide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, 1–31 (2000)
Millo, O., Katz, D., Cao, Y.W., Banin, U.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5751 (2001)
Najibi-Ilkhechi, N., Koozegar-Kaleji, B., Salahi, E.: Effect of heating rate on structural and optical properties of Si and Mg co-doped ZrO2 nanopowders. Opt. Quant. Electron. 47, 1187–1195 (2014)
Rahnama, A., Gharagozlou, M.: Preparation and properties of semiconductor CuO nanoparticles via a simple precipitation method at different reaction temperatures. Opt. Quant. Electron. 44, 313–322 (2012)
Sonawane, B.K., Bhole, M.P., Patil, D.: Structural, optical and electrical properties of post annealed Mg doped ZnO films for optoelectronics applications. Opt. Quant. Electron. 41, 17–26 (2009)
Tauc, J., Menth, J.: States in the gap. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 569, 8–10 (1972)
Wang, Y, Herron, N. J.: Phys. Chem. 95, 525–532 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghobadi, N., Khazaie, F. Fundamental role of the pH on the nanoparticle size and optical band gap in cobalt selenide nanostructure films. Opt Quant Electron 48, 165 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0447-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0447-8