Abstract
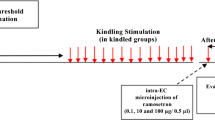
In this research, the involvement of CB1 and TRPV1 receptors in the possible protective effects of anandamide were investigated in the kindling model of epilepsy. The basolateral amygdala of the rat brain was chosen to put stimulating electrodes. Semi-rapid kindling was induced by a repetitive sub-threshold stimulation for 5–9 consecutive days. There were seven groups, six of which were kindled and used for drug testing by intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) microinjection. (i) Sham, (ii) control group received vehicles, (iii) anandamide (AEA; 100 ng/rat), (iv) capsazepine (TRPV1 antagonist; 100 ng/rat), (v) AM251 (CB1 antagonist; 100 ng/rat), (vi) AM251 + anandamide, and (vii) capsazepine + anandamide. The after-discharge duration, seizure duration, and stage five duration were measured in rats. Moreover, the expressions of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and the cAMP responsive element binding (CREB) proteins in the hippocampus were also studied. The anandamide-treated group showed a significant decrease in seizure scores, while no change was shown in seizure scores in the capsazepine- and AM251-treated groups compared with the control group. Co-administrations of either capsazepine + AEA or AM251 + AEA attenuated the protective effect of AEA against seizure. Furthermore, the group received AEA showed a decrease in the expressions of CREB and p-CREB possibly through the activation of the CB1 and TRPV1 receptors. Activation of CB1 and TRPV1 receptors might be involved in AEA anticonvulsant effect in kindling model of epilepsy. This effect could be due to suppression of CREB phosphorylation in hippocampal neurons.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEA:
-
Anandamide
- TRPV1:
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1
- AM251:
-
1-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-N-1-piperidinyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide
- ADD:
-
After-discharge duration
- SD:
-
Seizure duration
- S5D:
-
Stage five duration
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- CREB:
-
CAMP responsive element binding
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl-sulfoxide
References
Castillo PE, Younts TJ, Chavez AE, Hashimotodani Y (2012) Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 76:70–81
Howlett AC, Breivogel CS, Childers SR, Deadwyler SA, Hampson RE, Porrino LJ (2004) Cannabinoid physiology and pharmacology: 30 years of progress. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):345–358
Hofmann ME, Frazier CJ (2013) Marijuana, endocannabinoids, and epilepsy: potential and challenges for improved therapeutic intervention. Exp Neurol 244:43–50
Smart D, Gunthorpe MJ, Jerman JC, Nasir S, Gray J, Muir AI, Chambers JK, Randall AD, Davis JB (2000) The endogenous lipid anandamide is a full agonist at the human vanilloid receptor (hVR1). Br J Pharmacol 129:227–230
Kwan Cheung KA, Peiris H, Wallace G, Holland OJ, Mitchell MD (2019) The Interplay between the endocannabinoid system, epilepsy and cannabinoids. Int J Mol Sci 20
Kokona D, Thermos K (2015) Synthetic and endogenous cannabinoids protect retinal neurons from AMPA excitotoxicity in vivo, via activation of CB1 receptors: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Exp Eye Res 136:45–58
Abdel-Salam OME, Sleem AA, Mohamed Sayed MAE-B, Youness ER, Shaffie N (2019) Neuroprotective effects of low dose anandamide in pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling in rats. Biomed Pharmacol J 12:25–40
Chavez AE, Chiu CQ, Castillo PE (2010) TRPV1 activation by endogenous anandamide triggers postsynaptic long-term depression in dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 13:1511–1518
Naderi N, Ahmad-Molaei L, Mazar-Atabaki A, Ronaghi A, Shirazi-zand Z, Motiei-Langroudi SM, Eslahkar S (2012) L-type calcium channel mediates anticonvulsant effect of cannabinoids in acute and chronic murine models of seizure. Neurochem Res 37:279–287
Bhaskaran MD, Smith BN (2010) Cannabinoid-mediated inhibition of recurrent excitatory circuitry in the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 5:e10683
Busquets-Garcia A, Bains J, Marsicano G (2018) CB1 receptor signaling in the brain: extracting specificity from ubiquity. Neuropsychopharmacology 43:4–20
