Abstract
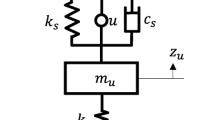
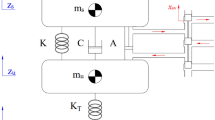
Application of the state-dependent Riccati equation and approximating sequence of Riccati equation techniques for the control of active suspension system considering nonlinear actuator dynamics will be investigated. First, equation of motion of the vehicle model is written in terms of the nonlinear state equations. Then, a performance index is formed for the minimization of the acceleration of the sprung mass, suspension deflection, velocity of the sprung mass, tire deflection, velocity of the unsprung mass, pressure decrease through the piston, and rate of pressure decrease through the piston. A sinusoidal bump and road roughness are considered as the road disturbances. After that, control input is expressed in terms of the Riccati differential equation variables and the state variables. Finally, quarter vehicle suspension system model of a Ford Fiesta Mk2 is taken into consideration in numerical simulations to test the performances of the both techniques. The results are compared to those of equivalent passive suspension system.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajamani, R., Hedrick, J.K.: Adaptive observers for active automotive suspensions: theory and experiment. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 3(1), 86–93 (1995)
Dangor, M., Dahunsi, O.A., Pedro, J.O., Ali, M.M.: Evolutionary algorithm-based PID controller tuning for nonlinear quarter-vehicle electrohydraulic vehicle suspensions. Nonlinear Dyn. 78, 2795–2810 (2014)
Renn, J.-C., Wu, T.-H.: Modeling and control of a new 1/4T servo-hydraulic vehicle active suspension system. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 15(3), 265–272 (2007)
Alleyne, A., Liu, R.: A simplified approach to force control for electro-hydraulic systems. Control Eng. Pract. 8, 1347–1356 (2000)
Alleyne, A., Hedrick, J.K.: Nonlinear adaptive control of active suspensions. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 3(1), 94–101 (1995)
Chen, P.-C., Huang, A.-C.: Adaptive sliding control of active suspension systems with uncertain hydraulic actuator dynamics. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 44(5), 357–368 (2006)
Lin, J., Lian, R.-J., Huang, C.-N., Sie, W.-T.: Enhanced fuzzy sliding mode controller for active suspension systems. Mechatronics 19, 1178–1190 (2009)
Lin, J.-S., Kanellakopoulos, I.: Nonlinear design of active suspensions. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 17, 45–49 (1997)
Fialho, I., Balas, G.J.: Road adaptive active suspension design using linear parameter-varying gain-scheduling. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 10(1), 43–54 (2002)
Gaspar, P., Szabo, Z., Szederkenyi, G., Bokor, J.: Design of a two-level controller for an active suspension system. Asian J. Control 14(3), 664–678 (2012)
Bui, T.H., Suh, J.H., Kim, S.B., Nguyen, T.T.: Hybrid control of an active suspension system with full-vehicle model using H\(\infty \), and nonlinear adaptive control methods. KSME Int. J. 16(12), 1613–1626 (2002)
Fateh, M.M., Zirkohi, M.M.: Adaptive impedance control of a hydraulic suspension system using particle swarm optimisation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 49(12), 1951–1965 (2011)
Chantranuwathana, S., Peng, H.: Adaptive robust force control for vehicle active suspensions. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 18, 83–102 (2004)
Sun, W., Gao, H., Yao, B.: Adaptive robust vibration control of full-vehicle active suspensions with electrohydraulic actuators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 21(6), 2417–2422 (2013)
Du, H., Zhang, N.: Fuzzy control for nonlinear uncertain electrohydraulic active suspensions with input constraint. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17(2), 343–356 (2009)
Lin, J., Lian, R.-J.: Intelligent control of active suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 58(2), 618–628 (2011)
Cloutier, J.R., D’Souza, C.N., Mracek C.P.: Nonlinear regulation and nonlinear H\(\infty \) control via the state-dependent Riccati equation technique: part 1, theory; part 2, examples. In: First International Conference on Nonlinear Problems in Aviation and Aerospace, Daytona Beach, FL, USA, pp. 117–141 (1996)
