Abstract
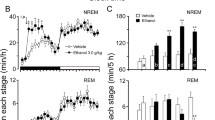
Ethanol is one of the most highly abused psychoactive compounds worldwide and induces sedation and hypnosis. The histaminergic system is involved in the regulation of sleep/wake function and is a crucial player in promoting wakefulness. To explore the role and mechanism of the histaminergic system in ethanol-induced sedation and hypnosis, we recorded locomotor activity (LMA) and electroencephalography (EEG)/electromyography (EMG) in mice using an infrared ray passive sensor recording system and an EEG/EMG recording system, respectively, after administration of ethanol. In vivo microdialysis coupled with high performance liquid chromatography and fluorometry technology were used to detect histamine release in the mouse frontal cortex (FrCx). The results revealed that ethanol significantly suppressed LMA of histamine receptor 1 (H1R)-knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice in the range of 1.5–2.5 g/kg, but suppression was remarkably stronger in WT mice than in H1R-KO mice. At 2.0 and 2.5 g/kg, ethanol remarkably increased non-rapid eye movement sleep and decreased wakefulness, respectively. Neurochemistry experimental data indicated that ethanol inhibited histamine release in the FrCx in a dose-dependent manner. These findings suggest that ethanol induces sedation and hypnosis via inhibiting histamine release in mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pesta DH, Angadi SS, Burtscher M, Roberts CK (2013) The effects of caffeine, nicotine, ethanol, and tetrahydrocannabinol on exercise performance. Nutr Metab 10:71
Ferreira MP, Willoughby D (2008) Alcohol consumption: the good, the bad, and the indifferent. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:12–20
Hattan DG, Eacho PI (1978) Relationship of ethanol blood level to REM and non-REM sleep time and distribution in the rat. Life Sci 22:839–846
Hill SY, Reyes RB (1978) Effects of chronic and acute ethanol administration on sleep in laboratory rats. J Stud Alcohol 39:47–55
Kubota T, De A, Brown RA, Simasko SM, Krueger JM (2002) Diurnal effects of acute and chronic administration of ethanol on sleep in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:1153–1161
Thakkar MM, Sharma R, Sahota P (2015) Alcohol disrupts sleep homeostasis. Alcohol 49:299–310
Fang T, Dong H, Xu XH, Yuan XS, Chen ZK, Chen JF, Qu WM, Huang ZL (2017) Adenosine A2A receptor mediates hypnotic effects of ethanol in mice. Sci Rep 7:12678
Ticho SR, Stojanovic M, Lekovic G, Radulovacki M (1992) Effects of ethanol injection to the preoptic area on sleep and temperature in rats. Alcohol 9:275–278
Brower KJ (2003) Insomnia, alcoholism and relapse. Sleep Med Rev 7:523–539
Brower KJ, Perron BE (2010) Prevalence and correlates of withdrawal-related insomnia among adults with alcohol dependence: results from a national survey. Am J Addict 19:238–244
Martin LJ, Zurek AA, Bonin RP, Oh GH, Kim JH, Mount HT, Orser BA (2011) The sedative but not the memory-blocking properties of ethanol are modulated by alpha5-subunit-containing gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Behav Brain Res 217:379–385
Blednov YA, Benavidez JM, Black M, Leiter CR, Osterndorff-Kahanek E, Johnson D, Borghese CM, Hanrahan JR, Johnston GA, Chebib M et al (2014) GABAA receptors containing rho1 subunits contribute to in vivo effects of ethanol in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e85525
Santerre JL, Gigante ED, Landin JD, Werner DF (2014) Molecular and behavioral characterization of adolescent protein kinase C following high dose ethanol exposure. Psychopharmacology 231:1809–1820
Sun Y, Jiang SY, Ni J, Luo YJ, Chen CR, Hong ZY, Yanagawa Y, Qu WM, Wang L, Huang ZL (2016) Ethanol inhibits histaminergic neurons in mouse tuberomammillary nucleus slices via potentiating GABAergic transmission onto the neurons at both pre- and postsynaptic sites. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:1325–1336
