Abstract
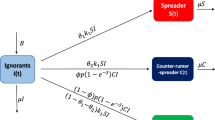
Rumors can spread quickly and widely, causing negative impacts on both society and individuals. Therefore, it is essential to prevent the propagation of rumors to maintain social stability and avoid potential harm to people’s lives. In order to accurately simulate the rumor spreading process, a new IS2TR rumor spreading model is proposed. The different psychology of people when rumor spreading is taken into account in this model, and rumor spreaders are classified as normal spreaders and malicious spreaders. In addition, this model adds truth spreaders, making it more consistent with the real rumor spreading process. First, we calculate the model’s equilibria and the basic reproduction number. Second, the local asymptotic stability and transcritical bifurcation of the equilibria are analyzed and proved in this model. Finally, the theoretical results are verified by numerical simulations, and we also analyze the comprehensive impact of adding malicious spreaders and truth spreaders to the model. A real dataset is then used to predict the rumor propagation process, and the final R-squared is 0.9487 which verifies the effectiveness in predicting rumor propagation trends.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used in this paper is publicly available at https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2563864.
References
Ghosh, M., Das, P., Das, P.: A comparative study of deterministic and stochastic dynamics of rumor propagation model with counter-rumor spreader. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 16875–16894 (2023)
Yu, Z., Sohail, A., Nofal, T.A., Taylor, T.: Explainability of neural network clustering in interpreting the COVID-19 emergency data. Fractals 30(5), 2240122 (2022)
Pan, W., Yan, W., Hu, Y., He, R., Wu, L.: Dynamic analysis of a SIDRW rumor propagation model considering the effect of media reports and rumor refuters. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 3925–3936 (2023)
Zhou, Y., Zhang, J., Zhu, C., Wang, H.: Modelling and analysis of rumour propagation based on stochastic optimal control. Alex. Eng. J. 61(12), 12869–12880 (2022)
Jiang, M., Gao, Q., Zhuang, J.: Reciprocal spreading and debunking processes of online misinformation: a new rumor spreading–debunking model with a case study. Physica A 565, 125572 (2021)
Li, J., Jiang, H., Yu, Z., Hu, C.: Dynamical analysis of rumor spreading model in homogeneous complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 359, 374–385 (2019)
Cheng, Y., Huo, L., Zhao, L.: Dynamical behaviors and control measures of rumor spreading model in consideration of the infected media and time delay. Inf. Sci. 564, 237–253 (2021)
Wang, Q., Liu, R., Jia, R.: Influence of opinion dynamics on rumor propagation in complex networks. Acta Phys. Sin 70(6), 068902 (2021)
Faustini, P.H.A., Covões, T.F.: Fake news detection in multiple platforms and language. Expert Syst. Appl. 158, 113503 (2020)
Yin, F., Jiang, X., Qian, X., Xia, X., Pan, Y., Wu, J.: Modeling and quantifying the influence of rumor and counter-rumor on information propagation dynamics. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 162, 112392 (2022)
Huo, L., Wang, L., Song, G.: Global stability of a two-mediums rumor spreading model with media coverage. Phys. A. 482, 757 (2017)
Wang, C., Tan, Z., Ye, Y., Wang, L., Cheong, K., Xie, N.: A rumor spreading model based on information entropy. Sci Rep. 7(1), 9615 (2017)
Yin, F., Lv, J., Zhang, X., Xia, X., Wu, J.: COVID-19 information propagation dynamics in the Chinese Sina-microblog. Math. Biosci. Eng. 17(3), 2676–2692 (2020)
Daley, D.J., Kendall, D.G.: Epidemic and rumors. Nature 204(4963), 1118 (1964)
Chen, H., Ai, C., Chen, B., Zhao, Y., Lai, K., He, L., Liu, Z.: The research on propagation modeling and governance strategies of online rumors based on behavior–attitude. Internet Res. 32(2), 620–639 (2022)
Sun, H., Sheng, Y., Cui, Q.: An uncertain SIR rumor spreading model. Adv. Differ. Equ. 286 (2021).
