Abstract
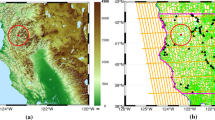
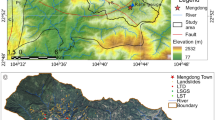
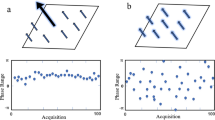
In eastern Qinghai Province, China, landslides are a frequent hazard, yet their large-scale monitoring and assessment are under-researched. This study utilized 31 Sentinel-1A satellite images from January 4, 2020, to August 9, 2022, and applied the Small Baseline Subset Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar (SBAS-InSAR) method to quantify surface subsidence and infer landslide deformation rates in the Loess Plateau. We identified 491 hazardous landslides, with 14 posing significant risks to the Yellow River, major highways, and over 10,000 residents. The average line-of-sight (LOS) surface displacement rate was 118 mm/year, peaking at 298 mm. Satellite imagery revealed rapid and continuous landslide front activity. The landslides' uneven distribution aligns with the area's complex geology and environment, predominantly occurring on 20°–40° slopes with the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index values below 0.3, and aligning with nearby faults in the Hualong basin. Detailed analysis of 14 key landslides showed a marked correlation between landslide movement and monthly precipitation, offering new insights into landslide deformation mechanisms and driving factors.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carey JM, Moore R, Petley DN (2015) Patterns of movement in the Ventnor landslide complex, Isle of Wight, southern England. Landslides 12:1107–1118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0538-1
Cellek S (2022) Effect of the slope angle and its classification on landslides. Himal Geol 43:85–95. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-2020-87
Chang WB, Xing AG, Wang P, Zhuang Y, Jin KP, He JY, Chai SF (2021) Analysis of Dangchuan 5(#) landslide on January 27, 2021, in Yongjing County, Gansu Province, China. Landslides 18:3615–3628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01743-0
Chen XZ, Cui YF (2017) The formation of the Wulipo landslide and the resulting debris flow in Dujiangyan City, China. J Mt Sci 14:1453–1466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4392-1
Dai K, Zhang L, Song C, Li Z, Zhuo G, Xu Q (2021) Quantitative analysis of sentinel-1 imagery geometric distortion and their suitability along Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Geomat Inf Sci Wuhan Univ 46:1450–1460. https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20210130
Dong J, Zhang L, Li M, Yu Y, Liao M, Gong J, Landslides HLJ (2018) Measuring precursory movements of the recent Xinmo landslide in Mao County, China with Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 datasets. Landslides 15:2479–2486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0914-8
Fan XM, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Li S, Peng DL (2017) A chemo-mechanical insight into the failure mechanism of frequently occurred landslides in the Loess Plateau Gansu Province China. Eng Geol 228:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.003
Fan X, Scaringi G, Korup O, West AJ, Westen CJv, Tanyas H, Hovius N, Hales T, Jibson RW, Allstadt KE, Zhang LM, Evans SG, Xu C, Li G, Pei X, Xu Q, Geophysics RHJRo, (2019) Earthquake-induced chains of geologic hazards: patterns, mechanisms and impacts. Rev Geophys 57:421–503. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000626
Gu TF, Zhang MS, Wang JD, Wang CX, Xu YJ, Wang X (2019) The effect of irrigation on slope stability in the Heifangtai Platform Gansu Province China. Eng Geol 248:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.10.02
Hu J, Li ZW, Ding XL, Zhu JJ, Zhang L, Sun Q (2014) Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: a review. Earth-Sci Rev 133:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.02.005
Huang Y, Xu C, Li L, He X, Cheng J, Xu X, Zhang X et al (2022) Inventory and spatial distribution of ancient landslides in Hualong County, China. Land 12(1):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010136
Huang YD, Xu C, Li L, He XL, Cheng J, Xu XW, Li JL, Zhang XJ (2023) Inventory and spatial distribution of ancient landslides in Hualong County China. Land 12:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010136
Jain N, Martha TR, Khanna K, Roy P, Kumar KV (2021) Major landslides in Kerala India during 2018–2020 period: an analysis using rainfall data and debris flow model. Landslides 18:3629–3645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01746-x
Jain S, Khosa R, Gosain AK (2022) Impact of landslide size and settings on landslide scaling relationship: a study from the Himalayan regions of India. Landslides 19(2):373–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01794-3