Nuutinen S, Vanhanen J, Pigni MC, Panula P (2011) Effects of histamine H3 receptor ligands on the rewarding, stimulant and motor-impairing effects of ethanol in DBA/2J mice. Neuropharmacology 60:1193–1199
Vanhanen J, Nuutinen S, Lintunen M, Maki T, Ramo J, Karlstedt K, Panula P (2013) Histamine is required for H(3) receptor-mediated alcohol reward inhibition, but not for alcohol consumption or stimulation. Br J Pharmacol 170:177–187
West RE Jr, Zweig A, Shih NY, Siegel MI, Egan RW, Clark MA (1990) Identification of two H3-histamine receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol 38:610–613
Verma L, Jain NS (2016) Central histaminergic transmission modulates the ethanol induced anxiolysis in mice. Behav Brain Res 313:38–52
Yoshikawa T, Nakamura T, Shibakusa T, Sugita M, Naganuma F, Iida T, Miura Y, Mohsen A, Harada R, Yanai K (2014) Insufficient intake of L-histidine reduces brain histamine and causes anxiety-like behaviors in male mice. J Nutr 144:1637–1641
Haas H, Panula P (2003) The role of histamine and the tuberomamillary nucleus in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:121–130
Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O (2008) Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 88:1183–1241
Hong ZY, Huang ZL, Qu WM, Eguchi N, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (2005) An adenosine A receptor agonist induces sleep by increasing GABA release in the tuberomammillary nucleus to inhibit histaminergic systems in rats. J Neurochem 92:1542–1549
Huang ZL, Mochizuki T, Qu WM, Hong ZY, Watanabe T, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (2006) Altered sleep-wake characteristics and lack of arousal response to H3 receptor antagonist in histamine H1 receptor knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4687–4692
Oishi Y, Huang ZL, Fredholm BB, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (2008) Adenosine in the tuberomammillary nucleus inhibits the histaminergic system via A1 receptors and promotes non-rapid eye movement sleep. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19992–19997
Tokunaga S, Tsutsui R, Obara Y, Ishida T, Kamei C (2009) Effects of histamine H1-antagonists on sleep-awake state in rats placed on a grid suspended over water or on sawdust. Biol Pharm Bull 32:51–54
Liu TY, Hong ZY, Qu WM, Huang ZL (2011) Advances in the study of histaminergic systems and sleep-wake regulation. Yao Xue Xue Bao 46:247–252
Huang ZL, Zhang Z, Qu WM (2014) Roles of adenosine and its receptors in sleep-wake regulation. Int Rev Neurobiol 119:349–371
Mochizuki T, Yamatodani A, Okakura K, Horii A, Inagaki N, Wada H (1992) Circadian rhythm of histamine release from the hypothalamus of freely moving rats. Physiol Behav 51:391–394
Takahashi K, Lin JS, Sakai K (2006) Neuronal activity of histaminergic tuberomammillary neurons during wake-sleep states in the mouse. J Neurosci 26:10292–10298
Lintunen M, Raatesalmi K, Sallmen T, Anichtchik O, Karlstedt K, Kaslin J, Kiianmaa K, Korpi ER, Panula P (2002) Low brain histamine content affects ethanol-induced motor impairment. Neurobiol Disord 9:94–105
Didone V, Quoilin C, Nyssen L, Closon C, Tirelli E, Quertemont E (2013) Effects of L-histidine and histamine H3 receptor modulators on ethanol-induced sedation in mice. Behav Brain Res 238:113–118
Nowak JZ, Maslinski C (1984) Ethanol-induced changes of histamine content in guinea-pig brain. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 36:647–651
Inoue I, Yanai K, Kitamura D, Taniuchi I, Kobayashi T, Niimura K, Watanabe T, Watanabe T (1996) Impaired locomotor activity and exploratory behavior in mice lacking histamine H1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13316–13320
Zhang Z, Wang HJ, Wang DR, Qu WM, Huang ZL (2017) Red light at intensities above 10 lx alters sleep-wake behavior in mice. Light Sci Appl 6:e16231
Nakamura W, Yamazaki S, Nakamura TJ, Shirakawa T, Block GD, Takumi T (2008) In vivo monitoring of circadian timing in freely moving mice. Curr Biol 18:381–385
