Abstract
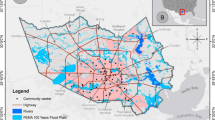
Flood risk has become a serious challenge for many cities, including New York City (NYC). Evaluating urban flood adaptability evaluation is crucial for regulating storm and rain risks. In this study, we proposed an integrated framework based on the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services (InVEST) model and Geographic Information System (GIS). First, the InVEST model was used to assess the water yield, soil conservation, and water quality purification in NYC. Second, the entropy weighting method was employed to determine the weights of indicators for computing the flood adaptability evaluation (FAE). Third, a spatial correlation of FAE was conducted and finally delineated the flood adaptability zones in GIS. The results show that: (1) The spatial distribution of FAE was uneven, high in the surrounding area and low in the center. (2) The Moran's I for FAE was 0.644, showing an overall positive spatial relationship of FAE. High-scoring clusters were located in the southeastern area while low-scoring clusters were in the northern, central, and southwestern areas. (3) The FAE in NYC can be divided into five categories: the lower-adapted zone (0.22–0.27), low-adapted zone (0.28–0.31), medium-adapted zone (0.32–0.36), high-adapted zone (0.37–0.43) and higher-adapted zone (0.44–0.50). These results of the study can provide evidence and recommendations for flood risk management in NYC and other cities worldwide.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All the data used for the study appear in Sect. 2.2 of the submitted article.
References
Adikari Y, Osti R, Noro T (2010) Flood-related disaster vulnerability: an impending crisis of megacities in Asia. J Flood Risk Manag 3:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-318X.2010.01068.x
Allen RG, Pruitt WO, Raes D et al (2005) Estimating evaporation from bare soil and the crop coefficient for the initial period using common soils information. J Irrig Drain Eng 131:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2005)131:1(14)
Anselin L (1995) Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr Anal 27:93–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1995.tb00338.x
Arup (2023) Arup GlobalSponge Cities Snapshot. https://www.arup.com/perspectives/publications/research/section/global-sponge-cities-snapshot. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Atlanta Regional Commission (2016) Edition of the Georgia Stormwater Management Manual Volumes 1 & 2. https://atlantaregional.org/natural-resources/water/georgia-stormwater-management-manual/. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Boruff BJ (2009) Environmental hazards: assessing risk and reducing disasters, 5th Edition – By Keith Smith and David N. Petley. Geogr Res 47:454–455. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-5871.2009.00611.x
Boulange J, Hanasaki N, Yamazaki D, Pokhrel Y (2021) Role of dams in reducing global flood exposure under climate change. Nat Commun 12:417. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20704-0
Cabrera JS, Lee HS (2020) Flood risk assessment for Davao Oriental in the Philippines using geographic information system-based multi-criteria analysis and the maximum entropy model. J Flood Risk Manag 13:e12607. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12607
Cai S, Fan J, Yang W (2021) Flooding risk assessment and analysis based on GIS and the TFN-AHP method: a case study of Chongqing, China. Atmosphere 12:623. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050623
Chen Y, Zhou H, Zhang H et al (2015) Urban flood risk warning under rapid urbanization. Environ Res 139:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.02.028
Chen Z, Mo C, Chen R, Peng B (2022) Assessment and zoning of rain and flood adaptability in the construction demonstration area of Sponge City in Changde City. J Natl Resources 37:2195–2208. https://doi.org/10.31497/zrzyxb.20220818. (in Chinese)
Diniz-Filho JAF, Bini LM, Hawkins BA (2003) Spatial autocorrelation and red herrings in geographical ecology. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 12:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1466-822X.2003.00322.x
District of Columbia, Department of Environment (2020) Stormwater Management Guide Book. https://doee.dc.gov/swguidebook. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Donohue RJ, Roderick ML, McVicar TR (2012) Roots, storms and soil pores: Incorporating key ecohydrological processes into Budyko’s hydrological model. J Hydrol 436–437:35–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.033
