Abstract
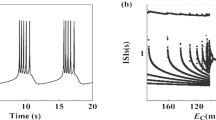
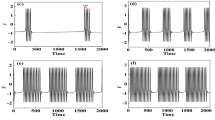
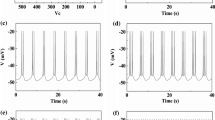
Based on the post-inhibitory rebound (PIR) spike induced by inhibitory current pulse, in the present paper, a novel counterintuitive phenomenon that the inhibitory autapse with time delay can induce the resting state changed to stable spiking pattern is identified near subcritical Hopf bifurcation of Hodgkin–Huxley model. The delayed inhibitory autaptic current pulse induced by the preceded action potential can induce the preceding PIR spike via the hyperpolarization, rebound, and depolarization processes, which is compared with spiking induced by excitatory autapse via only a depolarization process. The threshold of inhibitory or excitatory autaptic conductance to induce spiking with increasing time delay, and the threshold curve of inhibitory or excitatory pulse current to evoke a spike exhibit damping oscillations can be well interpreted with the damping dynamics of focus near subcritical Hopf bifurcation. However, due to PIR mechanism, the threshold conductance of inhibitory autapse is stronger than that of excitatory autapse, and the spiking period for inhibitory autapse, which is composed of time delay and durations of the other three processes, is longer than the one for excitatory autapse, which is composed of time delay and duration of only a depolarization process. Therefore, a linear correlation between spiking period and time delay is identified, which shows that autapse can modulate the spike timing related to temporal coding. The results present a novel viewpoint and a potential function that inhibitory autapse can facilitate spiking like the excitatory autapse and provide effective measures to modulate neuronal spiking pattern, which is related to subcritical Hopf bifurcation.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Izhikevich, E.M.: Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 10(6), 1171–1266 (2002)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Dynamical Systems in Neuroscience: The Geometry of Excitability and Bursting. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (2007)
Bean, B.P.: The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8(6), 451–465 (2007)
Bartos, M., Vida, I., Jonas, P.: Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8(1), 45–56 (2007)
Prescott, S.A., Ratté, S., De Schutter, E., Sejnowski, T.J.: Pyramidal neurons switch from integrators in vitro to resonators under in vivo-like conditions. J. Neurophysiol. 100(6), 3030–3042 (2008)
Zhao, Z.G., Gu, H.G.: Transitions between classes of neuronal excitability and bifurcations induced by autapse. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 7660 (2017)
Goldwyn, J.H., Slabe, B.R., Travers, J.B., Terman, D.: Gain control with A-type potassium current: I-A as a switch between divisive and subtractive inhibition. PLoS Comput. Biol. 14(7), e1006292 (2018)
Saada, R., Miller, N., Hurwitz, I., Susswein, A.J.: Autaptic excitation elicits persistent activity and a plateau potential in a neuron of known behavioral function. Curr. Biol. 19(6), 479–684 (2009)
Bacci, A., Huguenard, J.R., Prince, D.A.: Functional autaptic neurotransmission in fast-spiking interneurons: a novel form of feedback inhibition in the neocortex. J. Neurosci. 23(3), 859–866 (2003)
Guo, D.Q., Wang, Q.Y., Perc, M.: Complex synchronous behavior in interneuronal networks with delayed inhibitory and fast electrical synapses. Phys. Rev. E 85(6), 061905 (2012)
Hilscher, M.M., Leao, K.E., Leao, R.N.: Synchronization through nonreciprocal connections in a hybrid hippocampus microcircuit. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 7, 120 (2013)
Dodla, R., Rinzel, J.: Enhanced neuronal response induced by fast inhibition. Phys. Rev. E 73(1), 010903 (2006)
Dodla, R., Svirskis, G., Rinzel, J.: Well-timed, brief inhibition can promote spiking: postinhibitory facilitation. J. Neurophysiol. 95(4), 2664–2677 (2006)
Winograd, M., Destexhe, A., Sanchez-Vives, M.V.: Hyperpolarization-activated graded persistent activity in the prefrontal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105(20), 7298–7303 (2008)
Elgueta, C., Kohler, J., Bartos, M.: Persistent discharges in dentate gyrus perisoma-inhibiting interneurons require hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel activation. J. Neurosci. 35(10), 4131–4139 (2015)
Tikidji-hamburyan, R.A., Martinez, J.J., White, J.A., Canavier, C.C.: Resonant interneurons can increase robustness of gamma oscillations. J. Neurosci. 35(47), 15682–15695 (2015)
Zhao, Z.G., Jia, B., Gu, H.G.: Bifurcations and enhancement of neuronal firing induced by negative feedback. Nonlinear Dyn. 86(3), 1549–1560 (2016)