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Qu WM, Huang ZL, Xu XH, Matsumoto N, Urade Y (2008) Dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors are essential for the arousal effect of modafinil. J Neurosci 28:8462–8469
Wang TX, Yin D, Guo W, Liu YY, Li YD, Qu WM, Han WJ, Hong ZY, Huang ZL (2015) Antinociceptive and hypnotic activities of pregabalin in a neuropathic pain-like model in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 135:31–39
Tobler I, Deboer T, Fischer M (1997) Sleep and sleep regulation in normal and prion protein-deficient mice. J Neurosci 17:1869–1879
Yamatodani A, Fukuda H, Wada H, Iwaeda T, Watanabe T (1985) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of plasma and brain histamine without previous purification of biological samples: cation-exchange chromatography coupled with post-column derivatization fluorometry. J Chromatogr 344:115–123
Arnedt JT, Rohsenow DJ, Almeida AB, Hunt SK, Gokhale M, Gottlieb DJ, Howland J (2011) Sleep following alcohol intoxication in healthy, young adults: effects of sex and family history of alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:870–878
Lin JS, Hou Y, Sakai K, Jouvet M (1996) Histaminergic descending inputs to the mesopontine tegmentum and their role in the control of cortical activation and wakefulness in the cat. J Neurosci 16:1523–1537
Lin JS, Sakai K, Jouvet M (1994) Hypothalamo-preoptic histaminergic projections in sleep-wake control in the cat. Eur J Neurosci 6:618–625
Lin JS, Sakai K, Vanni-Mercier G, Arrang JM, Garbarg M, Schwartz JC, Jouvet M (1990) Involvement of histaminergic neurons in arousal mechanisms demonstrated with H3-receptor ligands in the cat. Brain Res 523:325–330
Chu M, Huang ZL, Qu WM, Eguchi N, Yao MH, Urade Y (2004) Extracellular histamine level in the frontal cortex is positively correlated with the amount of wakefulness in rats. Neurosci Res 49:417–420
Rozov SV, Zant JC, Karlstedt K, Porkka-Heiskanen T, Panula P (2014) Periodic properties of the histaminergic system of the mouse brain. Eur J Neurosci 39:218–228
Subramanian N, Schinzel W, Mitznegg P, Estler CJ (1980) Influence of ethanol on histamine metabolism and release in the rat brain. II. Regions of the histaminergic pathway. Pharmacology 20:42–45
Rawat AK (1980) Development of histaminergic pathways in brain as influenced by maternal alcoholism. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 27:91–103
Itoh Y, Nishibori M, Oishi R, Saeki K (1985) Changes in histamine metabolism in the mouse hypothalamus induced by acute administration of ethanol. J Neurochem 45:1880–1885
Prell GD, Bielkiewicz B, Mazurkiewicz-Kwilecki IM (1982) Rat brain histamine concentration, synthesis and metabolism: effect of acute ethanol administration. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:427–432
Smith A, Watson CJ, Frantz KJ, Eppler B, Kennedy RT, Peris J (2004) Differential increase in taurine levels by low-dose ethanol in the dorsal and ventral striatum revealed by microdialysis with on-line capillary electrophoresis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:1028–1038
Roberto M, Madamba SG, Stouffer DG, Parsons LH, Siggins GR (2004) Increased GABA release in the central amygdala of ethanol-dependent rats. J Neurosci 24:10159–10166
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671318 and 81171255 to ZYH) and the Programs for Science and Technology Development of Anhui Province (1501041157 to ZYH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZYH and ZLH designed the experiments and guided the writing of this article. ZQM, WSW, TXW and WX were responsible for performing experiments and writing the manuscript. WMQ contributed to acquire and analyze the data. Authors included in this article agreed with the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Wang, W., Wang, T. et al. Ethanol Induces Sedation and Hypnosis via Inhibiting Histamine Release in Mice. Neurochem Res 44, 1764–1772 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02813-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02813-5