Katona I (2015) Cannabis and endocannabinoid signaling in epilepsy. Handb Exp Pharmacol 231:285–316
Pacher P, Batkai S, Kunos G (2006) The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev 58:389–462
Carletti F, Gambino G, Rizzo V, Ferraro G, Sardo P (2016) Involvement of TRPV1 channels in the activity of the cannabinoid WIN 55,212–2 in an acute rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 122:56–65
Xu C, Hermes DJ, Nwanguma B, Jacobs IR, Mackie K, Mukhopadhyay S, Lichtman AH, Ignatowska-Jankowska B, Fitting S (2017) Endocannabinoids exert CB1 receptor-mediated neuroprotective effects in models of neuronal damage induced by HIV-1 Tat protein. Mol Cell Neurosci 83:92–102
Mnich K, Finn DP, Dowd E, Gorman AM (2010) Inhibition by anandamide of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell death in PC12 cells. Int J Cell Biol 2010:818497
Wartmann M, Campbell D, Subramanian A, Burstein SH, Davis RJ (1995) The MAP kinase signal transduction pathway is activated by the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide. FEBS Lett 359:133–136
Rueda D, Navarro B, Martinez-Serrano A, Guzman M, Galve-Roperh I (2002) The endocannabinoid anandamide inhibits neuronal progenitor cell differentiation through attenuation of the Rap1/B-Raf/ERK pathway. J Biol Chem 277:46645–46650
Ma T, Wu Y, Chen B, Zhang W, Jin L, Shen C, Wang Y, Liu Y (2019) D-Serine contributes to seizure development via ERK signaling. Front Neurosci 13:254
Glazova MV, Nikitina LS, Hudik KA, Kirillova OD, Dorofeeva NA, Korotkov AA, Chernigovskaya EV (2015) Inhibition of ERK1/2 signaling prevents epileptiform behavior in rats prone to audiogenic seizures. J Neurochem 132:218–229
Vilela LR, Gobira PH, Viana TG, Medeiros DC, Ferreira-Vieira TH, Doria JG, Rodrigues F, Aguiar DC, Pereira GS, Massessini AR, Ribeiro FM, de Oliveira AC, Moraes MF, Moreira FA (2015) Enhancement of endocannabinoid signaling protects against cocaine-induced neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 286:178–187
Dobovisek L, Hojnik M, Ferk P (2016) Overlapping molecular pathways between cannabinoid receptors type 1 and 2 and estrogens/androgens on the periphery and their involvement in the pathogenesis of common diseases (Review). Int J Mol Med 38:1642–1651
Bozzi Y, Dunleavy M, Henshall DC (2011) Cell signaling underlying epileptic behavior. Front Behav Neurosci 5:45
Lonze BE, Ginty DD (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35:605–623
Zhu X, Han X, Blendy JA, Porter BE (2012) Decreased CREB levels suppress epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 45:253–263
Zhu X, Dubey D, Bermudez C, Porter BE (2015) Suppressing cAMP response element-binding protein transcription shortens the duration of status epilepticus and decreases the number of spontaneous seizures in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsia 56:1870–1878
Shirazi-zand Z, Ahmad-Molaei L, Motamedi F, Naderi N (2013) The role of potassium BK channels in anticonvulsant effect of cannabidiol in pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock models of seizure in mice. Epilepsy & behavior : E&B 28:1–7
Paxinos GWG (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Chen S-D, Wang Y-L, Liang S-F, Shaw F-Z (2016) Rapid amygdala kindling causes motor seizure and comorbidity of anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in rats. Front Behav Neurosci 10
Cho C, Michailidis V, Lecker I, Collymore C, Hanwell D, Loka M, Danesh M, Pham C, Urban P, Bonin RP, Martin LJ (2019) Evaluating analgesic efficacy and administration route following craniotomy in mice using the grimace scale. Sci Rep 9:359
Ghotbedin Z, Janahmadi M, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J, Behzadi G, Semnanian S (2013) Electrical low frequency stimulation of the kindling site preserves the electrophysiological properties of the rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons from the destructive effects of amygdala kindling: the basis for a possible promising epilepsy therapy. Brain Stimul 6:515–523
Ghotbeddin Z, Heysieattalab S, Borjkhani M, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J, Semnanian S, Hosseinmardi N, Janahmadi M (2019) Ca(2+) channels involvement in low-frequency stimulation-mediated suppression of intrinsic excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in a rat amygdala kindling model. Neuroscience 406:234–248
