Abstract
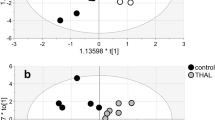
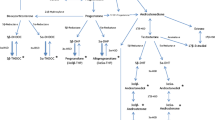
Valproic acid (VPA), an antiepileptic and mood stabilizer, modulates neurotransmission and gene expression by inhibiting histone deacetylase activity. It is reported that VPA may affects the steroid hormone level. In this study, VPA-induced acute metabolic alterations were investigated using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in prepubertal mice brain. In VPA-treated (400 mg/kg in saline solution, intraperitoneal) mice, cortisol levels were increased (female: P < 0.004, male: P < 0.003) and 17β-estradiol levels were decreased (Both P < 0.03). Furthermore, in the VPA-treated male mice, dihydrotestosterone levels were increased (P < 0.02) and testosterone were decreased (P < 0.002). The 4-hydroxylase activity was upregulated in the female VPA-treated mice (P < 0.01) and the 5α-reductase activity was increased in the male VPA-treated mice (P < 0.003). These results indicate sex specific differences in VPA-induced steroid metabolism in the brain cortex.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials are available upon requests.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Godin Y, Heiner L, Mark J, Mandel P (1969) Effects of DI-n‐propylacetate, an anticonvulsive compound, on GABA metabolism. J Neurochem 16:869–873. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb08975.x
Löscher W (1993) Effects of the antiepileptic drug valproate on metabolism and function of inhibitory and excitatory amino acids in the brain. Neurochem Res 18:485–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00967253
Luder AS, Parks JK, Frerman F, Parker WD (1990) Inactivation of beef brain alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex by valproic acid and valproic acid metabolites. Possible mechanism of anticonvulsant and toxic actions. J Clin Invest 86:1574–1581. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI114877
McCormick DA (1989) GABA as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in human cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 62:1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1989.62.5.1018
Stratton MS, Searcy BT, Tobet SA (2011) GABA regulates corticotropin releasing hormone levels in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in newborn mice. Physiol Behav 104:327. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSBEH.2011.01.003
Tran V, Hatalski CG, Yan XX, Baram TZ (1999) Effects of blocking GABA degradation on corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in selected brain regions. Epilepsia 40:1190–1197
Miller L, Foradori CD, Lalmansingh AS et al (2011) Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) participates in the down-regulation of corticotropin releasing hormone gene (crh) expression. Physiol Behav 104:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSBEH.2011.03.026
Zhang L, Li H, Li S, Zou X (2016) Reproductive and metabolic abnormalities in women taking valproate for bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 202:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2016.04.038
Xiaotian X, Hengzhong Z, Yao X et al (2013) Effects of antiepileptic drugs on reproductive endocrine function, sexual function and sperm parameters in Chinese Han men with epilepsy. J Clin Neurosci 20:1492–1497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2012.11.028
Glister C, Satchell L, Michael AE et al (2012) The anti-epileptic drug valproic acid (VPA) inhibits steroidogenesis in bovine theca and granulosa cells in vitro. PLoS One 7:e49553. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049553
Brion L, Gorostizaga A, Gómez NV et al (2011) Valproic acid alters mitochondrial cholesterol transport in Y1 adrenocortical cells. Toxicol Vitr 25:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIV.2010.08.006
Pesaresi M, Maschi O, Giatti S et al (2010) Sex differences in neuroactive steroid levels in the nervous system of diabetic and non-diabetic rats. Horm Behav 57:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2009.04.008
Göttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P et al (2001) Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J 20:6969–6978. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.24.6969
Bilo L, Meo R (2008) Polycystic ovary syndrome in women using valproate: a review. Gynecol Endocrinol 24:562–570. https://doi.org/10.1080/09513590802288259
Pennell PB (2009) Hormonal aspects of epilepsy. Neurol Clin 27:941–965
Taubøll E, Sveberg L, Svalheim S (2015) Interactions between hormones and epilepsy. Seizure 28:3–11
Banks WA (2012) Brain meets body: the blood-brain barrier as an endocrine interface. Endocrinology 153:4111–4119. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-1435
Diotel N, Charlier TD, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C et al (2018) Steroid transport, local synthesis, and signaling within the brain: roles in neurogenesis, neuroprotection, and sexual behaviors. Front Neurosci 12:84. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00084
Mellon SH, Vaudry H (2001) Biosynthesis of neurosteroids and regulation of their sysnthesis. Int Rev Neurobiol 46:33–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(01)46058-2
