Abstract
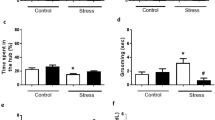
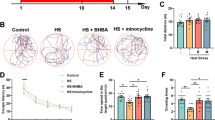
Exposure to heat stress (HS) has adverse effects on brain function, leading to anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment. Sericin is a silk derived protein with various neurobiological activities. The present study has investigated the effects of sericin on anxiety and cognitive impairments, in HS-received mice. The adult male mice were exposed to HS (43 ºC, 15 min once a day for 14 days) and simultaneously treated with 100, 150, and 200 mg/kg/day of sericin through oral gavage. Elevated plus-maze and Lashley III Maze tests were used to evaluate anxiety and learning and memory, respectively. The hippocampal BAX, BCL-2, caspase3, caspase9 and heat-shock protein-70 (HSP-70) were evaluated by western blotting and oxidative stress markers including malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), super oxide dismutase (SOD) as well as glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were evaluated by spectroscopy method. The serum was collected for the analysis of the corticosterone levels. Treatment with sericin in higher doses reversed anxiety-like behavior and cognitive deficit induced by HS. Moreover, heat exposure increased serum corticosterone, hippocampal MDA, apoptotic proteins and HSP-70 levels. Sericin administration decreased serum corticosterone and enhanced hippocampal antioxidant defense and attenuated apoptosis and HSP-70 levels. The results show that the protective effects of sericin against HS-mediated cognitive dysfunction and anxiety-like behavior is possibly through suppressing HSP-70, oxidative stress and apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhassan A, Adenkola A, Yusuf A, Bauchi Z, Saleh M, Ochigbo V (2010) Erythrocyte osmotic fragility of Wistar rats administered ascorbic acid during the hot-dry season. J Cell Anim Biol 4:029–033
Leon LR, Bouchama A (2011) Heat stroke. Compr Physiol 5:611–647
Sharma HS, Sharma A, Moessler H, Muresanu DF (2012) Neuroprotective effects of cerebrolysin, a combination of different active fragments of neurotrophic factors and peptides on the whole body hyperthermia-induced neurotoxicity: modulatory roles of co-morbidity factors and nanoparticle intoxication. Int Rev Neurobiol 102:249–276
Erfani M, Ghazi Tabatabaei Z, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Farokhi-Sisakht F, Farajdokht F, Mahmoudi J, Karimi P, Nasrolahi A (2019) Rosa canina L. methanolic extract prevents heat stress-induced memory dysfunction in rats. Exp Physiol 104:1544–1554
Lee W, Moon M, Kim HG, Lee TH, Oh MS (2015) Heat stress-induced memory impairment is associated with neuroinflammation in mice. J Neuroinflamm 12:102
Smith SM, Vale WW (2006) The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in neuroendocrine responses to stress. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 8:383
Moon M, Huh E, Lee W, Song E, Hwang D-S, Lee T, Oh M (2017) Coptidis rhizoma prevents heat stress-induced brain damage and cognitive impairment in mice. Nutrients 9:1057
Akbarian A, Michiels J, Degroote J, Majdeddin M, Golian A, De Smet S (2016) Association between heat stress and oxidative stress in poultry; mitochondrial dysfunction and dietary interventions with phytochemicals. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 7:37–37
Lin H, Decuypere E, Buyse J (2006) Acute heat stress induces oxidative stress in broiler chickens. Comp Biochem Physiol A 144:11–17
Mohammadi AB, Torbati M, Farajdokht F, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Fazljou SMB, Vatandoust SM, Golzari SE, Mahmoudi J (2019) Sericin alleviates restraint stress induced depressive-and anxiety-like behaviors via modulation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Brain Res 1715:47–56
Kim J, Yenari M (2017) Heat shock proteins and the stress response. Primer on cerebrovascular diseases. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 273–275
Reddy VS, Yadav B, Yadav CL, Anand M, Swain DK, Kumar D, Kritania D, Madan AK, Kumar J, Yadav S (2018) Effect of sericin supplementation on heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) expression, redox status and post thaw semen quality in goat. Cryobiology 84:33–39
Bechtold DA, Rush SJ, Brown IR (2000) Localization of the heat-shock protein Hsp70 to the synapse following hyperthermic stress in the brain. J Neurochem 74:641–646