Mracek, C.P., Cloutier, J.R.: Control designs for the nonlinear benchmark problem via the state-dependent Riccati equation method. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 8, 401–433 (1998)
Cloutier, J.R., Stansbery, D.T.: The capabilities and art of state-dependent Riccati equation-based design. In: American Control Conference, Anchorage, AK, USA, pp. 86–91 (2002)
Shamma, J.S., Cloutier, J.R.: Existence of SDRE stabilizing feedback. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 48, 513–517 (2003)
Cimen, T.: Systematic and effective design of nonlinear feedback controllers via the state-dependent Riccati equation (SDRE) method. Ann. Rev. Control 34, 32–51 (2010)
Cimen, T.: Survey of state-dependent Riccati equation in nonlinear optimal feedback control synthesis. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 35(4), 1025–1047 (2012)
Banks, S.P., Dinesh, K.: Approximate optimal control and stability of nonlinear finite and infinite-dimensional systems. Ann. Oper. Res. 98, 19–44 (2000)
Tomas-Rodriguez, M., Banks, S.P.: Linear approximations to nonlinear dynamical systems with applications to stability and spectral theory. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 20, 89–103 (2003)
Cimen, T., Banks, S.P.: Global optimal feedback control for general nonlinear systems with nonquadratic performance criteria. Syst. Control Lett. 53(5), 327–346 (2004)
Cimen, T., Banks, S.P.: Nonlinear optimal tracking control with application to super-tankers for autopilot design. Automatica 40(11), 1845–1863 (2004)
Kilicaslan, S., Banks, S.P.: A separation theorem for nonlinear systems. Automatica 45(4), 928–935 (2009)
Kilicaslan, S., Banks, S.P.: Existence of solutions of Riccati differential equations. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control Trans. ASME 134, 031001 (2012)
Banks, H.T., Lewis, B.M., Tran, H.T.: Nonlinear feedback controllers and compensators: a state-dependent Riccati equation approach. Comput. Optim. Appl. 37, 177–218 (2007)
Merritt, H.E.: Hydraulic Control Systems. Wiley, New York (1967)
Giua, A., Melas, M., Seatzu, C., Usai, G.: Design of a predictive semiactive suspension system. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 41(4), 277–300 (2004)
Pedro, J., Ekoru, J.: NARMA-L2 control of a nonlinear half-car servo-hydraulic vehicle suspension system. Acta Polytech. Hung. J. Appl. Sci. 10(4), 5–26 (2013)
Pedro, J.O., Dangor, M., Dahunsi, O.A., Ali, M.: Differential evolution-based PID control of nonlinear full-car electrohydraulic suspensions. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 1–13, Article ID 261582
Pedro, J.O., Dahunsi, O.A.: Neural network-based feedback linearization control of a servo-hydraulic vehicle suspension system. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 21(1), 137–147 (2011)
Du, H., Zhang, N.: Static output feedback control for electrohydraulic active suspensions via T-S fuzzy model approach. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control Trans. ASME 131(5), 051004 (2009)
Gysen, B.L.J., Paulides, J.J.H., Janssen, J.L.G., Lomonova, E.A.: Active electromagnetic suspension system for improved vehicle dynamics. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 59(3), 1156–1163 (2010)
Griffin, M.J.: Discomfort from feeling vehicle vibration. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 45(7–8), 679–698 (2007)
European Commission: Directive 2002/44/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 25 June 2002 on the minimum health and safety requirements regarding the exposure of workers to the risk arising from physical agents (vibration). Official Journal of the European Communities, Luxembourg (2002)
ISO 2631: Mechanical Vibration and Shock-Evaluation of Human Exposure to Whole-Body Vibration-Part 1: General Requirements. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland (2003)
Beltran-Carbajal, F., Chavez-Conde, E., Favela-Contreras, A., Chavez-Bracamontes, R.: Active nonlinear vehicle suspension based on real time estimation of perturbation signals. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Auburn, AL, USA, vol. s, pp. 437–442, Mart 14–16 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilicaslan, S. Control of active suspension system considering nonlinear actuator dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn 91, 1383–1394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3951-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3951-x