FAO Soils Portal (2008) Harmonized World Soil Database v1.2. https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/harmonized-world-soil-database-v12/en/. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Feng Z, Jin X, Chen T, Wu J (2021) Understanding trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services to support the decision-making in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 106:105446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105446
Fletcher TD, Shuster W, Hunt WF et al (2015) SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more: the evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J 12:525–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2014.916314
Getis A, Ord JK (2010) The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr Anal 24:189–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1992.tb00261.x
Goyen AG, Lees SJ, Phillips BC (2012) Analysis of allotment based storage, infiltration and reuse drainage strategies to minimize urbanization effects. Glob Solut Urban Drain 1:17. https://doi.org/10.1061/40644(2002)42
Hallegatte S, Vogt-Schilb A, Bangalore M, Rozenberg J (2017) Unbreakable. World Bank, Washington, DC
Hammond MJ, Chen AS, Djordjević S et al (2015) Urban flood impact assessment: a state-of-the-art review. Urban Water J 12:14–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2013.857421
Hong H, Panahi M, Shirzadi A et al (2018) Flood susceptibility assessment in Hengfeng area coupling adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system with genetic algorithm and differential evolution. Sci Total Environ 621:1124–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.114
Hu S, Cao M, Liu Q, Zhang T, Qiu H, Liu W, Song J (2014) Comparison of soil conservation functions of InVEST model from different perspectives. Geogr Res 33:2393–2406. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj201412016. (in Chinese)
Ji J, Chen J (2022) Urban flood resilience assessment using RAGA-PP and KL-TOPSIS model based on PSR framework: a case study of Jiangsu province, China. Water Sci Technol 86:3264–3280. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.404
Jun C, Ban Y, Li S (2014) Open access to Earth land-cover map. Nature 514:434–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/514434c
Lehner B, Grill G (2013) Global river hydrography and network routing: baseline data and new approaches to study the world’s large river systems. Hydrol Process 27:2171–2186. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9740
Li T, Liu K, Hu S, Bao Y (2014) Evaluation of ecological benefits of soil loss and soil conservation in Qinling Mountains based on InVEST model. Resources Environ the Yangtze River Basin 23:1242–1250. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201409009. (in Chinese)
Li Q, Wang F, Yu Y et al (2019) Comprehensive performance evaluation of LID practices for the sponge city construction: a case study in Guangxi, China. J Environ Manage 231:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.024
Luu C, Von Meding J, Mojtahedi M (2019) Analyzing Vietnam’s national disaster loss database for flood risk assessment using multiple linear regression-TOPSIS. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 40:101153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101153
Lyu H-M, Sun W-J, Shen S-L, Arulrajah A (2018) Flood risk assessment in metro systems of mega-cities using a GIS-based modeling approach. Sci Total Environ 626:1012–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.138
Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China (2018) Announcement of the Ministry of Water Resources on Approving the Issuance of Three Water Conservancy Industry Standards, including the "Guidelines for the Calculation of Soil Loss in Production and Construction Projects". http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2018-12/31/content_5440136.htm. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Mitchell G (2005) Mapping hazard from urban non-point pollution: a screening model to support sustainable urban drainage planning. J Environ Manage 74:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2004.08.002
Mojaddadi H, Pradhan B, Nampak H et al (2017) Ensemble machine-learning-based geospatial approach for flood risk assessment using multi-sensor remote-sensing data and GIS. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 8:1080–1102. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1294113
Morison PJ, Brown RR (2011) Understanding the nature of publics and local policy commitment to Water Sensitive Urban Design. Landsc Urban Plan 99:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.08.019
National Earth System Science Data Center (2023). http://www.geodata.cn/. Accessed on 19 March 2023).
