Abstract
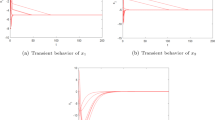
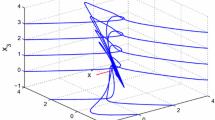
This paper proposes a neurodynamic approach to zero-one quadratic programming with linear constraints. Compared with one existing neurodynamic approach to such problems, the proposed one has lower dimensions of state variables and less computational cost, which makes the implementation easier. Under some suitable conditions, the stability and convergence properties of the proposed approach are established. Numerical simulation results and related comparisons show the efficiency of this proposed method in practical computation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, D, Sun, X: Nonlinear Integer Programming. Springer, New York (2006)
Hosseinian, S., Butenko, S.: Algorithms for the generalized independent set problem based on a quadratic optimization approach. Optim. Lett. 13, 1211–1222 (2019)
Krarup, J., Pruzan, P.A.: Computer aided layout design. Math. Prog. Study 9, 75–94 (1978)
Xu, C.T., He, X., Huang, T.W., Huang, J.J.: A combined neurodynamic approach to optimize the real-time price-based demand response management problem using mixed zero-one programming. Neural Computing Appl. 32, 8799–8809 (2020)
He, X., Chen, A., Chaovalitwongse, W.A., Lin, H.X.: An improved linearization technique for a class of quadratic 0-1 problems. Optim. Lett. 6, 31–41 (2012)
Pardalos, P.M., Rodgers, G.: Computational aspects of a branch and bound algorithm for quadratic zero-one programming. Computing 45, 131–144 (1990)
Lu, C., Guo, X.: Convex reformulation for binary quadratic programming problems via average objective value maximization. Optim. Lett. 9, 523–535 (2015)
Hoai, L.T., Tao, P.D.: A continuous approch for globally solving linearly constrained quadratic zero-one programming problems. Optimization 50, 93–120 (2001)
Zhu, W.X.: Penalty parameter for linearly constrained 0-1 quadratic programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 116, 229–239 (2003)
Billionnet, A., Elloumi, S., Plateau, M.C.: Improving the performance of standard solvers for quadratic 0-1 programs by a tight convex reformulation: the QCR method. Discrete. Appl. Math. 157, 1185–1197 (2009)
Liao, L.Z., Qi, H.D., Qi, L.Q.: Neurodynamical Optimization. J. Global Optim. 28, 175–195 (2004)
Ou, Y.G., Lin, H.C.: A continuous method model for solving general variational inequality. Inter. J. Comput. Math. 93, 1899–1920 (2016)
Yan, Z., Fan, J., Wang, J.: A collective neurodynamic approach to constrained global optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28, 1206–1215 (2017)
Mansoori, A., Erfanian, M.: A dynamic model to solve the absolute value equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 333, 28–35 (2018)
Sun, L.M., Liao, L.Z.: An interior point continuous path-following trajectory for linear programming. J. Ind. Manag. Optimi. 15, 1517–1534 (2019)
Che, H., Wang, J.: A collaborative neurodynamic approach to global and combinatorial optimization. Neural Netw. 114, 15–27 (2019)
Che, H., Wang, J.: A two-timescale duplex neurodynamic approach to mixed-integer optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31, 1–13 (2020)
Liu, S.X., Jiang, H.J., Zhang, L.W., Mei, X.H.: A neurodynamic optimization approach for complex-variables programming problem. Neural Netw. 129, 280–287 (2020)
Jiang, X.R., Qin, S.T., Xue, X.P.: A penalty-like neurodynamic approach to constrained nonsmooth distributed convex optimization. Neurocomputing 377, 225–233 (2020)
Mansoori, A., Effati, S.: An efficient neurodynamic model to solve nonlinear programming problems with fuzzy parameters. Neurocomputing 334, 125–133 (2019)
Nikseresht, A., Nazemi, A.: A novel neural network for solving semidefinite programming problems with some applications. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 350, 309–323 (2019)
Aourid, M., Do, X.D., Kaminska, B.: Penalty formulation for 0-1 linear programming problem: a neural network approach. IEEE Neural Netw. 2, 1092–1095 (1993)
Aourid, M., Kaminska, B.: Neural networks for solving the quadratic 0-1 programming problem under linear constraints. IEEE Neural Netw. 4, 1690–1693 (1995)
Ranjbar, M., Effati, S., Miri, S.M.: An artificial neural network for solving quadratic zero-one programming problems. Neurocomputing 235, 192–198 (2017)
Han, J.Y., Xiu, N.H., Qi, H.D.: Nonlinear Complementarity: Theory and Algorithm. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai (2006)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer, New York (2006)
Slotine, J.J.E., Li, W.: Applied Nonlinear Control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1991)
Zhang, S.W., Constantinides, A.G.: Lagrange programming neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 39, 441–452 (1992)
Han, Q.M., Liao, L.Z., Qi, H.D., Q, L.Q.: Stability analysis of gradient-based neural networks for optimization problems. J. Global Optim. 19, 363–381 (2001)
Horst, R., Pardalos, P.M., Thoai, N.V.: Introduction to Global Optimization. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2 (2000)
Hu, Y.Q.: Fundamentals and Applications of Operations Research, 4th edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing (2004)
Bazaraa, M.S., Jarvis, J.J., Sherali, H.D.: Linear Programming and Network Flows. Wiley, New York (1990)
Omidi, F., Abbasi, B., Nazemi, A.: An efficient dynamic model for solving a portfolio selection with uncertain chance constraint models. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 319, 43–55 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the anonymous referees and the associate editor for their valuable comments and constructive suggestions that greatly improved this paper.
Funding
This work is partially supported by NNSF of China (Nos. 11961018, 61762032) and NSF of Hainan Province (No. 120QN175)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, Y., Lin, H. A neurodynamic approach to zero-one quadratic programming. Numer Algor 88, 1251–1274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01075-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01075-z