Kunz RI, Brancalhão RMC, Ribeiro LdFC, Natali MRM (2016) Silkworm sericin: properties and biomedical applications. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8175701
Yellamma K (2014) Silk protein, sericin as a cognitive enhancer in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism 4:1000163
Deori M, Devi D, Kumari S, Hazarika A, Kalita H, Sarma R, Devi R (2016) Antioxidant effect of sericin in brain and peripheral tissues of oxidative stress induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Front Pharmacol 7:319
Salehpour F, Farajdokht F, Mahmoudi J, Erfani M, Farhoudi M, Karimi P, Rasta SH, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Hamblin MR, Gjedde A (2019) Photobiomodulation and coenzyme Q10 treatments attenuate cognitive impairment associated with model of transient global brain ischemia in artificially aged mice. Front Cell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00074
Pantic M, Minic M (2019) The evaluation of the effects of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin-induced alterations in exploratory activity in elevated plus maze test in rats. Serb J Exp Clin Res 20:65–72
Salehpour F, Farajdokht F, Cassano P, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Erfani M, Hamblin MR, Salimi MM, Karimi P, Rasta SH, Mahmoudi J (2019) Near-infrared photobiomodulation combined with coenzyme Q10 for depression in a mouse model of restraint stress: reduction in oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis. Brain Res Bull 144:213–222
Andalib S, Ziaee M, Mozafari F, Hosseini R, Anoush M (2019) Comparison of donepezil and riluzole in improving spatial memory of male Wistar rats. J Rep Pharm Sci 8:211
Ziaee M, Samini M, Bolourtchian M, Ghaffarzadeh M, Ahmadi M, Egbal MA, Khorrami A, Andalib S, Maleki-Dizaji N, Garjani A (2012) Synthesis of a novel siliconized analog of clofibrate (silafibrate) and comparison of their anti-inflammatory activities. Iran J Pharm Res 11:91
Ziaee M, Eghbal MA, Rahmani J, Ghaffarzadeh M, Khorrami A, Garjani A (2013) Biological evaluation of a siliconized analog of clofibrate (silafibrate) in rodents. Iran J Pharm Res 12:471
Nafisi S, Heidari R, Ghaffarzadeh M, Ziaee M, Hamzeiy H, Garjani A, Eghbal MA (2014) Cytoprotective effects of silafibrate, a newly-synthesised siliconated derivative of clofibrate, against acetaminophen-induced toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 65:169–177
Pourmemar E, Majdi A, Haramshahi M, Talebi M, Karimi P, Sadigh-Eteghad S (2017) Intranasal cerebrolysin attenuates learning and memory impairments in d-galactose-induced senescence in mice. Exp Gerontol 87:16–22
Piraki P, Hemmatfar A, Sharif MAS, Behpour N (2018) Evaluating the effect of vitamin C on myocardial angiogenesis under oxidative stress induced by exhaustive exercise in rat. J Pharm Sci 24:273–279
Borodovitsyna O, Flamini MD, Chandler DJ (2018) Acute stress persistently alters locus coeruleus function and anxiety-like behavior in adolescent rats. Neuroscience 373:7–19
Yue N, Li B, Yang L, Han Q-Q, Huang H-J, Wang Y-L, Wang J, Yu R, Wu G-C, Liu Q (2018) Electro-acupuncture alleviates chronic unpredictable stress-induced depressive-and anxiety-like behavior and hippocampal neuroinflammation in rat model of depression. Front Mol Neuorosci 11:149
Yuan W, Wu X, Yang F, Shang X, Zhang L (1989) Effects of ginseng root saponins on brain monoamines and serum corticosterone in heat-stressed mice. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 10:492–496
Mete F, Kilic E, Somay A, Yilmaz B (2012) Effects of heat stress on endocrine functions & behaviour in the pre-pubertal rat. Indian J Med Res 135:233
Sahin N, Tuzcu M, Orhan C, Onderci M, Eroksuz Y, Sahin K (2009) The effects of vitamin C and E supplementation on heat shock protein 70 response of ovary and brain in heat-stressed quail. Br Poult Sci 50:259–265
Pilcher JJ, Nadler E, Busch C (2002) Effects of hot and cold temperature exposure on performance: a meta-analytic review. Ergonomics 45:682–698
Gaoua N, Grantham J, Racinais S, El Massioui F (2012) Sensory displeasure reduces complex cognitive performance in the heat. J Environ Psychol 32:158–163
Sun G, Qian S, Jiang Q, Liu K, Li B, Li M, Zhao L, Zhou Z, von Deneen KM, Liu Y (2013) Hyperthermia-induced disruption of functional connectivity in the human brain network. PLoS ONE 8:e61157