New York Division of Engineering (2016) New York State Stormwater Management Design Manual. https://www.dec.ny.gov/chemical/29072.html. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Nguyen TT, Ngo HH, Guo W et al (2019) Implementation of a specific urban water management: Sponge City. Sci Total Environ 652:147–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.168
NYC Emergency Management (2014) NYC'S Risk Landscape: A Guide to Hazard Mitigation. https://a860-gpp.nyc.gov/concern/nyc_government_publications/9306sz780. Accessed on 19 March 2023
NYC Environmental Protection (2017) The Bluebelt Program. https://www.nyc.gov/site/dep/water/the-bluebelt-program.page. Accessed on 19 March 2023
NYC Environmental Protection (2022) NYC green infrastructure 2021 annual report. https://a860-gpp.nyc.gov/concern/parent/bv73c3028/file_sets/qr46r355g. Accessed on 19 March 2023
NYC Open Data (2013). https://opendata.cityofnewyork.us/. Accessed on 19 March 2023).
Pour SH, Wahab AKA, Shahid S et al (2020) Low impact development techniques to mitigate the impacts of climate-change-induced urban floods: Current trends, issues and challenges. Sustain Cities Soc 62:102373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102373
Pyke C, Warren MP, Johnson T et al (2011) Assessment of low impact development for managing stormwater with changing precipitation due to climate change. Landsc Urban Plan 103:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2011.07.006
Rao E, Xiao Y, Ouyang Z, Zheng H (2013) Spatial characteristics of soil conservation service and its impact factors in Hainan Island. Acta Ecol Sin 33:746–755. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201203240400. (in Chinese)
Rufat S, Botzen WJW (2022) Drivers and dimensions of flood risk perceptions: revealing an implicit selection bias and lessons for communication policies. Glob Environ Chang 73:102465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2022.102465
Shangguan W, Hengl T, Mendes de Jesus J et al (2017) Mapping the global depth to bedrock for land surface modeling. J Adv Model Syst 9:65–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016MS000686
Shao Z, Fu H, Li D et al (2019) Remote sensing monitoring of multi-scale watersheds impermeability for urban hydrological evaluation. Remote Sens Environ 232:111338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111338
Sharp R, Tallis H T, Ricketts T et al. (2018) InVEST 3.12.0 User’s Guide. https://naturalcapitalproject.stanford.edu/software/invest. Accessed on 26 November 2022
Souissi D, Zouhri L, Hammami S et al (2020) GIS-based MCDM: AHP modeling for flood susceptibility mapping of arid areas, southeastern Tunisia. Geocarto Int 35:991–1017. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1566405
Stefanidis S, Stathis D (2013) Assessment of flood hazard based on natural and anthropogenic factors using analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Nat Hazards 68:569–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0639-5
Sun S, Zhai J, Li Y et al (2020) Urban waterlogging risk assessment in well-developed region of Eastern China. Phys Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 115:102824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2019.102824
Tayyab M, Zhang J, Hussain M et al (2021) GIS-based urban flood resilience assessment using urban flood resilience model: a case study of Peshawar City, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Remote Sens 13:1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101864
Tellman B, Sullivan JA, Kuhn C et al (2021) Satellite imaging reveals increased proportion of population exposed to floods. Nature 596:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03695-w
The Minnesota Stormwater Steering Committee (2013) The Minnesota Stormwater Manual. https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Main_Page. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Thorne CR, Lawson EC, Ozawa C et al (2018) Overcoming uncertainty and barriers to adoption of Blue-Green Infrastructure for urban flood risk management. J Flood Risk Manag 11:S960–S972. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12218
UNDRR (2020) The Human Cost of Disasters: An Overview of the Last 20 Years (2000–2019). https://www.undrr.org/publication/human-cost-disasters-overview-last-20-years-2000-2019. Accessed on 13 March 2023
Voyde E, Fassman E, Simcock R (2010) Hydrology of an extensive living roof under sub-tropical climate conditions in Auckland, New Zealand. J Hydrol 394:384–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.09.013
Wang H, Ding L, Cheng X, Li N (2015a) Hydrological control index system of urban stormwater management in the United States and its referential significance. J Hydraul Eng 46:1261–1271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03695-w. (in Chinese)
