Abstract
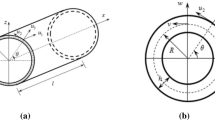
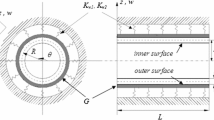
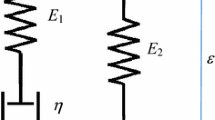
Vibration experiments are carried out on a slightly corrugated circular cylindrical shell made of polyethylene terephthalate fabric. The shell is liquid-filled, it is pressurized by a liquid column that applies a pressure of 100 mmHg, and the two edges are clamped to fix supports. Forced vibrations of the shell are experimentally studied in the linear (small amplitude) and in the geometrically nonlinear (large amplitude) regime. The large-amplitude vibrations of the liquid-filled shell are characterized by a strong softening behavior that cannot be captured by any quadratic nonlinear stiffness. Since compressed fibers do not carry load, a piecewise linear stiffness with viscous damping is thus introduced in a reduced-order model, resulting in a very good agreement between experimental and simulated responses. The stiffness parameters and the damping ratios are identified from the experimental results. The damping ratio grows linearly with the excitation amplitude, indicating a predominant hydrodynamic damping. In particular, the damping ratio increases 2.75 times from the small-amplitude vibrations to a maximum amplitude of 1.26 mm. This is a very significant increase that highlights the necessity to introduce nonlinear damping to model shell structures.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amabili, M., Païdoussis, M.P.: Review of studies on geometrically nonlinear vibrations and dynamics of circular cylindrical shells and panels, with and without fluid-structure interaction. Appl. Mech. Rev. 56(4), 349–356 (2003)
Alijani, F., Amabili, M.: Non-linear vibrations of shells: a literature review from 2003 to 2013. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 58, 233–257 (2014)
Chen, J.C., Babcock, C.D.: Nonlinear vibration of cylindrical shells. AIAA J. 13, 868–876 (1975)
Gonçalves, P.B., Batista, R.C.: Nonlinear vibration analysis of fluid-filled cylindrical shells. J. Sound Vib. 127, 133–143 (1988)
Amabili, M., Pellicano, F., Païdoussis, M.P.: Nonlinear dynamics and stability of circular cylindrical shells containing flowing fluid. Part III: Truncation effect without flow and experiments. J. Sound Vib. 237, 617–640 (2000)
Amabili, M.: Comparison of shell theories for large-amplitude vibrations of circular cylindrical shells: lagrangian approach. J. Sound Vib. 264, 1091–1125 (2003)
Amabili, M.: Nonlinear Vibrations and Stability of Shells and Plates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Amabili, M.: Nonlinear vibrations of angle-ply laminated circular cylindrical shells: skewed modes. Compos. Struct. 94, 3697–3709 (2012)
Pellicano, F.: Vibrations of circular cylindrical shells: theory and experiments. J. Sound Vib. 303, 154–170 (2007)
Jansen, E.L.: The effect of static loading and imperfections on the nonlinear vibrations of laminated cylindrical shells. J. Sound Vib. 315, 1035–1046 (2008)
Ribeiro, P.: On the influence of membrane inertia and shear deformation on the geometrically non-linear vibrations of open, cylindrical, laminated clamped shells. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69, 176–185 (2009)
Amabili, M., Balasubramanian, P., Ferrari, G.: Travelling wave and non-stationary response in nonlinear vibrations of water-filled circular cylindrical shells: experiments and simulations. J. Sound Vib. 381, 220–245 (2016)
Breslavsky, I.D., Amabili, M., Legrand, M.: Static and dynamic behavior of circular cylindrical shell made of hyperelastic arterial material. J. Appl. Mech. 83, 051002 (2016)
Amabili, M.: Nonlinear Mechanics of Shells and Plates in Composite, Soft and Biological Materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2018)
Amabili, M., Breslavsky, I.D., Reddy, J.N.: Nonlinear higher-order shell theory for incompressible biological hyperelastic materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 346, 841–861 (2019)
Bustos, C.A., García-Herrera, C.M., Celentano, D.J.: Modelling and simulation of the mechanical response of a Dacron graft in the pressurization test and an end-to-end anastomosis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 61, 36–44 (2016)
Amabili, M., Balasubramanian, P., Breslavsky, I., Ferrari, G., Tubaldi, E.: Viscoelastic characterization of woven Dacron for aortic grafts by using direction-dependent quasi-linear viscoelasticity. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 82, 282–290 (2018)
Ferrari, G., Balasubramanian, P., Tubaldi, E., Giovanniello, F., Amabili, M.: Experiments on dynamic behaviour of a Dacron aortic graft in a mock circulatory loop. J. Biomech. 86, 132–140 (2019)
Amabili, M., Balasubramanian, P., Ferrari, G., Franchini, G., Giovanniello, F., Tubaldi, E.: Identification of viscoelastic properties of Dacron aortic grafts subjected to physiological pulsatile flow. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 110, 103804 (2020)
Amabili, M., Garziera, R.: Vibrations of circular cylindrical shells with nonuniform constraints, elastic bed and added mass, part I: empty and fluid-filled shells. J. Fluids Struct. 14, 669–690 (2000)
Doedel, E.J., Champneys, A.R., Fairgrieve, T.F., Kuznetsov, Y.A., Sandstede, B., Wang, X.: Continuation and Bifurcation Software for Ordinary Differential Equations (with HomCont). AUTO97. Concordia University, Montreal (1997)
Amabili, M.: Nonlinear damping in nonlinear vibrations of rectangular plates: derivation from viscoelasticity and experimental validation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 118, 275–292 (2018)
Amabili, M.: Nonlinear damping in large-amplitude vibrations: modelling and experiments. Nonlinear Dyn. 93, 5–18 (2018)
Balasubramanian, P., Ferrari, G., Amabili, M.: Identification of the viscoelastic response and nonlinear damping of a rubber plate in nonlinear vibration regime. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 111, 376–398 (2018)
Amabili, M.: Derivation of nonlinear damping from viscoelasticity in case of nonlinear vibrations. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 1785–1797 (2019)
Colin, M., Thomas, O., Grondel, S., Cattan, E.: Very large amplitude vibrations of flexible structures: experimental identification and validation of a quadratic drag damping model. J. Fluids Struct. 97, 103056 (2020)
Elliot, S.J., Ghandchi Tehrani, M., Langley, R.S.: Nonlinear damping and quasi-linear modelling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 373, 20140402 (2015)
Amabili, M., Balasubramanian, P., Bozzo, I., Breslavsky, I.D., Ferrari, G., Franchini, G., Giovanniello, F., Pogue, C.: Nonlinear dynamics of human aortas for material characterization. Phys. Rev. X 10, 011015 (2020)
Acknowledgments
The last author acknowledges the financial support of the NSERC Discovery Grant, the Canada Foundation for Innovation John R. Evans Leaders Fund Award and the Canada Research Chair program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanian, P., Ferrari, G. & Amabili, M. Nonlinear vibrations of a fluid-filled, soft circular shell: experiments and system identification. Nonlinear Dyn 102, 1409–1418 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-06007-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-06007-5