Kong JX, Zhuang JQ, Zhan JW, Bai ZW, Leng YQ, Ma PH, Peng JB, Wang ZP, Gu TF, Sun JX, Fan HY (2021) A landslide in Heifangtai northwest of the Chinese Loess Plateau: triggered factors movement characteristics and failure mechanism. Landslides 18:3407–3419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01752-z
Li B, Xu Q, Cheng Q, Liu TX, Tang MG, Zheng G, Wang HY (2020a) Characteristics of discontinuities in Heifangtai landslide area in Gansu China. Acta Geotech 17:857–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-020-0872-0
Li ZY, Yang GS, Liu H (2020b) The influence of regional freeze-thaw cycles on loess landslides: analysis of strength deterioration of loess with changes in pore structure. Water 12:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113047
Lian B, Wang X, Zhan H, Wang J, Peng J, Gu T, Zhu R (2022) Creep mechanical and microstructural insights into the failure mechanism of loess landslides induced by dry-wet cycles in the Heifangtai platform China. Eng Geol 300:106589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106589
Liu X, Zhao C, Zhang Q, Yang C, Zhu W (2020) Heifangtai loess landslide type and failure mode analysis with ascending and descending Spot-mode TerraSAR-X datasets. Landslides 17:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01265-w
Ma SY, Qiu HJ, Hu S, Yang DD, Liu ZJ (2021) Characteristics and geomorphology change detection analysis of the Jiangdingya landslide on July 12 2018 China. Landslides 18:383–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01530-3
Maleki M, Mir Mohammad Hosseini SM (2019) Seismic performance of deep excavations restrained by anchorage system using quasi static approach. J Seismol Earthq Eng 21(2):11–21. https://doi.org/10.48303/JSEE.2019.240810
Maleki M, Mor Mohamma Hosseini SM (2022) Assessment of the pseudo-static seismic behavior in the soil nail walls using numerical analysis. Innov Infrastruct so 7(4):262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-022-00861-5
Maleki M, Khezri A, Nosrati M, Hosseini SMMM (2023) Seismic amplification factor and dynamic response of soil-nailed walls. Model Earth Syst Environ 9(1):1181–1198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-022-01543-y
Meng Q, Confuorto P, Peng Y, Raspini F, Bianchini S, Han S (2020) Regional recognition and classification of active loess landslides using two-dimensional deformation derived from Sentinel-1 interferometric radar data. Remote Sens 12:1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101541
Morar C, Lukić T, Basarin B, Valjarević A, Vujičić MD, Niemets L, Telebienieva I, Boros L (2021) Shaping sustainable urban environments by addressing the hydro-meteorological factors in landslide occurrence: Ciuperca Hill (Oradea, Romania). Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18095022
Pan B, Li J, Cao J (1996) The study of the geomorphic evolution and development of the Yellow River in the Hualong Basin. Mt Res 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.1996.03.003
Peng J, Wang S, Wang Q, Zhuang J, Huang W, Zhu X, Leng Y (2019) Distribution and genetic types of loess landslides in China. J Arid Environ 162:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.11.015
Prancevic JP, Lamb MP, McArdell BW, Rickli C, Kirchner JW (2020) Decreasing Landslide Erosion on Steeper Slopes in Soil-Mantled Landscapes. Geophys Res Lett 47(10):e2020GL087505. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL087505
Sahraoui OH, Hassaine B, Serief C, Hasni K (2006) Radar interferometry with Sarscape software. Isprs J Photogramm
Samia J, Temme A, Bregt A, Wallinga J, Guzzetti F, Ardizzone F, Rossi M (2017) Characterization and quantification of path dependency in landslide susceptibility. Geomorphology 292:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.04.039
Sassa K (2004) The international consortium on landslides. Landslides 1:91–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0012-6
Shi WH, Li YR, Zhang WW, Liu J, He SD, Mo P, Guan FF (2020) The loess landslide on 15 March 2019 in Shanxi Province, China. Landslides 17:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01342-0
Su XJ, Zhang Y, Meng XM, Yue DX, Ma JH, Guo FY, Zhou ZQ, Rehman MU, Khalid Z, Chen G, Zeng RQ, Zhao FM (2021) Landslide mapping and analysis along the China–Pakistan Karakoram Highway based on SBAS-InSAR detection in 2017. J Mt Sci 18:2540–2564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-021-6686-6
Su XJ, Zhang Y, Meng XM, Rehman MU, Khalid Z, Yue DX (2022) Updating inventory deformation and development characteristics of landslides in Hunza Valley NW Karakoram Pakistan by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens 14:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194907
Uwihirwe J, Hrachowitz M, Bogaard TA (2020) Landslide precipitation thresholds in Rwanda. Landslides 17:2469–2481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01457-9