Wang Z, Lai C, Chen X et al (2015b) Flood hazard risk assessment model based on random forest. J Hydrol 527:1130–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.06.008
Wang Y, Meng F, Liu H et al (2019) Assessing catchment scale flood resilience of urban areas using a grid cell based metric. Water Res 163:114852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114852
Wang M, Fang Y, Sweetapple C (2021) Assessing flood resilience of urban drainage system based on a ‘do-nothing’ benchmark. J Environ Manage 288:112472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112472
Ward PJ, Jongman B, Weiland FS et al (2013) Assessing flood risk at the global scale: model setup, results, and sensitivity. Environ Res Lett 8:044019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/4/044019
Willems P (2013) Revision of urban drainage design rules after assessment of climate change impacts on precipitation extremes at Uccle, Belgium. J Hydrol 496:166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.05.037
Williams JR, Arnold JG (1997) A system of erosion—sediment yield models. Soil Technol 11:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0933-3630(96)00114-6
Winsemius HC, Van Beek LPH, Jongman B et al (2013) A framework for global river flood risk assessments. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:1871–1892. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-17-1871-2013
Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (2017) Non-Agricultural Revisions to Chapter NR 151, Runoff Management Rule. https://dnr.wi.gov/topic/stormwater/documents/NR151_non-ag_FS.pdf. Accessed on 19 March 2023
Wu Z, Liu X, Liu B, Chu J, Pneg L (2013) Risk assessment of nitrogen and phosphorus loads in hainan island based on InVEST Model. J Trop Crops 34:1791–1797. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2013.09.029(inChinese)
Xia H, Yuan S, Prishchepov AV (2023) Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: implications for spatial planning and management. Resour Conserv Recycl 189:106767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106767
Xu X, Liu W, Scanlon BR et al (2013) Local and global factors controlling water-energy balances within the Budyko framework. Geophys Res Lett 40:6123–6129. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058324
Xu H, Ma C, Lian J et al (2018) Urban flooding risk assessment based on an integrated k-means cluster algorithm and improved entropy weight method in the region of Haikou, China. J Hydrol 563:975–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.06.060
Yang W, Xu K, Lian J et al (2018) Integrated flood vulnerability assessment approach based on TOPSIS and Shannon entropy methods. Ecol Ind 89:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.02.015
Yu K, Li D, Yuan H, Fu W, Qiao Q, Wang S (2015) “Sponge City”: theory and practice. Urban Plan 39:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1181/cpr20150605a. (in Chinese)
Zhang C, Li W, Zhang B, Liu M (2012) Water Yield of Xitiaoxi River basin based on InVEST Modeling. J Resources Ecol 3:50–54. https://doi.org/10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2012.01.008
Zhang K, Shalehy MH, Ezaz GT et al (2022) An integrated flood risk assessment approach based on coupled hydrological-hydraulic modeling and bottom-up hazard vulnerability analysis. Environ Model Softw 148:105279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105279
Zhao Y, Gong Z, Wang W, Luo K (2014) The comprehensive risk evaluation on rainstorm and flood disaster losses in China mainland from 2004 to 2009: based on the triangular gray correlation theory. Nat Hazards 71:1001–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0698-7
Zomer RJ, Xu J, Trabucco A (2022) Version 3 of the global aridity index and potential evapotranspiration database. Sci Data 9:409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01493-1
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51878593).
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51878593).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Song Yao and Zihan Chen; data curation, Song Yao; formal analysis, Song Yao and Zihan Chen; funding acquisition, Guoping Huang; methodology, Song Yao; resources, Guoping Huang; software, Song Yao; supervision, Guoping Huang; validation, Song Yao; visualization, Song Yao; writing—original draft preparation, Song Yao and Zihan Chen; writing—review and editing, Song Yao. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, S., Huang, G. & Chen, Z. Evaluation of urban flood adaptability based on the InVEST model and GIS: A case study of New York City, USA. Nat Hazards (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06632-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06632-y