Abstract
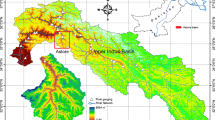
The water-runoff in the plateau mountainous areas is mainly contributed by precipitation, snowmelt and glacial meltwater; the different runoff components result from different mechanism of runoff generation. Plateau mountainous areas have not only a unique hydrological cycle mechanism but also are sensitive to climate change. Glacier and snow meltwater in the plateau mountainous areas have a large proportion in runoff and are a main water resources for industrial, agricultural and domestic water use in the basin. Two commonly used model, HBV and SRM, were selected for the quantitative analysis of snowmelt runoff contribution and the hydrological response to climate change scenarios in the Nyang River Basin in the southeastern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Based on the characteristics of the models, the HBV model was used to analyze the runoff composition, while the SRM model was used to analyze the runoff in climate change scenarios. The results showed that both models have a good performance in modeling the hydrological processes in the basin. The snow melts mainly concentrate in May, in the average annual precipitation, rainfall and snowfall accounted for 85% and 15%, respectively. From the results of sensitivity analysis, the increase in temperature would accelerate the melting of snow in April and May and turns the snowfall into rainfall in October. However, the change in precipitation mainly affects the runoff in July, August and September, when precipitation is dominated by rain. The results indicate that the timing of the effects of temperature and precipitation on the runoff process is different.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudu S, Sheng ZP, Cui CL, Saydi M, Sabzi HZ, King JP (2016) Integration of aspect and slope in snowmelt runoff modeling in a mountain watershed. Water Sci Eng 9:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2016.07.002
Archer DR, Forsythe N, Fowler HJ, Shah SM (2010) Sustainability of water resources management in the Indus Basin under changing climatic and socio economic conditions. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14:1669–1680. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-14-1669-2010
Barnett TP, Adam JC, Lettenmaier DP (2005) Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 438:303–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04141
Bilal M, Nazeer M, Nichol JE (2017) Validation of MODIS and VIIRS derived aerosol optical depth over complex coastal waters. Atmos Res 186:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.11.009
Bin Q, Yulan Z, Shichang K, Mika S (2019) Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: major ions and trace elements in rivers of the “Water Tower of Asia”. Sci Total Environ 649:571–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.316
Bolch T (2007) Climate change and glacier retreat in northern Tien Shan (Kazakhstan/Kyrgyzstan) using remote sensing data. Glob Planet Change 56:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.07.009
Ding L, Ji Z, Zhang X, Liu S, Cao R (2018) Downscaling of surface air temperature over the Tibetan Plateau based on DEM. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 73:136–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2018.05.017
Feddema JJ (1998) Estimated impacts of soil degradation on the African water balance and climate. Climate Res 10:127–141. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr010127
Firouzi S, Sadeghian MS (2016) Application of snow melt runoff model in a Mountainous Basin of Iran. J Geosci Environ Prot 04:74–81. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2016.42009
Gaddam VK, Kulkarni AV, Gupta AK (2018) Assessment of snow-glacier melt and rainfall contribution to stream runoff in Baspa Basin, Indian. Himal Environ Monit Assess 190:154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6520-y
Gao H, He X, Ye B, Pu J (2012) Modeling the runoff and glacier mass balance in a small watershed on the Central Tibetan Plateau, China, from 1955 to 2008. Hydrol Process 26:1593–1603. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8256
Hock R (2005) Glacier melt: a review of processes and their modelling. Prog Phys Geogr 29(3):362–391. https://doi.org/10.1191/0309133305pp453ra
Hong M, Cheng G (2003) A test of Snowmelt Runoff Model (SRM) for the Gongnaisi River basin in the western Tianshan Mountains, China. Chin Sci Bull 48:2253–2259. https://doi.org/10.1360/03wd0135
Huang CS, Yang T, Yeh HD (2018) Review of analytical models to stream depletion induced by pumping: guide to model selection. J Hydrol 561:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.015
Huss M (2017) Present and future contribution of glacier storage change to runoff from macroscale drainage basins in Europe. Water Resour Res 47:W07511. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR010299
Immerzeel WW, Droogers, De Jong SM, Bierkens MFP (2009) Large-scale monitoring of snow cover and runoff simulation in Himalayan river basins using remote sensing. Remote Sens Environ 113:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.08.010
Immerzeel WW, Beek LPH, Van Bierkens MFP (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328:1382–1385. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183188
Jain SK, Goswami A, Saraf AK (2010) Assessment of snowmelt runoff using remote sensing and effect of climate change on runoff. Water Resour Manag 24:1763–1777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9523-1
Jarvis A, Reuter HI, Nelson A, Guevara E (2008) Hole filled seamless SRTM data V4. International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT). http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org. Accessed 21 Nov 2018
Kääb A, Berthier E, Nuth C, Gardelle J, Arnaud Y (2012) Contrasting patterns of early twenty-first-century glacier mass change in the Himalayas. Nature 488:495–498. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11324
Kaser G, Großhauser M, Marzeion B (2010) Contribution potential of glaciers to water availability in different climate regimes. PNAS 107(47):20223–20227. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008162107/-/DCSupplemental
Knight J, Harrison S, Jones DB (2019) Rock glaciers and the geomorphological evolution of deglacierizing mountains. Geomorphology 324:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.09.020
