Abstract
We examine whether unscheduled communication of members of the European Central Bank’s (ECB) Governing Council affects financial market comovements. To assess comovements, we employ well-defined measures of stock market and government bond yield coexceedances, i.e., the measures of whether markets jointly decrease or increase and by how much. We use the daily data from 2008 to 2014 for the four largest euro area countries, Germany, France, Italy and Spain, in a quantile regression framework and control for persistence in coexceedances and a comprehensive set of relevant factors capturing returns and volatility in various segments of financial markets. We find that central bank communication often contributes to greater coexceedances but only when there are extreme events in the financial markets. The results also suggest that markets perceive the ECB’s communication as a euro area-wide shock, but propagation of this shock depends on the financial (in)stability of individual euro area countries.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We understand unscheduled communication to be any verbal or written statement by a member of a policy-making body (the Governing Council in the case of the ECB, i.e., the executive board of the ECB and national central bank governors) that occurs outside of any scheduled release of a central bank.
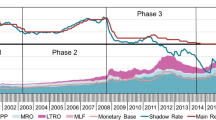
In our sample, a secondary market purchase program is actively helping to restore confidence in the segment of Italian and Spanish bond market and 3-year long-term refinancing operations are more broadly helping to improve liquidity conditions in the stressed markets of the euro area.
References
Albuquerque R, Vega C (2009) Economic news and international stock market co-movement. Rev Financ 13(3):401–465
Bae K-H, Karolyi GA, Stulz RM (2003) A new approach to measuring financial contagion. Rev Financ Stud 16(3):717–763
Baruník J, Kočenda E, Vácha L (2016) Gold, oil, and stocks: dynamic correlations. Int Rev Econ Financ 42:186–201
Baur D, Schulze N (2005) Coexceedances in financial markets - a quantile regression analysis of contagion. Emerg Mark Rev 6(1):21–43
Beck M-K, Hayo B, Neuenkirch M (2013) Central bank communication and correlation between financial markets: Canada and the United States. J Int Econ Econ Policy 10(2):277–296
Bekaert G, Ehrmann M, Fratzscher M, Mehl A (2014) The global crisis and equity market contagion. J Financ 69(6):2597–2649
Belke A (2018) Central bank communication and transparency: the ECB and the European Parliament. Int J of Monet Econ Financ 11(5):416–435
Blinder ASM, Ehrmann M, Fratzscher JDH, Jansen D-J (2008) Central bank communication and monetary policy: A survey of theory and evidence. J Econ Lit 46(4):910–945
Blinder A, Ehrmann M, De Haan J, Jansen D-J (2017) Necessity as the mother of invention: monetary policy after the crisis. Econ Policy 32(92):707–755
Born B, Ehrmann M, Fratzscher M (2014) Central bank communication on financial stability. Econ J 124(577):701–734
Briere M (2006) "Market reactions to central bank communication policies: Reading interest rate options smiles", Working Papers CEB 38, ULB - Universite Libre de Bruxelles
Brunnermeier MK, Pedersen LH (2009) Market liquidity and funding liquidity. Rev Financ Stud 22(6):2201–2238
Caballero RJ, Krishnamurthy A (2008) Collective risk management in a flight to quality episode. J Financ 63(5):2195–2230
Cieslak A, Schrimpf A (2019) Non-monetary news in central bank communication. J Int Econ 118:295–315
Coenen G, Ehrmann M, Gaballo G, Hoffmann P, Nakov A, Nardelli S, Persson E, Strasser G (2017) "Communication of monetary policy in unconventional times", European Central Bank working paper, No. 2080
Coenen G, Ehrmann M, Gaballo G, Hoffmann P, Nakov A, Nardelli S, Persson E, Strasser G (2018) More, and more forward-looking: central bank communication after the crisis. In: Eijffinger S, Masciandaro D (eds) Hawks and doves: deeds and words - economics and politics of monetary policymaking, a VoxEU.org eBook. CEPR Press, London
Dincer N, Eichengreen B (2014) Central bank transparency and independence: updates and new measures. Int J Cent Bank 10(1):189–253
Ehrmann M, Fratzscher M (2007a) Communication by central bank committee members: different strategies, same effectiveness? J Money Credit Bank 39(2–3):509–541
Ehrmann M, Fratzscher M (2007b) The timing of central bank communication. Eur J Polit Econ 23(1):124–145
Forbes KJ, Rigobon R (2002) No contagion, only interdependence: measuring stock market comovements. J Financ 57(5):2223–2261
Gertler P, Horvath R (2018) Central bank communication and financial markets: high-frequency evidence. J Financ Stab 36:336–345
Guo F, Chen CR, Huang YS (2011) Markets contagion during financial crisis: a regime-switching approach. Int Rev Econ Financ 20(1):95–109
Hansen S, McMahon M (2018) How central bank communication generates market news. In: Eijffinger S, Masciandaro D (eds) Hawks and doves: deeds and words - economics and politics of monetary policymaking, a VoxEU.org eBook. CEPR Press, London
Hayo B, Neuenkirch M (2012) Domestic or U.S. news: what drives Canadian financial markets? Econ Inq 50(3):690–706
Hayo B, Kutan AM, Neuenkirch M (2010) The impact of U.S. central bank communication on European and pacific equity markets. Econ Lett 108(2):172–174
Hayo B, Kutan A, Neuenkirch M (2015) Financial market reaction to Federal Reserve communications: does the global financial crisis make a difference? Empirica 42(1):185–203
Horváth R, Lyocsa S (2018) Stock market contagion: a new approach. Open Econ Rev:391–412
Horváth R, Vaško D (2016) Central bank transparency and financial stability. J Financ Stab 22:45–56
Horváth R, Baumohl E, Lyocsa S (2018) Stock market contagion in central and Eastern Europe: unexpected volatility and extreme co-exceedance. Eur J Financ 24(5):391–412
Leombroni, M. & A. Vedolin, & G. Venter & P. Whelan (2018) Central Bank communication and the yield curve. CEPR Discussion Paper No. DP12970
Longin F, Solnik B (2001) Extreme correlation of international equity markets. J Financ 56(2):649–679
Matejka F, Steiner J, Stewart C (2017) Rational inattention dynamics: inertia and delay in decision-making. Econometrica 85(2):521–553
Pastor L, Veronesi P (2012) Uncertainty about government policy and stock prices. J Financ 67(4):1219–1264
Ranaldo A, Rossi E (2010) The reaction of asset markets to Swiss National Bank communication. J Int Money Financ 29(3):486–503
Acknowledgements
We thank two anonymous referees, Ansgar Belke, Michal Hlavacek, Stefan Lyocsa and Jakub Seidler for their helpful comments. The views in this paper do not represent the views of the National Bank of Slovakia. Horvath appreciate the support of the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic, no. 19-15650S. Online Appendix is available at http://ies.fsv.cuni.cz/en/staff/horvath.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 252 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gertler, P., Horváth, R. & Jonášová, J. Central Bank Communication and Financial Market Comovements in the Euro Area. Open Econ Rev 31, 257–272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11079-019-09561-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11079-019-09561-7