Wang HB, Wu SR, Shi JS, Hazards BLJN (2013) Qualitative hazard and risk assessment of landslides: a practical framework for a case study in China. Nat Hazards 69:1153–1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-0008-1
Wang Q, Yu W, Xu B, Wei G (2019) Assessing the use of GACOS products for SBAS-INSAR deformation monitoring: a case in Southern California. Sensors 19(18):3894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183894
Wang B, He L, He ZW, Qu R, Kang GC (2023) Study of early identification method for large landslides in high vegetation coverage areas of Southwest China. Front Ecol Evol 11:17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1169028
Xie ML, Zhao WH, Ju NP, He CY, Huang HD, Cui QH (2020) Landslide evolution assessment based on InSAR and real-time monitoring of a large reactivated landslide Wenchuan China. Eng Geol 277:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105781
Yao JM, Yao X, Liu XH (2022) Landslide detection and mapping based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR: a case study in Gongjue County Tibet China. Remote Sens 14:19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194728
Yin YP, Zheng WM, Liu YP, Zhang JL, Li XC (2010) Integration of GPS with InSAR to monitoring of the Jiaju landslide in Sichuan China. Landslides 7:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-010-0225-9
Yu LC, Yan CH, Guo SL, Li H, Tan JZ, Liu G, Xu CH, Liu Y (2023) Mechanism analysis of Zulongding landslide on gentle piedmont slope: a creeping landslide triggered by rainfall. Nat Hazards (dordr). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-023-06051-5
Zhang JJ, Gao B, Huang H, Chen L, Li YL, Yang DX (2022a) SBAS-InSAR-based landslide susceptibility mapping along the North Lancang River Tibetan Plateau. Front Earth Sci 10:15. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.901889
Zhang C, Li Z, Yu C, Chen B, Ding M, Zhu W, Peng J et al (2022b) An integrated framework for wide-area active landslide detection with InSAR observations and SAR pixel offsets. Landslides 19(12):2905–2923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01954-z
Zhao B, Wang YS, Chen M, Luo YH, Liang RF, Li J (2019) Typical characteristics of large-scale landslides in the transition belt between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. Arab J Geosci 12:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4612-9
Zhao L, Liang R, Shi X, Dai K, Cheng J, Cao J (2021) Detecting and analyzing the displacement of a small-magnitude earthquake cluster in Rong County, China by the Gacos Based Insar Technology. Remote Sens 13(20):4137. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204137
Zheng F, Shao S, Wang S (2021) Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the strength behaviour of recompacted loess in true triaxial tests 181:103172. Cold Reg Sci Technol 181:103172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103172
Zhuang JQ, Peng JB, Wang GH, Javed I, Wang Y, Li W (2018a) Distribution and characteristics of landslide in Loess Plateau: a case study in Shaanxi province. Eng Geol 236:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.00
Zhuang JQ, Peng JB, Xu C, Li ZH, Densmore A, Milledge D, Iqbal J, Cui YF (2018b) Distribution and characteristics of loess landslides triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan Earthquake Northwest of China. Geomorphology 314:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.04.012
Zhuang JQ, Ma PH, Zhan JW, Zhu Y, Kong JX, Zhu XH, Leng YQ, Peng JB (2022) Empirical relationships of the landslides in the Chinese Loess Plateau and affect factors analysis Geomatics Natural Hazards & Risk 13:250–266. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 13:250–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.2020174
Zieher T, Bremer M, Rutzinger M, Pfeiffer J, Fritzmann P, Wichmann V (2019) Assessment of landslide-induced displacement and deformation of above-ground objects using UAV-borne and airborne laser scanning data. ISPRS Ann Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci 4:461–467. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-annals-IV-2-W5-461-2019
Zumpano V, Pisano L, Malek Ž, Micu M, Aucelli PP, Rosskopf CM, Parise M et al (2018) Economic losses for rural land value due to landslides. Front Earth Sci 6:13. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2018.00097
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant number: 2022YFC3003205) and the Science and Technology Research Project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant number: KJQN202100624).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Kou, P., Xu, Q. et al. Analysis of landslide deformation in eastern Qinghai Province, Northwest China, using SBAS-InSAR. Nat Hazards 120, 5763–5784 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06442-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06442-2