Abstract
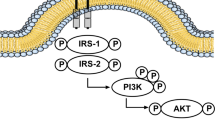
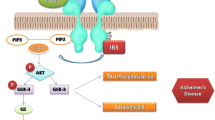
Recent studies continue to find evidence linking Type 2 diabetes (T2D) with Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common cause of dementia, a general term for memory loss and other cognitive abilities serious enough to interfere with daily life. Insulin resistance or dysfunction of insulin signaling is a universal feature of T2D, the main culprit for altered glucose metabolism and its interdependence on cell death pathways, forming the basis of linking T2D with AD as it may exacerbate Aβ accumulation, tau hyperphosphorylation and devastates glucose transportation, energy metabolism, hippocampal framework and promulgate inflammatory pathways. The current work demonstrates the basic mechanisms of the insulin resistance mediates dysregulation of bioenergetics and progress to AD as a mechanistic link between diabetes mellitus and AD. This work also aimed to provide a potential and feasible zone to succeed in the development of therapies in AD by enhanced hypometabolism and altered insulin signaling.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen TT, Giau VV, Vo TK (2017) Current advances in transdermal delivery of drugs for Alzheimer's disease. Indian J Pharmacol 49(2):145–154
Bedse G et al (2015) Aberrant insulin signaling in Alzheimer's disease: current knowledge. Front Neurosci 9:204–204
Correia SC et al (2012) Insulin signaling, glucose metabolism and mitochondria: major players in Alzheimer's disease and diabetes interrelation. Brain Res 1441:64–78
Duarte JMN (2015) Metabolic alterations associated to brain dysfunction in diabetes. Aging Dis 6(5):304–321
De Felice FG, Lourenco MV, Ferreira ST (2014) How does brain insulin resistance develop in Alzheimer's disease? Alzheimer's Dement 10(1 Supplement):S26–S32
Gabbouj S et al (2019) Altered insulin signaling in Alzheimer's disease brain - special emphasis on PI3K-Akt pathway. Front Neurosci 13:629–629
Talbot K et al (2012) Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J Clin Invest 122(4):1316–1338
Van Giau V, An SSA, Hulme JP (2018) Mitochondrial therapeutic interventions in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci 395:62–70
Ghasemi R et al (2013) Brain insulin dysregulation: implication for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Neurobiol 47(3):1045–1065
Nasoohi S, Parveen K, Ishrat T (2018) Metabolic syndrome, brain insulin resistance, and Alzheimer's disease: thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) and inflammasome as core amplifiers. J Alzheimers Dis 66(3):857–885
Martyn JAJ, Kaneki M, Yasuhara S (2008) Obesity-induced insulin resistance and hyperglycemia: etiologic factors and molecular mechanisms. Anesthesiology 109(1):137–148
Baker LD et al (2011) Insulin resistance and Alzheimer-like reductions in regional cerebral glucose metabolism for cognitively normal adults with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes. Arch Neurol 68(1):51–57
Lee S-H et al (2016) Insulin in the nervous system and the mind: functions in metabolism, memory, and mood. Mol Metab 5(8):589–601
Ferreira LSS et al (2018) Insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci 12:830
Rorbach-Dolata A, Piwowar A (2019) Neurometabolic evidence supporting the hypothesis of increased incidence of type 3 diabetes mellitus in the 21st century. BioMed Res Int 2019:8
Ormazabal V et al (2018) Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17(1):122
Weinstein G et al (2019) Association of metformin, sulfonylurea and insulin use with brain structure and function and risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease: pooled analysis from 5 cohorts. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0212293
de la Monte SM (2014) Type 3 diabetes is sporadic Alzheimers disease: mini-review. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24(12):1954–1960
Caberlotto L et al (2019) Cross-disease analysis of Alzheimer’s disease and type-2 diabetes highlights the role of autophagy in the pathophysiology of two highly comorbid diseases. Sci Rep 9(1):3965
Steen E et al (2005) Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease–is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis 7(1):63–80
Hubbard SR (2013) The insulin receptor: both a prototypical and atypical receptor tyrosine kinase. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(3):a008946