Jia, B.: Negative feedback mediated by fast inhibitory autapse enhances neuronal oscillations near a Hopf bifurcation point. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 28(2), 1850030 (2018)
Zhao, Z.G., Gu, H.G.: The influence of single neuron dynamics and network topology on time delay-induced multiple synchronous behaviors in inhibitory coupled network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 80, 96–108 (2015)
Gu, H.G., Zhao, Z.G.: Dynamics of time delay-induced multiple synchronous behaviors in inhibitory coupled neurons. PLoS ONE 10(9), e0138593 (2015)
Jia, B., Wu, Y.C., He, D., Guo, B.H., Xue, L.: Dynamics of transitions from anti-phase to multiple in-phase synchronizations in inhibitory coupled bursting neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(3), 1599–1618 (2018)
Wang, Q.Y., Chen, G.R., Perc, M.: Synchronous bursts on scale-free neuronal networks with attractive and repulsive coupling. PLoS ONE 6(1), e15851 (2011)
Li, L., Zhao, Z.G., Gu, H.G.: Bifurcations of time-delay-induced multiple transitions between bifurcations in-phase and anti-phase synchronizations in neurons with excitatory or inhibitory synapses. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29(11), 1950147 (2019)
Ding, X.L., Li, Y.Y.: Period-adding bifurcation of neural firings induced by inhibitory autapses with time-delay. Acta Phys. Sin. 65(21), 210502 (2016). (in chinese)
Cao, B., Guan, L.N., Gu, H.G.: Bifurcation mechanism of not increase but decrease of spike number within a neural burst induced by excitatory effect. Acta Phys. Sin. 67(24), 240502 (2018). (in chinese)
Wu, F.Q., Gu, H.G., Li, Y.Y.: Inhibitory electromagnetic induction current induced enhancement instead of reduction of neural bursting activities. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 79, 104924 (2019)
Van Der Loos, H., Glaser, E.M.: Autapses in neocortex cerebri: synapses between a pyramidal cell’s axon and its own dendrites. Brain Res. 48, 355–360 (1972)
Jiang, M., Zhu, J., Liu, Y.P., Yang, M.P., Tian, C.P., Jiang, S., Wang, Y., Guo, H., Wang, K., Shu, Y.: Enhancement of asynchronous release from fast-spiking interneuron in human and rat epileptic neocortex. PLoS Biol. 10(5), e1001324 (2012)
Yin, L.P., Zheng, R., Ke, W., He, Q.S., Zhang, Y., Li, J.L., Wang, B., Mi, Z., Long, Y.S., Rasch, M.J.: Autapses enhance bursting and coincidence detection in neocortical pyramidal cells. Nat. Commun. 9, 4890 (2018)
Bacci, A., Huguenard, J.R.: Enhancement of spike-timing precision by autaptic transmission in neocortical inhibitory interneurons. Neuron 49(1), 119–130 (2006)
Cobb, S.R., Halasy, K., Vida, I., Nyiri, G., Tamas, G., Buhl, E.H., Somogyi, P.: Synaptic effects of identified interneurons innervating both interneurons and pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 79(3), 629–648 (1997)
Li, Y.Y., Schmid, G., Hanggi, P., Schimansky-Geier, L.: Spontaneous spiking in an autaptic Hodgkin–Huxley setup. Phys. Rev. E 82(6), 061907 (2010)
Yao, Y.G., Ma, J.: Signal transmission by autapse with constant or time-periodic coupling intensity in the FitzHugh–Nagumo neuron. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 227(7–9), 757–766 (2018)
Ge, M.Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, Z.K., Peng, Y.X., Kang, W.J., Yang, L.J., Jia, Y.: Autaptic modulation-induced neuronal electrical activities and wave propagation on network under electromagnetic induction. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 227(7–9), 799–809 (2018)
Xu, Y., Ying, H.P., Jia, Y., Ma, J., Hayat, T.: Autaptic regulation of electrical activities in neuron under electromagnetic induction. Sci. Rep. 7, 4352 (2017)
Qin, H.X., Ma, J., Jin, W.Y., Wang, C.N.: Dynamics of electric activities in neuron and neurons of network induced by autapses. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57(5), 936–946 (2014)
Wang, H.T., Wang, L.F., Chen, Y.L., Chen, Y.: Effect of autaptic activity on the response of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Chaos 24(3), 033122 (2014)
Hashemi, M., Valizadeh, A., Azizi, Y.: Effect of duration of synaptic activity on spike rate of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with delayed feedback. Phys. Rev. E 85(2), 021917 (2012)
Guo, D.Q., Wu, S.D., Chen, M.M., Perc, M., Zhang, Y.S., Ma, J.L., Cui, Y., Xu, P., Xia, Y., Yao, D.Z.: Regulation of irregular neuronal firing by autaptic transmission. Sci. Rep. 6, 26096 (2016)
Wang, H.T., Ma, J., Chen, Y.L., Chen, Y.: Effect of an autapse on the firing pattern transition in a bursting neuron. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19(9), 3242–3254 (2014)