Akwa Y, Morfin RF, Robel P, Baulieu EE (1992) Neurosteroid metabolism. 7 alpha-Hydroxylation of dehydroepiandrosterone and pregnenolone by rat brain microsomes. Biochem J 288(Pt 3):959–964. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ2880959
Baulieu EE (1991) Neurosteroids: a new function in the brain. Biol Cell 71:3–10
Paul SM, Purdy RH (1992) Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J 6:2311–2322
Taubøll E, Gregoraszczuk EL, Kołodziej A et al (2003) Valproate inhibits the conversion of testosterone to estradiol and acts as an apoptotic agent in growing porcine ovarian follicular cells. Epilepsia 44:1014–1021. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1528-1157.2003.60702.x
Taubøll E, Wójtowicz AK, Ropstad E, Gregoraszczuk EL (2002) Valproate irreversibly alters steroid secretion patterns from porcine follicular cells in vitro. Reprod Toxicol 16:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6238(02)00020-5
Von Krogh K, Harjen H, Almås C et al (2010) The effect of valproate and levetiracetam on steroidogenesis in forskolin-stimulated H295R cells. Epilepsia 51:2280–2288. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02702.x
Gregoraszczuk E, Wójtowicz AK, Taubøll E, Ropstad E (2000) Valproate-induced alterations in testosterone, estradiol and progesterone secretion from porcine follicular cells isolated from small- and medium-sized ovarian follicles. Seizure 9:480–485. https://doi.org/10.1053/SEIZ.2000.0443
Inada H, Chihara K, Yamashita A et al (2012) Evaluation of ovarian toxicity of sodium valproate (VPA) using cultured rat ovarian follicles. J Toxicol Sci 37:587–594. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.37.587
Sukhorum W, Iamsaard S (2017) Changes in testicular function proteins and sperm acrosome status in rats treated with valproic acid. Reprod Fertil Dev 29:1585. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD16205
Tringali G, Aubry JM, Moscianese K et al (2004) Valproic acid inhibits corticotropin-releasing factor synthesis and release from the rat hypothalamus in vitro: evidence for the involvement of GABAergic neurotransmission. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29:459–466
Stout S, Owens MJ, Lindsey KP et al (2001) Effects of sodium valproate on corticotropin-releasing factor systems in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:624–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00243-8
Gilmor ML, Skelton KH, Nemeroff CB, Owens MJ (2003) The effects of chronic treatment with the mood stabilizers valproic acid and lithium on corticotropin-releasing factor neuronal systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.102.045419
Hsing AW, Stanczyk FZ, Bélanger A et al (2007) Reproducibility of serum sex steroid assays in men by RIA and mass spectrometry. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:1004–1008. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0792
Wood L, Ducroq DH, Fraser HL et al (2008) Measurement of urinary free cortisol by tandem mass spectrometry and comparison with results obtained by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and two commercial immunoassays. Ann Clin Biochem 45:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1258/acb.2007.007119
Dubey RK, Jackson EK (2001) Invited review: cardiovascular protective effects of 17β-estradiol metabolites. J Appl Physiol 91:1868–1883. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.2001.91.4.1868
Weaver ICG, Meaney MJ, Szyf M (2006) Maternal care effects on the hippocampal transcriptome and anxiety-mediated behaviors in the offspring that are reversible in adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:3480–3485. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507526103
Murray EK, Hien A, de Vries GJ, Forger NG (2009) Epigenetic control of sexual differentiation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Endocrinology 150:4241–4247. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-0458
Tsai H-W, Grant PA, Rissman EF (2009) Sex differences in histone modifications in the neonatal mouse brain. Epigenetics 4:47–53
Bell MR (2018) Comparing postnatal development of gonadal hormones and associated social behaviors in rats, mice, and humans. Endocrinology 159:2596–2613. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2018-00220
Funding
This work was supported by both the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2017R1D1A3B03033533) and Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (Grant No. KK1807-C32 and SI1805-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Eulji University (EUIACUC17-12).
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Research Involving Human and Animal Participants
This study was not for human study and consents are not necessary.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, SH., Chai, J.H., Chang, SY. et al. Acute Valproate Exposure Induces Sex-Specific Changes in Steroid Hormone Metabolism in the Cerebral Cortex of Juvenile Mice. Neurochem Res 45, 2044–2051 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03065-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03065-4