Hubbard SR (1997) Crystal structure of the activated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in complex with peptide substrate and ATP analog. EMBO J 16(18):5572–5581
Bosco D et al (2011) Possible implications of insulin resistance and glucose metabolism in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 15(9):1807–1821
Chiu SL, Chen CM, Cline HT (2008) Insulin receptor signaling regulates synapse number, dendritic plasticity, and circuit function in vivo. Neuron 58(5):708–719
Lee CC, Huang CC, Hsu KS (2011) Insulin promotes dendritic spine and synapse formation by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Rac1 signaling pathways. Neuropharmacology 61(4):867–879
Peineau S et al (2007) LTP inhibits LTD in the hippocampus via regulation of GSK3beta. Neuron 53(5):703–717
Kim SJ, Han Y (2005) Insulin inhibits AMPA-induced neuronal damage via stimulation of protein kinase B (Akt). J Neural Transm (Vienna) 112(2):179–191
Tomita T (2016) Apoptosis in pancreatic β-islet cells in Type 2 diabetes. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 16(3):162–179
Frolich L et al (1998) Brain insulin and insulin receptors in aging and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 105(4–5):423–438
Kivipelto M et al (2005) Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 62(10):1556–1560
Razay G, Vreugdenhil A, Wilcock G (2006) Obesity, abdominal obesity and Alzheimer disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22(2):173–176
Kullmann S et al (2016) Brain insulin resistance at the crossroads of metabolic and cognitive disorders in humans. Physiol Rev 96(4):1169–1209
Lillioja S et al (1993) Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Prospective studies of Pima Indians. N Engl J Med 329(27):1988–1992
Li J et al (2019) Therapeutic mechanisms of herbal medicines against insulin resistance: a review. Front Pharmacol 10:661
Kapogiannis D et al (2015) Dysfunctionally phosphorylated type 1 insulin receptor substrate in neural-derived blood exosomes of preclinical Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J 29(2):589–596
Fontaine JF et al (2009) MedlineRanker: flexible ranking of biomedical literature. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W141–W146
Wang G (2014) Raison d'être of insulin resistance: the adjustable threshold hypothesis. J R Soc 11(101):20140892–20140892
Nisr RB, Affourtit C (2014) Insulin acutely improves mitochondrial function of rat and human skeletal muscle by increasing coupling efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim et Biophys Acta 1837(2):270–276
Sivitz WI, Yorek MA (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes: from molecular mechanisms to functional significance and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 12(4):537–577
Bucht G et al (1983) Changes in blood glucose and insulin secretion in patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Acta Med Scand 213(5):387–392
Matioli MNPS, Nitrini R (2015) Mechanisms linking brain insulin resistance to Alzheimer's disease. Dement Neuropsychol 9(2):96–102
Ma QL et al (2009) Beta-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin. J Neurosci 29(28):9078–9089
Velazquez R et al (2017) Central insulin dysregulation and energy dyshomeostasis in two mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 58:1–13
Ruiz HH et al (2016) Increased susceptibility to metabolic dysregulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease is associated with impaired hypothalamic insulin signaling and elevated BCAA levels. Alzheimers Dement 12(8):851–861
Long-Smith CM et al (2013) The diabetes drug liraglutide ameliorates aberrant insulin receptor localisation and signalling in parallel with decreasing both amyloid-beta plaque and glial pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuromol Med 15(1):102–114
Bomfim TR et al (2012) An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's disease- associated Abeta oligomers. J Clin Invest 122(4):1339–1353
Clarke JR et al (2015) Alzheimer-associated Abeta oligomers impact the central nervous system to induce peripheral metabolic deregulation. EMBO Mol Med 7(2):190–210
Biessels GJ, Reagan LP (2015) Hippocampal insulin resistance and cognitive dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(11):660–671
