Abstract
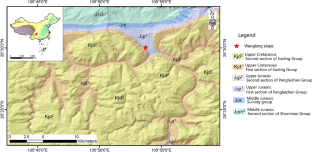
Taking the Chishui Wanglong slope as a case study, the actual deformation characteristics of the slope were obtained through geological field surveys. Using the base contact friction experiment and PFC discrete element numerical simulation, the deformation and failure mechanism of the low-dip red bed soft-hard interbedded slope were investigated. The results indicate that the Wanglong slope is a typical low-dip red bed slope with a soft-hard interbedded structure, characterized by falling and toppling failure as the primary deformation modes. The deformation and failure of the slope are primarily controlled by the depth of the concave cavity formed by differential weathering. Comprehensive analysis reveals that the slope's deformation and failure evolution process can be described as unloading cracks expansion stage, differential weathering stage, and slope deformation and failure stage. The findings of this study can be applied to develop a theoretical framework for determining the prevention and control measures of this type of engineering slope in the Chishui red bed area, which is crucial for reducing the potential risk of geological disasters.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Due to the nature of this research, participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly, so supporting data is not available.
References
Bolton MD, Nakata Y, Cheng YP (2008) Micro- and macro-mechanical behaviour of DEM crushable materials. Géotechnique 58(6):471–480. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2008.58.6.471
Castro-Filgueira U, Alejano LR, Arzúa J, Ivars DM (2017) Sensitivity analysis of the micro-parameters used in a PFC analysis towards the mechanical properties of rocks. Proc Eng 191:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.05.208
Chang W, Wang P, Wang H, Chai S, Yu Y, Xu S (2021) Simulation of the Q2 loess slope with seepage fissure failure and seismic response via discrete element method. Bull Eng Geol Env 80(4):3495–3511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02139-z
Cheng Q, Zhou Y, Huang S (2004) Distortion and failure character of excavation slope in approximate level red beds. Rock Soil Mech-Wuhan 25:1311–1314
Cundall PA, Hart RD (1992) Numerical modelling of discontinua. Eng Comput 9(2):101–113. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb023851
Dong S, Feng W, Feng W, Yin Y, Hu R, Dai H (2019) Examination of rainfall-induced landslide failure mechanisms via a centrifuge physical simulation test. Open J Geol 09(13):1004–1021. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2019.913102
Fan X-M, Xu Q, Zhang Z-Y, Meng D-S, Tang R (2009) The genetic mechanism of a translational landslide. Bull Eng Geol Env 68(2):231–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-009-0194-1
Feng W, Shi Y, Chai H (2004) Study of mechanism of deformation failure of a low-angle bedded high slope with physical simulation method. China J Highw Transp 17(2):32–36
Hai-bo M, Kun-long Y, Gong-hui W (2016) Dynamic mechanism of intermittent reactivation of deep-seated reservoir ancient landslide. Rock Soil Mech 37(9):2645–2653
He H, Dong X, Du S, Guo H, Yan Y, Chen G (2024) Study on the stability of cut slopes caused by rural housing construction in red bed areas: a case study of Wanyuan City, China. Sustainability 16:1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031344
Huang R, Zhao S, Song X (2008) Formation and mechanical analysis of Tiantai landslide of Xuanhan county, Sichuan province
Huang R (2012) Mechanisms of large-scale landslides in China. Bull Eng Geol Env 71(1):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0403-6
Jian W, Wang Z, Yin K (2009) Mechanism of the Anlesi landslide in the three gorges reservoir, China. Eng Geol 108(1–2):86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.06.017
Krasnovskii AA, Mirenkov VE (2009) Determination of boundary conditions in rocks under compression[J]. J Min Sci 45(04):315–323
Li WC, Li HJ, Dai FC, Lee LM (2012) Discrete element modeling of a rainfall-induced flowslide. Eng Geol 149–150:22–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.08.006
Liang Y, Li D, Lu X, Yang X, Pan X, Mu H et al (2010) Soil erosion changes over the past five decades in the red soil region of Southern China. J Mt Sci 7(1):92–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-010-1052-0
Liu J, Wang P, Liu J (2015) Macro- and micro-mechanical characteristics of crushed rock aggregate subjected to direct shearing. Transp Geotech 2:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2014.07.007
Luo Y, Xia B, Li J, Zhang Z (2010) Quantitative evaluation for danger level of geologic hazards in the region of three parallel rivers. Environ Sci Technol 09