Morales JC, Alvarez-Ferradas C, Roncagliolo M, Fuenzalida M, Wellmann M, Nualart FJ, Bonansco C (2014) A new rapid kindling variant for induction of cortical epileptogenesis in freely moving rats. Front Cell Neurosci 8:200
Beheshti Nasr SM, Moghimi A, Mohammad-Zadeh M, Shamsizadeh A, Noorbakhsh SM (2013) The effect of minocycline on seizures induced by amygdala kindling in rats. Seizure 22:670–674
Colangeli R, Morena M, Pittman QJ, Hill MN, Teskey GC (2020) Anandamide signaling augmentation rescues amygdala synaptic function and comorbid emotional alterations in a model of epilepsy. J Neurosci 40:6068–6081
Fernandez-Solari J, Prestifilippo JP, Vissio P, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Bornstein SR, Rettori V, Elverdin JC (2009) Anandamide injected into the lateral ventricle of the brain inhibits submandibular salivary secretion by attenuating parasympathetic neurotransmission. Braz J Med Biol Res 42:537–544
Reis GM, Pacheco D, Perez AC, Klein A, Ramos MA, Duarte ID (2009) Opioid receptor and NO/cGMP pathway as a mechanism of peripheral antinociceptive action of the cannabinoid receptor agonist anandamide. Life Sci 85:351–356
Naderi N, Majidi M, Mousavi Z, Khoramian Tusi S, Mansouri Z, Khodagholi F (2012) The interaction between intrathecal administration of low doses of palmitoylethanolamide and AM251 in formalin-induced pain related behavior and spinal cord IL1-beta expression in rats. Neurochem Res 37:778–785
Shirazi M, Izadi M, Amin M, Rezvani ME, Roohbakhsh A, Shamsizadeh A (2014) Involvement of central TRPV1 receptors in pentylenetetrazole and amygdala-induced kindling in male rats. Neurol Sci 35:1235–1241
Rosenberg EC, Patra PH, Whalley BJ (2017) Therapeutic effects of cannabinoids in animal models of seizures, epilepsy, epileptogenesis, and epilepsy-related neuroprotection. Epilepsy Behav 70:319–327
Fraga D, Zanoni CI, Rae GA, Parada CA, Souza GE (2009) Endogenous cannabinoids induce fever through the activation of CB1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 157:1494–1501
Racine R, Rose PA, Burnham WM (1977) Afterdischarge thresholds and kindling rates in dorsal and ventral hippocampus and dentate gyrus. Can J Neurol Sci 4:273–278
Manna SS, Umathe SN (2012) Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 channels in the pro-convulsant effect of anandamide in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures. Epilepsy Res 100:113–124
von Ruden EL, Jafari M, Bogdanovic RM, Wotjak CT, Potschka H (2015) Analysis in conditional cannabinoid 1 receptor-knockout mice reveals neuronal subpopulation-specific effects on epileptogenesis in the kindling paradigm. Neurobiol Dis 73:334–347
Zou S, Kumar U (2018) Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci 19
Gerdeman G, Lovinger DM (2001) CB1 cannabinoid receptor inhibits synaptic release of glutamate in rat dorsolateral striatum. J Neurophysiol 85:468–471
Chen CY, Li W, Qu KP, Chen CR (2013) Piperine exerts anti-seizure effects via the TRPV1 receptor in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 714:288–294
Lee TH, Lee JG, Yon JM, Oh KW, Baek IJ, Nahm SS, Lee BJ, Yun YW, Nam SY (2011) Capsaicin prevents kainic acid-induced epileptogenesis in mice. Neurochem Int 58:634–640
Suemaru K, Yoshikawa M, Aso H, Watanabe M (2018) TRPV1 mediates the anticonvulsant effects of acetaminophen in mice. Epilepsy Res 145:153–159
Barrett KT, Wilson RJ, Scantlebury MH (2016) TRPV1 deletion exacerbates hyperthermic seizures in an age-dependent manner in mice. Epilepsy Res 128:27–34
Naziroglu M (2015) TRPV1 Channel: A Potential Drug Target for Treating Epilepsy. Curr Neuropharmacol 13:239–247
Gonzalez-Reyes LE, Ladas TP, Chiang CC, Durand DM (2013) TRPV1 antagonist capsazepine suppresses 4-AP-induced epileptiform activity in vitro and electrographic seizures in vivo. Exp Neurol 250:321–332
Cristino L, Bisogno T, Di Marzo V (2020) Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 16:9–29
Naderi N, Shafieirad E, Lakpoor D, Rahimi A, Mousavi Z (2015) Interaction between cannabinoid compounds and capsazepine in protection against acute pentylenetetrazole-induced seizure in mice. Iran J Pharm Res 14:115–120