Chakrabarti S et al (2015) Metabolic risk factors of sporadic Alzheimer's disease: implications in the pathology, pathogenesis and treatment. Aging Dis 6(4):282–299
de la Monte SM (2012) Brain insulin resistance and deficiency as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 9(1):35–66
Patterson C et al (2007) General risk factors for dementia: a systematic evidence review. Alzheimers Dement 3(4):341–347
Hoyer S, Oesterreich K, Wagner O (1988) Glucose metabolism as the site of the primary abnormality in early-onset dementia of Alzheimer type? J Neurol 235(3):143–148
Lying-Tunell U et al (1981) Cerebral blood flow and metabolic rate of oxygen, glucose, lactate, pyruvate, ketone bodies and amino acids. Acta Neurol Scand 63(6):337–350
Ogawa M et al (1996) Altered energy metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci 139(1):78–82
Chen Z, Zhong C (2013) Decoding Alzheimer's disease from perturbed cerebral glucose metabolism: implications for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Prog Neurobiol 108:21–43
Costantini LC et al (2008) Hypometabolism as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease. BMC Neurosci 9(Suppl 2):S16–S16
Cunnane S et al (2011) Brain fuel metabolism, aging, and Alzheimer's disease. Nutrition 27(1):3–20
Cunnane SC et al (2016) Can ketones help rescue brain fuel supply in later life? Implications for cognitive health during aging and the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Front Mol Neurosci 9:53–53
Maher PA, Schubert DR (2009) Metabolic links between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Expert Rev Neurother 9(5):617–630
Matsuzaki T et al (2010) Insulin resistance is associated with the pathology of Alzheimer disease: the Hisayama study. Neurology 75(9):764–770
Fukuyama H et al (1994) Altered cerebral energy metabolism in Alzheimer's disease: a PET study. J Nucl Med 35(1):1–6
Folch J et al (2018) The implication of the brain insulin receptor in late onset Alzheimer's disease dementia. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 11(1):11
Kim EJ et al (2005) Glucose metabolism in early onset versus late onset Alzheimer's disease: an SPM analysis of 120 patients. Brain 128(Pt 8):1790–1801
Wang Q et al (2019) Insulin resistance and systemic metabolic changes in oral glucose tolerance test in 5340 individuals: an interventional study. BMC Med 17(1):217
Baranowski BJ, Bott KN, MacPherson REK (2018) Evaluation of neuropathological effects of a high-fat high-sucrose diet in middle-aged male C57BL6/J mice. Physiol Rep 6(11):e13729
Butterfield DA, Halliwell B (2019) Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 20(3):148–160
Dienel GA (2019) Brain glucose metabolism: integration of energetics with function. Physiol Rev 99(1):949–1045
Liu Y et al (2008) Decreased glucose transporters correlate to abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer disease. FEBS Lett 582(2):359–364
Yoo DY et al (2016) Chronic type 2 diabetes reduces the integrity of the blood-brain barrier by reducing tight junction proteins in the hippocampus. J Vet Med Sci 78(6):957–962
Prasad S et al (2014) Diabetes mellitus and blood-brain barrier dysfunction: an overview. J Pharmacovigil 2(2):125
Rosales-Corral S et al (2015) Diabetes and Alzheimer disease, two overlapping pathologies with the same background: oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:14
Straub RH (2014) Insulin resistance, selfish brain, and selfish immune system: an evolutionarily positively selected program used in chronic inflammatory diseases. Arthr Res Ther 16(Suppl 2):S4–S4
Hemonnot A-L et al (2019) Microglia in Alzheimer disease: well-known targets and new opportunities. Front Aging Neurosci 11:33–41
Erol A (2008) An integrated and unifying hypothesis for the metabolic basis of sporadic Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 13(3):241–253
de la Monte SM (2017) Insulin resistance and neurodegeneration: progress towards the development of new therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease. Drugs 77(1):47–65
Su F, Bai F, Zhang Z (2016) Inflammatory cytokines and Alzheimer's disease: a review from the perspective of genetic polymorphisms. Neurosci Bull 32(5):469–480
Bagyinszky E et al (2017) Role of inflammatory molecules in the Alzheimer's disease progression and diagnosis. J Neurol Sci 376:242–254