Mujahid A, Akiba Y, Toyomizu M (2007) Acute heat stress induces oxidative stress and decreases adaptation in young white leghorn cockerels by downregulation of avian uncoupling protein. Poult Sci J 86:364–371
Cui Y, Hao Y, Li J, Bao W, Li G, Gao Y, Gu X (2016) Chronic heat stress induces immune response, oxidative stress response, and apoptosis of finishing pig liver: a proteomic approach. Int J Mol Sci 17:393
Habashy WS, Milfort MC, Rekaya R, Aggrey SE (2019) Cellular antioxidant enzyme activity and biomarkers for oxidative stress are affected by heat stress. Int J Biometeorol 63:1569–1584
Seyedaghamiri F, Farajdokht F, Vatandoust SM, Mahmoudi J, Khabbaz A, Sadigh-Eteghad S (2021) Sericin modulates learning and memory behaviors by tuning of antioxidant, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers in the hippocampus of aged mice. Mol Biol Rep 48(2):1371–82
Zhaorigetu S, Yanaka N, Sasaki M, Watanabe H, Kato N (2003) Inhibitory effects of silk protein, sericin on UVB-induced acute damage and tumor promotion by reducing oxidative stress in the skin of hairless mouse. J Photochem Photobiol B 71:11–17
Dash R, Acharya C, Bindu P, Kundu S (2008) Antioxidant potential of silk protein sericin against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in skin fibroblasts. Bmb Rep 41:236–241
Chauhan NR, Kumar R, Gupta A, Meena RC, Nanda S, Mishra KP, Singh SB (2020) Heat stress induced oxidative damage and perturbation in BDNF/ERK1/2/CREB axis in hippocampus impairs spatial memory. Behav Brain Res 396:112895
Gu X, Hao Y, Wang X (2012) Overexpression of heat shock protein 70 and its relationship to intestine under acute heat stress in broilers: 2. Intestinal oxidative stress. Poult Sci J 91:790–799
Yu J, Bao E, Yan J, Lei L (2008) Expression and localization of Hsps in the heart and blood vessel of heat-stressed broilers. Cell Stress Chaperones 13:327–335
Kurashova N, Madaeva I, Kolesnikova L (2020) Expression of HSP70 heat-shock proteins under oxidative Stress. Adv Gerontol 10:20–25
Wang X, Chen M, Zhou J, Zhang X (2014) HSP27, 70 and 90, anti-apoptotic proteins, in clinical cancer therapy. Int J Oncol 45:18–30
Yang H, Chowdhury VS, Han G, Zhang R, Furuse M (2019) Flavangenol regulates gene expression of HSPs, anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative factors to protect primary chick brain cells exposed to high temperature. J Therm Biol 81:1–11
Zf L, Jj Ji, Zheng D, Su L, Peng T (2019) Calpain-2 protects against heat stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and heart dysfunction by blocking p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Cell Physiol 234:10761–10770
Wang Y, Yang C, Hassan NA (2019) HO-1 reduces heat stress-induced apoptosis in bovine granulosa cells by suppressing oxidative stress. Aging (Albany Ny) 11:5535
Zhai R, Dong X, Feng L, Li S, Hu Z (2019) The effect of heat stress on autophagy and apoptosis of rumen, abomasum, duodenum, liver and kidney cells in calves. Animals 9:854
Gong S, Zhang J, Guo Z, Fu W (2018) Senkyunolide A protects neural cells against corticosterone-induced apoptosis by modulating protein phosphatase 2A and α-synuclein signaling. Drug Des Dev Ther 12:1865
Woo H, Hong CJ, Jung S, Choe S, Yu S-W (2018) Chronic restraint stress induces hippocampal memory deficits by impairing insulin signaling. Mol Brain 11:37
Chen Z, He Y, Song C, Dong Z, Su Z, Xue J (2012) Sericin can reduce hippocampal neuronal apoptosis by activating the Akt signal transduction pathway in a rat model of diabetes mellitus. Neural Regen Res 7:197
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by a grant (NO. A-10-1266-1) from Maragheh University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM, FF, SS-E and MZ designed the study. LH and SMV performed the experiments and the data analyses. JM, SS-E, and MZ contributed to figure design. JM, LH, and FF wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, J., Hosseini, L., Sadigh-Eteghad, S. et al. Sericin Alleviates Thermal Stress Induced Anxiety-Like Behavior and Cognitive Impairment Through Regulation of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Heat-Shock Protein-70 in the Hippocampus. Neurochem Res 46, 2307–2316 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03370-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03370-6