Di Marzo V (2018) New approaches and challenges to targeting the endocannabinoid system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17:623–639
Di Marzo V, De Petrocellis L (2012) Why do cannabinoid receptors have more than one endogenous ligand? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:3216–3228
Storozhuk MV, Moroz OF, Zholos AV (2019) Multifunctional TRPV1 ion channels in physiology and pathology with focus on the brain, vasculature, and some visceral systems. Biomed Res Int 2019:5806321
Hanack C, Moroni M, Lima WC, Wende H, Kirchner M, Adelfinger L, Schrenk-Siemens K, Tappe-Theodor A, Wetzel C, Kuich PH, Gassmann M, Roggenkamp D, Bettler B, Lewin GR, Selbach M, Siemens J (2015) GABA blocks pathological but not acute TRPV1 pain signals. Cell 160:759–770
Sigel E, Baur R, Racz I, Marazzi J, Smart TG, Zimmer A, Gertsch J (2011) The major central endocannabinoid directly acts at GABA(A) receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:18150–18155
Huang CC, Chen YL, Lo SW, Hsu KS (2002) Activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase suppresses the presynaptic cannabinoid inhibition of glutamatergic transmission at corticostriatal synapses. Mol Pharmacol 61:578–585
Derbenev AV, Monroe MJ, Glatzer NR, Smith BN (2006) Vanilloid-mediated heterosynaptic facilitation of inhibitory synaptic input to neurons of the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. J Neurosci 26:9666–9672
Chavez AE, Hernandez VM, Rodenas-Ruano A, Chan CS, Castillo PE (2014) Compartment-specific modulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission by TRPV1 channels in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 34:16621–16629
Toth A, Blumberg PM, Boczan J (2009) Anandamide and the vanilloid receptor (TRPV1). Vitam Horm 81:389–419
Laprairie RB, Bagher AM, Kelly ME, Dupre DJ, Denovan-Wright EM (2014) Type 1 cannabinoid receptor ligands display functional selectivity in a cell culture model of striatal medium spiny projection neurons. J Biol Chem 289:24845–24862
Ozaita A, Puighermanal E, Maldonado R (2007) Regulation of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 pathway by cannabinoids in the brain. J Neurochem 102:1105–1114
Molina-Holgado F, Pinteaux E, Heenan L, Moore JD, Rothwell NJ, Gibson RM (2005) Neuroprotective effects of the synthetic cannabinoid HU-210 in primary cortical neurons are mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci 28:189–194
Brighton PJ, McDonald J, Taylor AH, Challiss RA, Lambert DG, Konje JC, Willets JM (2009) Characterization of anandamide-stimulated cannabinoid receptor signaling in human ULTR myometrial smooth muscle cells. Mol Endocrinol 23:1415–1427
Basavarajappa BS, Nagre NN, Xie S, Subbanna S (2014) Elevation of endogenous anandamide impairs LTP, learning, and memory through CB1 receptor signaling in mice. Hippocampus 24:808–818
Isokawa M (2009) Time-dependent induction of CREB phosphorylation in the hippocampus by the endogenous cannabinoid. Neurosci Lett 457:53–57
Gibon J, Deloulme JC, Chevallier T, Ladeveze E, Abrous DN, Bouron A (2013) The antidepressant hyperforin increases the phosphorylation of CREB and the expression of TrkB in a tissue-specific manner. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:189–198
Gunaydin C, Arslan G, Bilge SS (2020) Proconvulsant effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde in pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling model of epilepsy: the role of TRPA1 channels. Neurosci Lett 721:134823
Thiel G, Lesch A, Rubil S, Backes TM, Rossler OG (2018) Regulation of gene transcription following stimulation of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 335:167–189
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Leila Ahmad-Molaei for her technical assistance. The study was supported by Neuroscience Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: NN, MS. Performed the experiments: SK, HZ. Analyzed the data: NN, SK. Wrote the paper: SK, NN.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaksar, S., Salimi, M., Zeinoddini, H. et al. The Role of the Possible Receptors and Intracellular Pathways in Protective Effect of Exogenous Anandamide in Kindling Model of Epilepsy. Neurochem Res 47, 1226–1242 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03517-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03517-5