Giau VV et al (2018) Gut microbiota and their neuroinflammatory implications in Alzheimer's disease. Nutrients 10(11):1765
Ferreira ST et al (2014) Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 10(1 Suppl):S76–83
Park CR et al (2000) Intracerebroventricular insulin enhances memory in a passive-avoidance task. Physiol Behav 68(4):509–514
Kandimalla R, Thirumala V, Reddy PH (2017) Is Alzheimer's disease a type 3 diabetes? A critical appraisal. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863(5):1078–1089
Nguyen NH et al (2020) Potential antidiabetic activity of extracts and isolated compound from Adenosma bracteosum (Bonati). Biomolecules 10(2):201
de Matos AM, de Macedo MP, Rauter AP (2018) Bridging type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease: assembling the puzzle pieces in the quest for the molecules with therapeutic and preventive potential. Med Res Rev 38(1):261–324
Ayaz M et al (2019) Flavonoids as prospective neuroprotectants and their therapeutic propensity in aging associated neurological disorders. Front Aging Neurosci 11:155
Canhada S et al (2018) Omega-3 fatty acids' supplementation in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review. Nutr Neurosci 21(8):529–538
Ajith TA (2018) A recent update on the effects of omega-3 fatty acids in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Clin Pharmacol 13(4):252–260
Broom GM, Shaw IC, Rucklidge JJ (2019) The ketogenic diet as a potential treatment and prevention strategy for Alzheimer's disease. Nutrition 60:118–121
Giau VV et al (2015) Role of apolipoprotein E in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:1723–1737
Frederiksen KS et al (2018) Effects of physical exercise on Alzheimer's disease biomarkers: a systematic review of intervention studies. J Alzheimers Dis 61(1):359–372
De Felice FG et al (2009) Protection of synapses against Alzheimer's-linked toxins: insulin signaling prevents the pathogenic binding of Abeta oligomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(6):1971–1976
Lourenco MV et al (2013) TNF-alpha mediates PKR-dependent memory impairment and brain IRS-1 inhibition induced by Alzheimer's beta-amyloid oligomers in mice and monkeys. Cell Metab 18(6):831–843
Craft S et al (2003) Insulin dose-response effects on memory and plasma amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer's disease: interactions with apolipoprotein E genotype. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28(6):809–822
Reger MA et al (2008) Intranasal insulin administration dose-dependently modulates verbal memory and plasma amyloid-beta in memory-impaired older adults. J Alzheimers Dis 13(3):323–331
Reger MA et al (2006) Effects of intranasal insulin on cognition in memory-impaired older adults: modulation by APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging 27(3):451–458
Reger MA et al (2008) Intranasal insulin improves cognition and modulates beta-amyloid in early AD. Neurology 70(6):440–448
Benedict C et al (2008) Differential sensitivity of men and women to anorexigenic and memory-improving effects of intranasal insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(4):1339–1344
Batista AF et al (2018) The diabetes drug liraglutide reverses cognitive impairment in mice and attenuates insulin receptor and synaptic pathology in a non-human primate model of Alzheimer's disease. J Pathol 245(1):85–100
McClean PL et al (2011) The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 31(17):6587–6594
McClean PL, Holscher C (2014) Liraglutide can reverse memory impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in aged APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 76(Pt A):57–67
Perry T et al (2002) Protection and reversal of excitotoxic neuronal damage by glucagon-like peptide-1 and exendin-4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302(3):881–888
Escribano L et al (2010) Rosiglitazone rescues memory impairment in Alzheimer's transgenic mice: mechanisms involving a reduced amyloid and tau pathology. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(7):1593–1604
Funding
This work did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.T., Ta, Q.T.H., Nguyen, T.T.D. et al. Role of Insulin Resistance in the Alzheimer's Disease Progression. Neurochem Res 45, 1481–1491 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03031-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03031-0