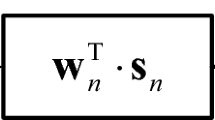Abstract
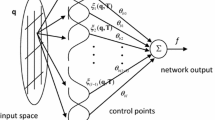
This paper presents a new scheme for the control of unknown block-oriented nonlinear systems using spline adaptive filter (SAF). The principle of adaptive inverse control (AIC) is utilized as the control structure in this scheme. First, the mathematical model of the unknown controlled plant was established through SAF, which consists of a linear FIR filter and a nonlinear spline interpolation function. The controller is obtained by adaptively establishing the inverse model of linear FIR filter and nonlinear spline function, respectively. In this process, a shift form DCT-LMS with variable learning rate (VL-DCTS-LMS) algorithm is proposed in order to adapt the inverse of FIR filter, and a modified Newton–Raphson method is used for directly calculating the inverse of spline interpolation function. Considering the steady-state error resulted by the plant modeling inaccuracy, filtered error feedback is introduced into the plant input in order to eliminate the control error. The effectiveness of the proposed control scheme is verified by several numerical examples, including some additional discussions and a comparison with other control methods.

































Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Astrom, K.J., Wittenmark, B.: Adaptive Control, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Prentice (1994)
Widrow, B., Stearns, S.D.: Adaptive Signal Processing. Prentice Hall, Prentice (1985)
Haykin, S.: Adaptive Filter Theory, 5th edn. Pearson Education, London (2003)
Widrow, B., Walach, E.: Adaptive Inverse Control. Prentice Hall, Prentice (1996)
Dang, Y., Han, C.: Adaptive inverse control based on volterra polynomial basis function neural networks. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 34(9), 8–12 (2000)
Plett, G.L.: Adaptive inverse control of linear and nonlinear systems using dynamic neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(2), 360–376 (2003)
Wang, H., Pi, D., Sun, Y.: Online SVM regression algorithm-based adaptive inverse control. Neurocomputing 70(4), 952–959 (2007)
Chen, X., Hisayama, T., Su, C.Y.: Pseudo-inverse-based adaptive control for uncertain discrete time systems preceded by hysteresis. Automatica 45(2), 469–476 (2009)
Wang, H., Xie, Y.: Adaptive inverse dynamics control of robots with uncertain kinematics and dynamics. Automatica 45(9), 2114–2119 (2009)
Li, L., Park, I.M., Brockmeier, A.J., Chen, B., Seth, S., Francis, J.T., Sanchez, J.C., Principe, J.C.: Adaptive inverse control of neural spatiotemporal spike patterns with a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) framework. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 21(4), 532–543 (2013)
Zhang, X., Li, Z., Su, C., Lin, Y., Fu, Y.: Implementable adaptive inverse control of hysteretic systems via output feedback with application to piezoelectric positioning stages. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 63(9), 5733–5743 (2016)
Mehedi, I.M.: Time varying back propagating algorithm for mimo adaptive inverse controller. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 8(2), 370–377 (2017)
Lutfy, O.F.: Adaptive direct inverse control scheme utilizing a global best artificial bee colony to control nonlinear systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(6), 2873–2888 (2018)
Fallah, M., Moetakefimani, B.: Adaptive inverse control of chatter vibrations in internal turning operations. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 129, 91–111 (2019)
Giri, F., Bai, E.W.: Block-Oriented Nonlinear System Identification. Springer, London (2010)
Vörös, J.: Modelling and identification of nonlinear cascade systems with backlash input and static output nonlinearities. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 24(6), 593–609 (2018)
Wang, D., Yan, Y., Liu, Y., Ding, J.: Model recovery for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical orthogonal matching pursuit method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 345, 135–145 (2019)
Wang, D., Zhang, S., Gan, M., Qiu, J.: A novel EM identification method for Hammerstein systems with missing output data. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 16(4), 2500–2508 (2020)
Hagenblad, A., Ljung, L., Wills, A.: Maximum likelihood identification of wiener models. Automatica 44(11), 2697–2705 (2008)
Scarpiniti, M., Comminiello, D., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Nonlinear spline adaptive filtering. Signal Process. 93(4), 772–783 (2013)
Scarpiniti, M., Comminiello, D., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Hammerstein uniform cubic spline adaptive filters: learning and convergence properties. Signal Process. 100, 112–123 (2014)
Scarpiniti, M., Comminiello, D., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Novel cascade spline architectures for the identification of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 62(7), 1825–1835 (2015a)
Scarpiniti, M., Comminiello, D., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Nonlinear system identification using IIR spline adaptive filters. Signal Process. 108, 30–35 (2015b)
Scarpiniti, M., Comminiello, D., Scarano, G., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Steady-state performance of spline adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(4), 816–828 (2016)
Rathod, M., Patel, V., George, N.V.: Generalized spline nonlinear adaptive filters. Expert Syst. Appl. 83, 122–130 (2017)
Yang, L., Liu, J., Yan, R., Chen, X.: Spline adaptive filter with arctangent-momentum strategy for nonlinear system identification. Signal Process. 164, 99–109 (2019)
Liu, C., Jiang, M., Tang, X., Liu, X.: Hammerstein subband spline adaptive filter for nonlinear system identification. Presented at the (2018)
Yang, L., Liu, J., Zhao, Z., Yan, R., Chen, X.: Interval variable step-size spline adaptive filter for the identification of nonlinear block-oriented system. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(3), 1629–1643 (2019)
Murthy, N.R., Swamy, M.N.S.: On the computation of running discrete cosine and sine transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40(6), 1430–1437 (1992)
Nikias, C.L., Shao, M.: Signal Processing with Alpha-Stable Distributions and Applications. Wiley, Location (1995)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51705396, 51835009, 51911530774).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Liu, J., Zhang, Q. et al. Spline adaptive inverse control scheme with filtered error feedback. Nonlinear Dyn 106, 2309–2328 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06882-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06882-6