Guo, D.Q., Chen, M.M., Perc, M., Wu, S.D., Xia, C., Zhang, Y.S., Xu, P., Xia, Y., Yao, D.Z.: Firing regulation of fast-spiking interneurons by autaptic inhibition. Europhys. Lett. 114(3), 30001 (2016)
Song, X.L., Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Autapse-induced firing patterns transitions in the Morris–Lecar neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(4), 2341–2350 (2019)
Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M., Baysal, V., Perc, M.: Autapse-induced multiple coherence resonance in single neurons and neuronal networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 30914 (2016)
Song, X.L., Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Coherence resonance in an autaptic Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with time delay. Nonlinear Dyn. 94(1), 141–150 (2018)
Uzun, R.: Influences of autapse and channel blockage on multiple coherence resonance in a single neuron. Appl. Math. Comput. 315, 203–210 (2017)
Connelly, W.M.: Autaptic connections and synaptic depression constrain and promote gamma oscillations. PLoS ONE 9(2), e89995 (2014)
Wu, Y.N., Gong, Y.B., Wang, Q.: Autaptic activity-induced synchronization transitions in Newman–Watts network of Hodgkin–Huxley neurons. Chaos 25(4), 043113 (2015)
Yilmaz, E., Baysal, V., Perc, M., Ozer, M.: Enhancement of pacemaker induced stochastic resonance by an autapse in a scale-free neuronal network. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59(3), 364–370 (2016)
Qin, H.X., Wu, Y., Wang, C.N., Ma, J.: Emitting waves from defects in network with autapses. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 23(1–3), 164–174 (2015)
Qin, H.X., Ma, J., Wang, C.N., Chu, R.: Autapse-induced target wave, spiral wave in regular network of neurons. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57(10), 1918–1926 (2014)
Ma, J., Song, X.L., Tang, J., Wang, C.N.: Wave emitting and propagation induced by autapse in a forward feedback neuronal network. Neurocomputing 167, 378–389 (2015)
Yilmaz, E., Baysal, V., Ozer, M., Perc, M.: Autaptic pacemaker mediated propagation of weak rhythmic activity across small-world neuronal networks. Physica A 444, 538–546 (2016)
Li, Y.Y., Gu, H.G., Ding, X.L.: Bifurcations of enhanced neuronal bursting activities induced by the negative current mediated by inhibitory autapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2091–2105 (2019)
Wechselberger, M.: Existence and bifurcation of canards in R-3 in the case of a folded node. SIAM J. App. Dyn. Syst. 4(1), 101–139 (2005)
Zhao, Z.G., Li, L., Gu, H.G.: Dynamical mechanism of hyperpolarization-activated non-specific cation current induced resonance and spike-timing precision in a neuronal model. Front. Cell Neurosci. 12, 62 (2018)
Hodgkin, A.L.: The local electric changes associated with repetitive action in a non-medullated axon. J. Physiol. 107(2), 165–181 (1948)
Jalil, S., Belykh, I., Shilnikov, A.: Spikes matter for phase-locked bursting in inhibitory neurons. Phys. Rev. E 85, 036214 (2012)
Somers, D., Kopell, N.: Rapid synchronization through fast threshold modulation. Biol. Cybern. 68, 393–407 (1993)
Wang, X.J., Buzsáki, G.: Gamma oscillation by synaptic inhibition in a hippocampal interneuronal network model. J. Neurosci. 16, 6402–6413 (1996)
Ermentrout, B.: Simulating, Analyzing, and Animating Dynamical Systems: A Guide to XPPAUT for Researchers and Students. SIAM, Philadelphia (2002)
Zhang, X.J., Gu, H.G.: The influences of dynamics of Hopf bifurcation on the conduction failure of action potentials along nerve C-fiber. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29(7), 19500093 (2019)
Guo, D.Q., Perc, M., Liu, T.J., Yao, D.Z.: Functional importance of noise in neuronal information processing. Europhys. Lett. 124(5), 50001 (2018)
Guo, D.Q., Perc, M., Zhang, Y.S., Xu, P., Yao, D.Z.: Frequency-difference-dependent stochastic resonance in neural systems. Phys. Rev. E 96(2), 022415 (2017)
Perc, M.: Stochastic resonance on weakly paced scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 78(3), 036105 (2008)
Uzuntarla, M., Uzun, R., Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M., Perc, M.: Noise-delayed decay in the response of a scale-free neuronal network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 56, 202–208 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11802085, 11572225, and 11872276, and the Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province under Grant No. 20B110003.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Li, L., Gu, H. et al. Different dynamics of repetitive neural spiking induced by inhibitory and excitatory autapses near subcritical Hopf bifurcation. Nonlinear Dyn 99, 1129–1154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05342-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05342-6