Yu, Z., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Cong, X., Li, X., & Mostafa, A. M.: Mathematical modeling and simulation for COVID-19 with mutant and quarantined strategy. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 181, 114656 (2024)
Sudbury, A.J.: The proportion of the population never hearing a rumor. J. Appl. Probab. 22, 443–446 (1985)
Zanette, D.H.: Critical behavior of propagation on small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 64(5), 050901 (2001)
Zanette, D.H.: Dynamics of rumor propagation on small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 65(4), 041908 (2002)
Moreno, Y., Nekovee, M., Pacheco, A.: Dynamics of rumor spreading in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 69, 066130 (2004)
Zhou, J., Liu, Z., Li, B.: Influence of network structure on rumor propagation. Phys. Lett. A 368(6), 458–463 (2007)
Nekovee, M., Moreno, Y., Bianconi, G., Marsili, M.: Theory of rumor spreading in complex social networks. Physica A 374(1), 457–470 (2007)
Gu, J., Cai, X.: The forget-remember mechanism for 2-statc spreading. arXiv: Adaptation and Self-Organizing Systems, 0702021 (2007).
Gu, J., Li, W., Cai, X.: The effect of the forget-remember mechanism on spreading. Eur. Phys. J. B 62(2), 247–255 (2008)
Zhao, L., Wang, J., Chen, Y.: SIHR rumor spreading model in social networks. Physica A 391(7), 2444–2453 (2012)
Zan, Y., Wu, J., Li, P., Yu, Q.: SICR rumor spreading model in complex networks: counterattack and self-resistance. Physica A 405, 159–170 (2014)
Xiao, Y., Chen, D., Wei, S., Li, Q., Wang, H., Xu, M.: Rumor propagation dynamic model based on evolutionary game and anti-rumor. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 523–539 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Xu, J.: A dynamic competition and predation model for rumor and rumor-refutation. IEEE Access 9, 9117–9129 (2021)
Zan, Y.: DSIR double-rumors spreading model in complex networks. Chaos Soliton Fract 110, 191 (2018)
Wang, J., Zhao, L., Huang, R.: 2SI2R rumor spreading model in homogeneous networks. Physica A 413, 153–161 (2014)
Yang, S., Jiang, H., Hu, C., Yu, J., Li, J.: Dynamics of the rumor spreading model with hesitation mechanism in heterogenous networks and bilingual environment. Adv. Differ. Equ. 1, 2020 (2020)
Zhang, J., Guo, H., Jing, W.J., Jin, Z.: Dynamic analysis of rumor propagation model based on true information spreader. Acta Physica Sinica 68(15), 150501 (2019)
Lin, Y., Wang, X., Hao, F., Jiang, Y.: Dynamic control of fraud information spreading in mobile social networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernetics Syst. 51(6), 3725–3738 (2019)
Diekmann, O., Heesterbeek, J.A.P., Metz, J.A.J.: On the definition and the computation of the basic reproduction ratio R0 in models for infectious diseases in heterogeneous populations. J. Math. Biol. 28, 365–382 (1990)
Wolf, A., Swift, J.B., Swinney, H.L., Vastano, J.A.: Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica D 16(3), 285–317 (1985)
DeJesus, E.X., Kaufman, C.: Routh-Hurwitz criterion in the examination of eigenvalues of a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Phys. Rev. A 35(12), 5288–5290 (1987)
Castillo-Chavez, C., Song, B.J.: Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1(2), 361–404 (2004)
Bodaghi, A.: Newly emerged rumors in twitter, Zenodo (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62273272, 62303375 and 61873277, in part by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province under Grant 2023-YBGY-243, in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province under Grant 2020JQ-758, in part by the Youth Innovation Team of Shaanxi Universities, and in part by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R1007), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhenhua Yu: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft. Haiyan Zi: Writing – original draft, Software, Validation. Yun Zhang: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. Shixing Wu: Formal analysis, Reviewing and editing. Xuya Cong: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. Almetwally M. Mostafa: Software, Validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
The authors state that this article complies with ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z., Zi, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Dynamic modeling and simulation of double-rumor spreaders in online social networks with IS2TR model. Nonlinear Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09538-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09538-3