Konz M, Seibert J (2010) On the value of glacier mass balances for hydrological model calibration. J Hydrol 385:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.02.025
Martinec J, Rango A, Roberts R (2007) Snowmelt runoff model user’s manual, updated edition 2007, WinSRM version 1.11. USDA Jornada Experimental Range, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA
Oliver JE (2013) Intergovernmental panel in climate change (IPCC). Encycl Energy Nat Resour Environ Econ 26:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3266-8_109
Phan V, Lindenbergh R, Menenti M (2014) Orientation dependent glacial changes at the Tibetan Plateau derived from 2003–2009 ICESat laser altimetry. Cryosphere Discuss 8:2425–2463. https://doi.org/10.5194/tcd-8-2425-2014
Qiu L, You J, Qiao F et al (2014) Simulation of snowmelt runoff in ungauged basins based on MODIS: a case study in the Lhasa River basin. J Beijing Norm Univ 28(6):1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0837-4
Ran Y, Li X, Lu L (2010) Evaluation of four remote sensing based land cover products over China. Int J Remote Sens 31:391–401. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160902893451
Rohrer M, Salzmann N, Stoffel M, Kulkarni AV (2013) Missing (in situ) snow cover data hampers climate change and runoff studies in the Greater Himalayas. Sci Total Environ 468–469:S60–S70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.056
Ruane AC, Phillips MM, Rosenzweig C (2018) Climate shifts within major agricultural seasons for +1.5 and +2.0 C worlds: HAPPI projections and AgMIP modeling scenarios. Agric For Meteorol 259:329–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.05.013
Seibert J, Vis MJP (2012) Teaching hydrological modeling with a user-friendly catchment-runoff-model software package. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:3315–3325. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-3315-2012
Shad MS, Roshan MH, Ildoromi A (2014) Integration of the MODIS snow cover produced into snowmelt runoff modeling. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 42:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-013-0279-y
Stewart IT, Prowse TD (2010) Changes in snowpack and snowmelt runoff for key mountain regions. Hydrol Process 23:78–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7128
Sun M, Yao X, Zhongqin LI, Zhang M (2015) Hydrological processes of glacier and snow melting and runoff in the Urumqi River source region, eastern Tianshan Mountains, China. J Geog Sci 25:149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-015-1159-x
Verdhen A, Chahar BR, Sharma OP (2014) Springtime Snowmelt and Streamflow Predictions in the Himalayan Mountains. J Hydrol Eng 19:1452–1461. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000816
Wagnon P, Linda A, Arnaud Y et al (2007) Four years of mass balance on Chhota Shigri Glacier, Himachal Pradesh, India, a new benchmark glacier in the western Himalaya. J Glaciol 53:603–611. https://doi.org/10.3189/002214307784409306
Wang XJ, Liu HL, Bao AM (2012) A simulation analysis of the impact of climate change on runoff in the Manas River. J Glaciol Geocryol 34:1220–1228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z
White CJ, Tanton TW, Rycroft DW (2014) The Impact of Climate Change on the Water Resources of the Amu Darya Basin in Central Asia. Water Resour Manag 28:5267–5281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0716-x
Xin YF et al (2018) Surface energy balance closure at ten sites over the Tibetan plateau. Agric For Meteorol 259:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.05.007
Yong Z, Hirabayashi Y, Qiao L, Liu S (2015) Glacier runoff and its impact in a highly glacierized catchment in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: past and future trends. J Glaciol 61:713–730. https://doi.org/10.3189/2015JoG14J188
You Q, Jiang Z, Dai W, Pepin N, Kang S (2017) Simulation of temperature extremes in the Tibetan Plateau from CMIP5 models and comparison with gridded observations. Clim Dyn 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3928-y
Yu Z (2000) Assessing the response of subgrid hydrologic processes to atmospheric forcing with a hydrologic model system. Glob Planet Change 25(1–2):1–17
Yu Z, Barron EJ, Schwartz FW (2000) Retrospective simulation of a storm event: a first step in coupled climate/hydrologic modeling. Geophys Res Lett 27(16):2561–2564
Yu Z, Fu X, Luo L, Lü H, Ju Q, Liu D, Kalin DA, Huang D, Yang C, Zhao C (2014) One-dimensional soil temperature simulation with Common Land Model by assimilating in situ observations and MODISLST with the ensemble particle filter. Water Resour Res 50(8):6950–6965
Zhang YC, Li BL, Bao AM, Zhou CH, Chen X, Zhang XR (2007) Study on snowmelt runoff simulation in the Kaidu River basin. Sci China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-007-5007-4
Zhang X, Qin X, Xu C, Liu Y (2018) Simulation of runoff and glacier mass balance and sensitivity analysis in a glacierized basin, north-eastern Qinhai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Water 10:1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091259
Zhu M, Yao T, Wei Y, Xu B, Wu G, Wang X (2017) Differences in mass balance behavior for three glaciers from different climatic regions on the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3817-4
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China. (2016YFC0402704); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51539003); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019B10914).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haoyu Jin helped in conceptualization; Qin Ju contributed to data curation; formal analysis was done by Huanghe Gu; funding acquisition was done by Zhongbo Yu and Wei Li; investigation was done by Henan Gu; Jie Hao contributed to methodology; project administration was done by Zhongbo Yu; Wei Li and Qin Ju contributed to resources; Henan Gu contributed to software; supervision was done by Zhongbo Yu; validation was done by Jie Hao; visualization was done by Huanghe Gu; Haoyu Jin and Qin Ju contributed to writing—original draft; Haoyu Jin and Qin Ju contributed to writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Ju, Q., Yu, Z. et al. Simulation of snowmelt runoff and sensitivity analysis in the Nyang River Basin, southeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Nat Hazards 99, 931–950 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03784-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03784-0