Abstract
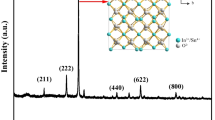
RF magnetron sputtering technique was employed to deposit Li-doped ZnO thin films onto quartz substrate at different substrate temperatures ranging from room temperature (RT) to 500 \(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\). X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that the deposited films had a hexagonal-wurtzite crystal structure with preferred orientation along the c-axis. Increasing the substrate temperature improved the crystallinity and caused a significant increase in the crystallite size (182 nm) for the film deposited at 500 \(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\). The energy band gap of the films deposited at RT, 350, 400, 450 and 500 \(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\) were found to be 3.292, 3.282, 3.281, 3.28 and 3.269 eV, respectively. All films exhibited a broad UV-violet emission band centered on 407 nm and attributed to the radiative recombination processes near the band edge. A Hall mobility of \(\sim \)33.3 \(\hbox {cm}^{2}\)/V s, concentration (\(n\)) of \(\sim \)7.6 \(\times 10^{18}\,\hbox {cm}^{-3}\) and resistivity of \(\sim \)39.7 \(\Omega \)-cm were obtained for the film deposited at 500 \(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\). The results show that the substrate temperature plays a crucial role in the structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghamalyan, N., Goulanian, E.K., Hovsepyan, R., Vardanyan, E., Zerrouk, A.: Effect of lithium impurity on the opto-electrical properties of zinc oxide films. phys. Status Solidi A 199, 425–430 (2003)
Bender, M., Fortunato, E., Nunes, P., Ferreira, I., Marques, A., Martins, R., Katsarakis, N., Cimalla, V., Kiriakidis, G.: Generation of optical bistability in a fiber Fabry–Perot resonator using mode-locked picosecond pulses. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 435–437 (2003)
Bertazzi, F., Bellotti, E., Furno, E., Goano, M.: Experimental electron mobility in ZnO: a reassessment through Monte Carlo simulation. J. Mater. Sci Mater. Electron. 38, 1677–1683 (2009)
Chu, S., Olmedo, M., Yang, Z., Kong, J., Liu, J.L.: Electrically pumped ultraviolet ZnO diode lasers on Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 181106 (2008)
Fortunato, E., Raniero, L., Silva, L., Gonçalves, A., Pimentel, A., Barquinha, P., Aguas, H., Pereira, L., Gonçalves, G., Ferreira, I.: Highly stable transparent and conducting gallium-doped zinc oxide thin films for photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 92, 1605–1610 (2008)
Fortunato, E., Goncalves, A., Pimentel, A., Barquinha, P., Goncalves, G., Pereira, L., Ferreira, I., Martins, R.: Zinc oxide, a multifunctional material: from material to device applications. Appl. Phys. A 96, 197–205 (2009)
Lee, E.-C., Chang, K.: Possible p-type doping with group-I elements in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 70, 115210–115214 (2004)
Liu, K., Sakurai, M., Aono, M.: ZnO-based ultraviolet photodetectors. Sensors 10, 8604–8634 (2010)
Lu, J.G., Zhang, Y.Z., Ye, Z.Z., Zeng, Y.J., He, H.P., Zhu, L.P., Huang, J.Y., Wang, L., Yuan, J., Zhao, B.H., Li, X.H.: Control of p- and n-type conductivities in Li-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 112113 (2006)
Onodera, A., Tamaki, N., Kawamura, Y., Yamashita, H.: Dielectric activity and ferroelectricity in piezoelectric semiconductor Li-doped ZnO. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 5160–5162 (1996)
Özgür, Ü., Alivov, Y.I., Liu, C., Teke, A., Reshchikov, M.A., Doǧan, S., Avrutin, V., Cho, S.J., Morkoç, H.: A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005)
Park, C., Zhang, S., Wei, S.: Origin of p-type doping difficulty in ZnO: the impurity perspective. Phys. Rev. B 66, 073202–073203 (2002)
Ruankham, P., Sagawa, T., Sakaguchi, H., Yoshikawa, S.: Vertically-aligned ZnO nanorods doped with lithium for polymer solar cells: defect related photovoltaic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 9710–9715 (2011)
Salman, K.A., Omar, K., Hassan, Z.: Nanocrystalline ZnO film grown on porous silicon layer by radio frequency sputtering system. Mater. Lett. 68, 51–53 (2012)
Sanon, G., Rup, R., Mansingh, A.: Growth and characterization of tin oxide films prepared by chemical vapour deposition. Thin Solid Films 190, 287–301 (1989)
Shinde, S.S., Bhosale, C.H., Rajpure, K.Y., Photoch, J.: Photoelectrochemical properties of highly mobilized Li-doped ZnO thin films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 120, 1–9 (2013)
Srikant, V., Clarke, D.R.: Optical absorption edge of ZnO thin films: the effect of substrate. J. Appl. Phys. 81, 6357–6364 (1997)
Tan, S.T., Chen, B.J., Sun, X.W., Fan, W.J.: Blueshift of optical band gap in ZnO thin films grown by metal-organic chemical-vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 013505 (2005)
Wardle, M.G., Goss, J.P., Briddon, P.R.: Theory of Li in ZnO: a limitation for Li-based p-type doping. Phys. Rev. B 71, 155205 (2005)
Willander, M., Nur, O., Sadaf, J.R., Qadir, M.I., Zaman, S., Zainelabdin, A., Bano, N., Hussain, I.: Luminescence from zinc oxide nanostructures and polymers and their hybrid devices. Materials 3, 2643–2667 (2010)
Zahedi, F., Dariani, R.S., Rozati, S.M.: Effect of substrate temperature on the properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 245–249 (2013)
Zeng, Y.J., Ye, Z.Z., Lu, J.G., Xu, W.Z., Zhu, L.P., Zhao, B.H., Limpijumnong, S.: Identification of acceptor states in Li-doped p-type ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 1–3(2006)
Zhang, D.H., Xue, Z.Y., Wang, Q.P.: The mechanisms of blue emission from ZnO films deposited on glass substrate by r.f. magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 35, 2837–2840 (2002)
Acknowledgments
This work has been partly supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-10-0066), 863 project Grants (2013AA031502) and the project of 2011RFLXG006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babikier, M., Li, Q., Wang, J. et al. Li doped ZnO thin film: effect of substrate temperature on structure, optical and electrical properties. Opt Quant Electron 47, 3655–3665 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-015-0256-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-015-0256-5