Ma S, Wei J, Xu C, Shao X, Xu S, Chai S et al (2020) UAV survey and numerical modeling of loess landslides: an example from Zaoling, southern Shanxi Province, China. Nat Hazards 104(1):1125–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04207-1
Marat AR, Tămaş T, Samşudean C, Gheorghiu R (2022) Physico-mechanical and mineralogical investigations of red bed slopes (Cluj-Napoca, Romania). Bull Eng Geol Environ 81:78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02542-6
Potyondy DO, Cundall PA (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(8):1329–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
Shangde X, Huiming T, Ruixuan T, Huagang Q (2016) Study on deformation and failure modes of red layer slope in Enshi Basin. J Eng Geol 24(6):1080–1087
Shi C, Li D, Chen K, Zhou J (2016) Failure mechanism and stability analysis of the Zhenggang landslide in Yunnan Province of China using 3D particle flow code simulation. J Mt Sci 13(5):891–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3399-0
Tang C, Hu J, Lin M, Angelier J, Lu C, Chan Y et al (2009) The Tsaoling landslide triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan: Insights from a discrete element simulation. Eng Geol 106(1–2):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.02.011
Tang H, Yong R, Ez Eldin MAM (2017) Stability analysis of stratified rock slopes with spatially variable strength parameters: the case of Qianjiangping landslide. Bull Eng Geol Env 76(3):839–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0876-4
Wu Q, Zhang B, Tang H et al (2023) Theoretical study on stability evolution of soft and hard interbedded bedding reservoir slopes. J Mt Sci 20:2744–2755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8073-y
Wu LZ, Zhang LM, Zhou Y, Xu Q, Yu B, Liu GG et al (2018) Theoretical analysis and model test for rainfall-induced shallow landslides in the red-bed area of Sichuan. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1343–1353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1126-0
Wu Y, Zhang M, Yang L, Liu T, Zhang T, Sun Q et al (2021) Failure mechanisms and dynamics of the Shanzao rockslide in Yongjia County, China on 10 August 2019. Landslides 18(7):2565–2574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01673-x
Xie J, Yang G, Qin Y, Xu X (2020) Deformation failure mechanism and motion laws of near-horizontal thick-layer with thin-layer columnar dangerous rock mass in the chishui red bed area. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science. IOP Publishing, p 022045 2
Xu Q, Liu H, Ran J, Li W, Sun X (2016) Field monitoring of groundwater responses to heavy rainfalls and the early warning of the Kualiangzi landslide in Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Landslides 13(6):1555–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0717-3
Yan Q, Li X, Tang X, Wu Y, He S (2021) Investigation of the strength recovery characteristics of a red-bed landslide soil by SHS and ultrasonic experiments. Bull Eng Geol Env 80(7):5271–5278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02263-w
Yin Y, Cheng Y, Liang J, Wang W (2016) Heavy-rainfall-induced catastrophic rockslide-debris flow at Sanxicun, Dujiangyan, after the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake. Landslides 13(1):9–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0554-9
Zhang M, Yin Y, Huang B (2015) Mechanisms of rainfall-induced landslides in gently inclined red beds in the eastern Sichuan Basin. SW China Landslides 12(5):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0611-4
Zheng D, Frost JD, Huang RQ, Liu FZ (2015) Failure process and modes of rockfall induced by underground mining: a case study of Kaiyang Phosphorite Mine rockfalls. Eng Geol 197:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.011
Zhong Y, Su H, Pan H (2017) Deformation characteristics and mechanism of an excavation slope in red bed area of Chengren highway. Coal Geol Explor 45(2):96–100. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.02.017
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Research Program of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (ZK [2021] Basic 200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, GY and YQ; methodology, GY and YQ; software, YQ; validation, YQ and BL; formal analysis, GY and BL; investigation, YQ, BL and JX; resources, GY; data curation, BL and JX; writing—original draft preparation, YQ; writing—review and editing, GY; visualization, YQ; supervision, YQ; project administration, GY; funding acquisition, GY All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yigen, Q., Genlan, Y., Bangyu, L. et al. Study on deformation and failure mechanism of low-dip red bed slope with soft-hard interbedded structure: a case study of Chishui, China. Nat Hazards (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06617-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06617-x




